You can not select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
203 lines
12 KiB
203 lines
12 KiB
--- |
|
comments: true |
|
description: Learn how to use oriented object detection models with Ultralytics YOLO. Instructions on training, validation, image prediction, and model export. |
|
keywords: yolov8, oriented object detection, Ultralytics, DOTA dataset, rotated object detection, object detection, model training, model validation, image prediction, model export |
|
--- |
|
|
|
# Oriented Bounding Boxes Object Detection |
|
|
|
<!-- obb task poster --> |
|
|
|
Oriented object detection goes a step further than object detection and introduce an extra angle to locate objects more accurate in an image. |
|
|
|
The output of an oriented object detector is a set of rotated bounding boxes that exactly enclose the objects in the image, along with class labels and confidence scores for each box. Object detection is a good choice when you need to identify objects of interest in a scene, but don't need to know exactly where the object is or its exact shape. |
|
|
|
<!-- youtube video link for obb task --> |
|
|
|
!!! Tip "Tip" |
|
|
|
YOLOv8 OBB models use the `-obb` suffix, i.e. `yolov8n-obb.pt` and are pretrained on [DOTAv1](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/DOTAv1.yaml). |
|
|
|
<table> |
|
<tr> |
|
<td align="center"> |
|
<iframe loading="lazy" width="720" height="405" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/Z7Z9pHF8wJc" |
|
title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" |
|
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" |
|
allowfullscreen> |
|
</iframe> |
|
<br> |
|
<strong>Watch:</strong> Object Detection using Ultralytics YOLOv8 Oriented Bounding Boxes (YOLOv8-OBB) |
|
</td> |
|
<td align="center"> |
|
<iframe loading="lazy" width="720" height="405" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/uZ7SymQfqKI" |
|
title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0" |
|
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" |
|
allowfullscreen> |
|
</iframe> |
|
<br> |
|
<strong>Watch:</strong> Object Detection with YOLOv8-OBB using Ultralytics HUB |
|
</td> |
|
</tr> |
|
</table> |
|
|
|
## Visual Samples |
|
|
|
| Ships Detection using OBB | Vehicle Detection using OBB | |
|
|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| |
|
|  | 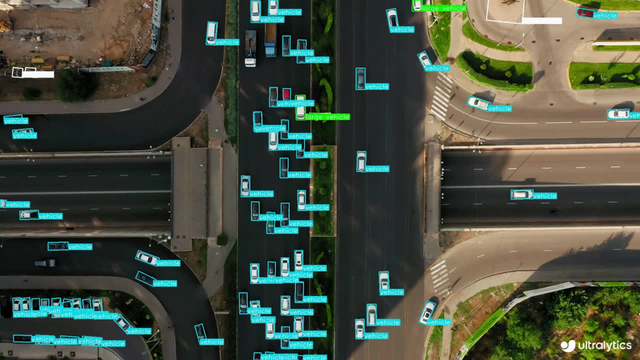 | |
|
|
|
## [Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8) |
|
|
|
YOLOv8 pretrained OBB models are shown here, which are pretrained on the [DOTAv1](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/DOTAv1.yaml) dataset. |
|
|
|
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use. |
|
|
|
| Model | size<br><sup>(pixels) | mAP<sup>test<br>50 | Speed<br><sup>CPU ONNX<br>(ms) | Speed<br><sup>A100 TensorRT<br>(ms) | params<br><sup>(M) | FLOPs<br><sup>(B) | |
|
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------|--------------------|--------------------------------|-------------------------------------|--------------------|-------------------| |
|
| [YOLOv8n-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8n-obb.pt) | 1024 | 78.0 | 204.77 | 3.57 | 3.1 | 23.3 | |
|
| [YOLOv8s-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8s-obb.pt) | 1024 | 79.5 | 424.88 | 4.07 | 11.4 | 76.3 | |
|
| [YOLOv8m-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8m-obb.pt) | 1024 | 80.5 | 763.48 | 7.61 | 26.4 | 208.6 | |
|
| [YOLOv8l-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8l-obb.pt) | 1024 | 80.7 | 1278.42 | 11.83 | 44.5 | 433.8 | |
|
| [YOLOv8x-obb](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v8.2.0/yolov8x-obb.pt) | 1024 | 81.36 | 1759.10 | 13.23 | 69.5 | 676.7 | |
|
|
|
- **mAP<sup>test</sup>** values are for single-model multiscale on [DOTAv1 test](https://captain-whu.github.io/DOTA/index.html) dataset. <br>Reproduce by `yolo val obb data=DOTAv1.yaml device=0 split=test` and submit merged results to [DOTA evaluation](https://captain-whu.github.io/DOTA/evaluation.html). |
|
- **Speed** averaged over DOTAv1 val images using an [Amazon EC2 P4d](https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/p4/) instance. <br>Reproduce by `yolo val obb data=DOTAv1.yaml batch=1 device=0|cpu` |
|
|
|
## Train |
|
|
|
Train YOLOv8n-obb on the `dota8.yaml` dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. For a full list of available arguments see the [Configuration](../usage/cfg.md) page. |
|
|
|
!!! Example |
|
|
|
=== "Python" |
|
|
|
```python |
|
from ultralytics import YOLO |
|
|
|
# Load a model |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.yaml') # build a new model from YAML |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training) |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.yaml').load('yolov8n.pt') # build from YAML and transfer weights |
|
|
|
# Train the model |
|
results = model.train(data='dota8.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640) |
|
``` |
|
=== "CLI" |
|
|
|
```bash |
|
# Build a new model from YAML and start training from scratch |
|
yolo obb train data=dota8.yaml model=yolov8n-obb.yaml epochs=100 imgsz=640 |
