5.3 KiB
| comments | description | keywords |
|---|---|---|
| true | Learn how COCO, a leading dataset for object detection and segmentation, integrates with Ultralytics. Discover ways to use it for training YOLO models. | Ultralytics, COCO dataset, object detection, YOLO, YOLO model training, image segmentation, computer vision, deep learning models |
COCO Dataset
The COCO (Common Objects in Context) dataset is a large-scale object detection, segmentation, and captioning dataset. It is designed to encourage research on a wide variety of object categories and is commonly used for benchmarking computer vision models. It is an essential dataset for researchers and developers working on object detection, segmentation, and pose estimation tasks.
Key Features
- COCO contains 330K images, with 200K images having annotations for object detection, segmentation, and captioning tasks.
- The dataset comprises 80 object categories, including common objects like cars, bicycles, and animals, as well as more specific categories such as umbrellas, handbags, and sports equipment.
- Annotations include object bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and captions for each image.
- COCO provides standardized evaluation metrics like mean Average Precision (mAP) for object detection, and mean Average Recall (mAR) for segmentation tasks, making it suitable for comparing model performance.
Dataset Structure
The COCO dataset is split into three subsets:
- Train2017: This subset contains 118K images for training object detection, segmentation, and captioning models.
- Val2017: This subset has 5K images used for validation purposes during model training.
- Test2017: This subset consists of 20K images used for testing and benchmarking the trained models. Ground truth annotations for this subset are not publicly available, and the results are submitted to the COCO evaluation server for performance evaluation.
Applications
The COCO dataset is widely used for training and evaluating deep learning models in object detection (such as YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and SSD), instance segmentation (such as Mask R-CNN), and keypoint detection (such as OpenPose). The dataset's diverse set of object categories, large number of annotated images, and standardized evaluation metrics make it an essential resource for computer vision researchers and practitioners.
Dataset YAML
A YAML (Yet Another Markup Language) file is used to define the dataset configuration. It contains information about the dataset's paths, classes, and other relevant information. In the case of the COCO dataset, the coco.yaml file is maintained at https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco.yaml.
!!! example "ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco.yaml"
```yaml
--8<-- "ultralytics/cfg/datasets/coco.yaml"
```
Usage
To train a YOLOv8n model on the COCO dataset for 100 epochs with an image size of 640, you can use the following code snippets. For a comprehensive list of available arguments, refer to the model Training page.
!!! example "Train Example"
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
# Train the model
model.train(data='coco.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640)
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Start training from a pretrained *.pt model
yolo detect train data=coco.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
```
Sample Images and Annotations
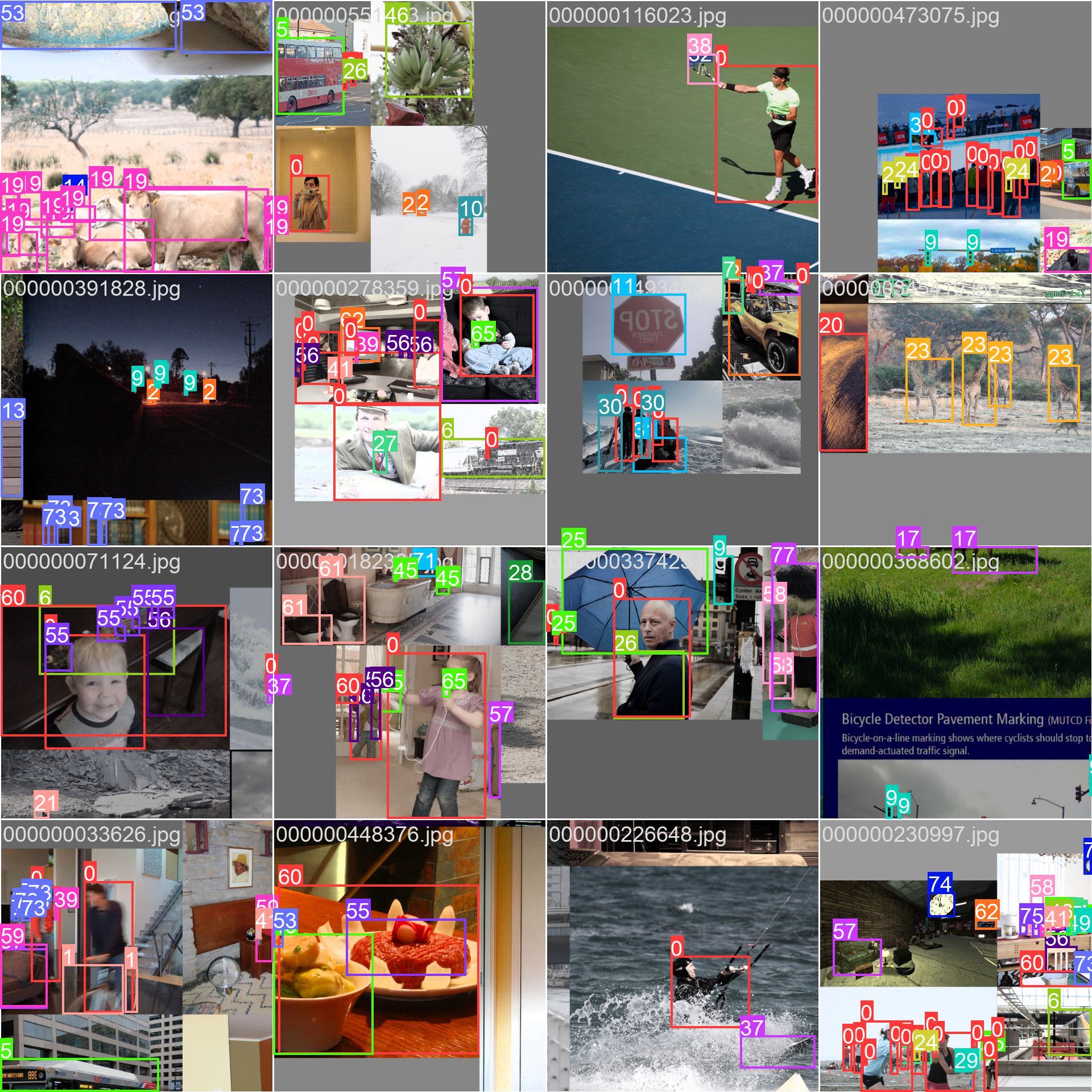
The COCO dataset contains a diverse set of images with various object categories and complex scenes. Here are some examples of images from the dataset, along with their corresponding annotations:
- Mosaiced Image: This image demonstrates a training batch composed of mosaiced dataset images. Mosaicing is a technique used during training that combines multiple images into a single image to increase the variety of objects and scenes within each training batch. This helps improve the model's ability to generalize to different object sizes, aspect ratios, and contexts.
The example showcases the variety and complexity of the images in the COCO dataset and the benefits of using mosaicing during the training process.
Citations and Acknowledgments
If you use the COCO dataset in your research or development work, please cite the following paper:
@misc{lin2015microsoft,
title={Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context},
author={Tsung-Yi Lin and Michael Maire and Serge Belongie and Lubomir Bourdev and Ross Girshick and James Hays and Pietro Perona and Deva Ramanan and C. Lawrence Zitnick and Piotr Dollár},
year={2015},
eprint={1405.0312},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
We would like to acknowledge the COCO Consortium for creating and maintaining this valuable resource for the computer vision community. For more information about the COCO dataset and its creators, visit the COCO dataset website.