---
comments: true
description: Learn essential data preprocessing techniques for annotated computer vision data, including resizing, normalizing, augmenting, and splitting datasets for optimal model training.
keywords: data preprocessing, computer vision, image resizing, normalization, data augmentation, training dataset, validation dataset, test dataset, YOLOv8
---
# Data Preprocessing Techniques for Annotated Computer Vision Data
## Introduction
After you've defined your computer vision [project's goals](./defining-project-goals.md) and [collected and annotated data](./data-collection-and-annotation.md), the next step is to preprocess annotated data and prepare it for model training. Clean and consistent data are vital to creating a model that performs well.
Preprocessing is a step in the [computer vision project workflow](./steps-of-a-cv-project.md) that includes resizing images, normalizing pixel values, augmenting the dataset, and splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets. Let's explore the essential techniques and best practices for cleaning your data!
## Importance of Data Preprocessing
We are already collecting and annotating our data carefully with multiple considerations in mind. Then, what makes data preprocessing so important to a computer vision project? Well, data preprocessing is all about getting your data into a suitable format for training that reduces the computational load and helps improve model performance. Here are some common issues in raw data that preprocessing addresses:
- **Noise**: Irrelevant or random variations in data.
- **Inconsistency**: Variations in image sizes, formats, and quality.
- **Imbalance**: Unequal distribution of classes or categories in the dataset.
## Data Preprocessing Techniques
One of the first and foremost steps in data preprocessing is resizing. Some models are designed to handle variable input sizes, but many models require a consistent input size. Resizing images makes them uniform and reduces computational complexity.
### Resizing Images
You can resize your images using the following methods:
- **Bilinear Interpolation**: Smooths pixel values by taking a weighted average of the four nearest pixel values.
- **Nearest Neighbor**: Assigns the nearest pixel value without averaging, leading to a blocky image but faster computation.
To make resizing a simpler task, you can use the following tools:
- **OpenCV**: A popular computer vision library with extensive functions for image processing.
- **PIL (Pillow)**: A Python Imaging Library for opening, manipulating, and saving image files.
With respect to YOLOv8, the 'imgsz' parameter during [model training](../modes/train.md) allows for flexible input sizes. When set to a specific size, such as 640, the model will resize input images so their largest dimension is 640 pixels while maintaining the original aspect ratio.
By evaluating your model's and dataset's specific needs, you can determine whether resizing is a necessary preprocessing step or if your model can efficiently handle images of varying sizes.
### Normalizing Pixel Values
Another preprocessing technique is normalization. Normalization scales the pixel values to a standard range, which helps in faster convergence during training and improves model performance. Here are some common normalization techniques:
- **Min-Max Scaling**: Scales pixel values to a range of 0 to 1.
- **Z-Score Normalization**: Scales pixel values based on their mean and standard deviation.
With respect to YOLOv8, normalization is seamlessly handled as part of its preprocessing pipeline during model training. YOLOv8 automatically performs several preprocessing steps, including conversion to RGB, scaling pixel values to the range [0, 1], and normalization using predefined mean and standard deviation values.
### Splitting the Dataset
Once you've cleaned the data, you are ready to split the dataset. Splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets is done to ensure that the model can be evaluated on unseen data to assess its generalization performance. A common split is 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing. There are various tools and libraries that you can use to split your data like scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
Consider the following when splitting your dataset:
- **Maintaining Data Distribution**: Ensure that the data distribution of classes is maintained across training, validation, and test sets.
- **Avoiding Data Leakage**: Typically, data augmentation is done after the dataset is split. Data augmentation and any other preprocessing should only be applied to the training set to prevent information from the validation or test sets from influencing the model training. -**Balancing Classes**: For imbalanced datasets, consider techniques such as oversampling the minority class or under-sampling the majority class within the training set.
### What is Data Augmentation?
The most commonly discussed data preprocessing step is data augmentation. Data augmentation artificially increases the size of the dataset by creating modified versions of images. By augmenting your data, you can reduce overfitting and improve model generalization.
Here are some other benefits of data augmentation:
- **Creates a More Robust Dataset**: Data augmentation can make the model more robust to variations and distortions in the input data. This includes changes in lighting, orientation, and scale.
- **Cost-Effective**: Data augmentation is a cost-effective way to increase the amount of training data without collecting and labeling new data.