|
|
|
# Start training from a pretrained *.pt model |
|
yolo obb train data=dota8.yaml model=yolov8n-obb.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 |
|
|
|
# Build a new model from YAML, transfer pretrained weights to it and start training |
|
yolo obb train data=dota8.yaml model=yolov8n-obb.yaml pretrained=yolov8n-obb.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 |
|
``` |
|
|
|
### Dataset format |
|
|
|
OBB dataset format can be found in detail in the [Dataset Guide](../datasets/obb/index.md). |
|
|
|
## Val |
|
|
|
Validate trained YOLOv8n-obb model accuracy on the DOTA8 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` |
|
retains its training `data` and arguments as model attributes. |
|
|
|
!!! Example |
|
|
|
=== "Python" |
|
|
|
```python |
|
from ultralytics import YOLO |
|
|
|
# Load a model |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.pt') # load an official model |
|
model = YOLO('path/to/best.pt') # load a custom model |
|
|
|
# Validate the model |
|
metrics = model.val(data='dota8.yaml') # no arguments needed, dataset and settings remembered |
|
metrics.box.map # map50-95(B) |
|
metrics.box.map50 # map50(B) |
|
metrics.box.map75 # map75(B) |
|
metrics.box.maps # a list contains map50-95(B) of each category |
|
``` |
|
=== "CLI" |
|
|
|
```bash |
|
yolo obb val model=yolov8n-obb.pt data=dota8.yaml # val official model |
|
yolo obb val model=path/to/best.pt data=path/to/data.yaml # val custom model |
|
``` |
|
|
|
## Predict |
|
|
|
Use a trained YOLOv8n-obb model to run predictions on images. |
|
|
|
!!! Example |
|
|
|
=== "Python" |
|
|
|
```python |
|
from ultralytics import YOLO |
|
|
|
# Load a model |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.pt') # load an official model |
|
model = YOLO('path/to/best.pt') # load a custom model |
|
|
|
# Predict with the model |
|
results = model('https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg') # predict on an image |
|
``` |
|
=== "CLI" |
|
|
|
```bash |
|
yolo obb predict model=yolov8n-obb.pt source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with official model |
|
yolo obb predict model=path/to/best.pt source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with custom model |
|
``` |
|
|
|
See full `predict` mode details in the [Predict](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/predict/) page. |
|
|
|
## Export |
|
|
|
Export a YOLOv8n-obb model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc. |
|
|
|
!!! Example |
|
|
|
=== "Python" |
|
|
|
```python |
|
from ultralytics import YOLO |
|
|
|
# Load a model |
|
model = YOLO('yolov8n-obb.pt') # load an official model |
|
model = YOLO('path/to/best.pt') # load a custom trained model |
|
|
|
# Export the model |
|
model.export(format='onnx') |
|
``` |
|
=== "CLI" |
|
|
|
```bash |
|
yolo export model=yolov8n-obb.pt format=onnx # export official model |
|
yolo export model=path/to/best.pt format=onnx # export custom trained model |
|
``` |
|
|
|
Available YOLOv8-obb export formats are in the table below. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-obb.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes. |
|
|
|
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments | |
|
|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|-----------|--------------------------------------------------------------| |
|
| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n-obb.pt` | ✅ | - | |
|
| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n-obb.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize`, `batch` | |
|
| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n-obb.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset`, `batch` | |
|
| [OpenVINO](../integrations/openvino.md) | `openvino` | `yolov8n-obb_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | |
|
| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n-obb.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace`, `batch` | |
|
| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n-obb.mlpackage` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms`, `batch` | |
|
| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n-obb_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras`, `int8`, `batch` | |
|
| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n-obb.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz`, `batch` | |
|
| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n-obb.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | |
|
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-obb_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | |
|
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-obb_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `batch` | |
|
| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-obb_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `batch` | |
|
| [NCNN](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-obb_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `batch` | |
|
|
|
See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page.
|
|
|