- **Better Use of Data**: Every available data point is used to its maximum potential by creating new variations
#### Data Augmentation Methods
Common augmentation techniques include flipping, rotation, scaling, and color adjustments. Several libraries, such as Albumentations, Imgaug, and TensorFlow's ImageDataGenerator, can generate these augmentations.

With respect to YOLOv8, you can [augment your custom dataset](../modes/train.md) by modifying the dataset configuration file, a .yaml file. In this file, you can add an augmentation section with parameters that specify how you want to augment your data.
The [Ultralytics YOLOv8 repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main) supports a wide range of data augmentations. You can apply various transformations such as:
- Random Crops
- Flipping: Images can be flipped horizontally or vertically.
- Rotation: Images can be rotated by specific angles.
- Distortion
Also, you can adjust the intensity of these augmentation techniques through specific parameters to generate more data variety.
## A Case Study of Preprocessing
Consider a project aimed at developing a model to detect and classify different types of vehicles in traffic images using YOLOv8. We've collected traffic images and annotated them with bounding boxes and labels.
Here's what each step of preprocessing would look like for this project:
- Resizing Images: Since YOLOv8 handles flexible input sizes and performs resizing automatically, manual resizing is not required. The model will adjust the image size according to the specified 'imgsz' parameter during training.
- Normalizing Pixel Values: YOLOv8 automatically normalizes pixel values to a range of 0 to 1 during preprocessing, so it's not required.
- Splitting the Dataset: Divide the dataset into training (70%), validation (20%), and test (10%) sets using tools like scikit-learn.
- Data Augmentation: Modify the dataset configuration file (.yaml) to include data augmentation techniques such as random crops, horizontal flips, and brightness adjustments.
These steps make sure the dataset is prepared without any potential issues and is ready for Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA).
## Exploratory Data Analysis Techniques
After preprocessing and augmenting your dataset, the next step is to gain insights through Exploratory Data Analysis. EDA uses statistical techniques and visualization tools to understand the patterns and distributions in your data. You can identify issues like class imbalances or outliers and make informed decisions about further data preprocessing or model training adjustments.
### Statistical EDA Techniques
Statistical techniques often begin with calculating basic metrics such as mean, median, standard deviation, and range. These metrics provide a quick overview of your image dataset's properties, such as pixel intensity distributions. Understanding these basic statistics helps you grasp the overall quality and characteristics of your data, allowing you to spot any irregularities early on.
### Visual EDA Techniques
Visualizations are key in EDA for image datasets. For example, class imbalance analysis is another vital aspect of EDA. It helps determine if certain classes are underrepresented in your dataset, Visualizing the distribution of different image classes or categories using bar charts can quickly reveal any imbalances. Similarly, outliers can be identified using visualization tools like box plots, which highlight anomalies in pixel intensity or feature distributions. Outlier detection prevents unusual data points from skewing your results.
Common tools for visualizations include:
- Histograms and Box Plots: Useful for understanding the distribution of pixel values and identifying outliers.
- Scatter Plots: Helpful for exploring relationships between image features or annotations.
- Heatmaps: Effective for visualizing the distribution of pixel intensities or the spatial distribution of annotated features within images.
### Using Ultralytics Explorer for EDA
For a more advanced approach to EDA, you can use the Ultralytics Explorer tool. It offers robust capabilities for exploring computer vision datasets. By supporting semantic search, SQL queries, and vector similarity search, the tool makes it easy to analyze and understand your data. With Ultralytics Explorer, you can create embeddings for your dataset to find similar images, run SQL queries for detailed analysis, and perform semantic searches, all through a user-friendly graphical interface.
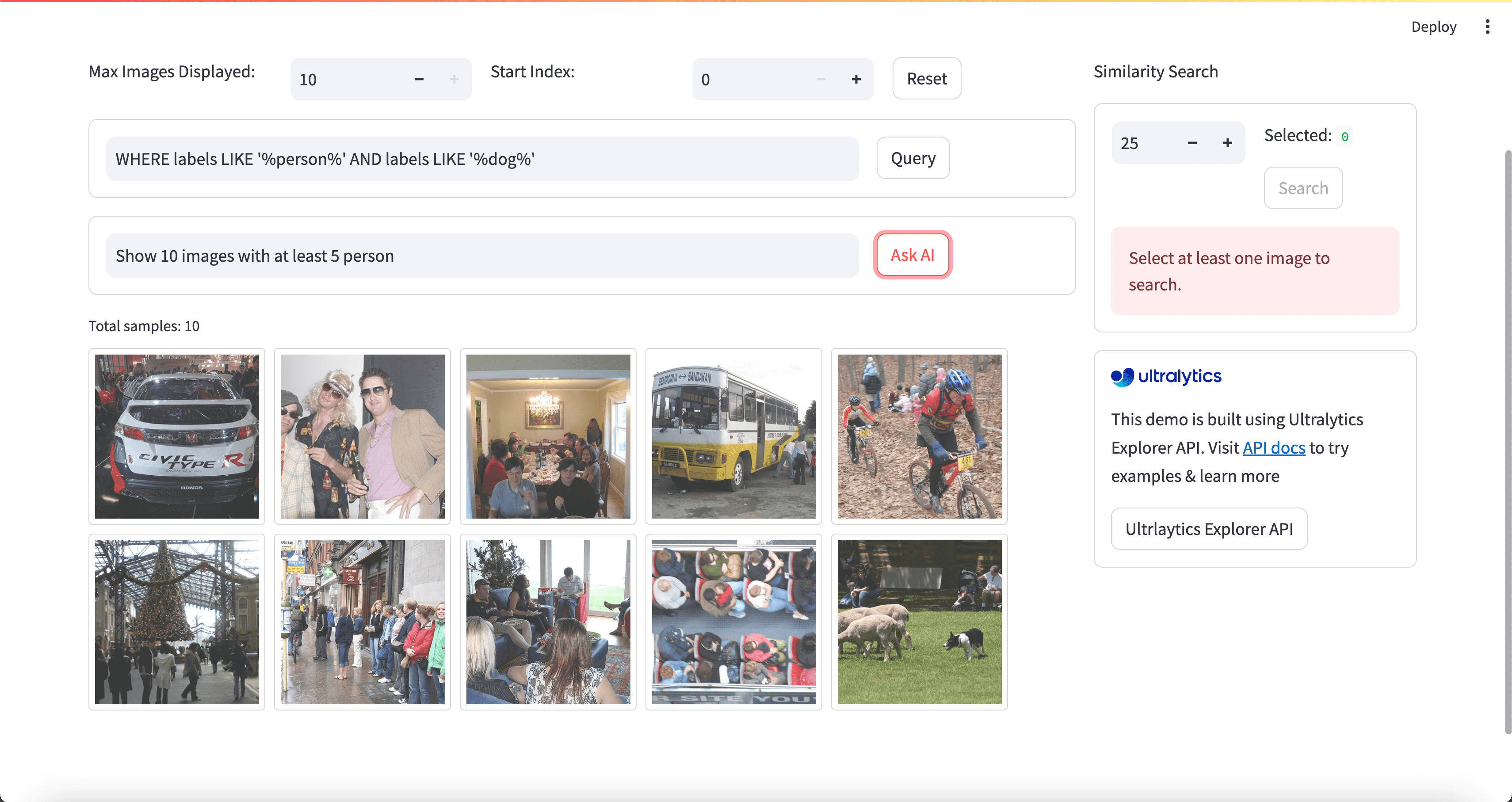
## FAQs
Here are some questions that might come up while you prepare your dataset:
- **Q1:** How much preprocessing is too much?
- **A1:** Preprocessing is essential but should be balanced. Overdoing it can lead to loss of critical information, overfitting, increased complexity, and higher computational costs. Focus on necessary steps like resizing, normalization, and basic augmentation, adjusting based on model performance.
- **Q2:** What are the common pitfalls in EDA?
- **A2:** Common pitfalls in Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) include ignoring data quality issues like missing values and outliers, confirmation bias, overfitting visualizations, neglecting data distribution, and overlooking correlations. A systematic approach helps gain accurate and valuable insights.
## Reach Out and Connect
Having discussions about your project with other computer vision enthusiasts can give you new ideas from different perspectives. Here are some great ways to learn, troubleshoot, and network:
### Channels to Connect with the Community
- **GitHub Issues:** Visit the YOLOv8 GitHub repository and use the [Issues tab](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues) to raise questions, report bugs, and suggest features. The community and maintainers are there to help with any issues you face.
- **Ultralytics Discord Server:** Join the [Ultralytics Discord server](https://ultralytics.com/discord/) to connect with other users and developers, get support, share knowledge, and brainstorm ideas.
### Official Documentation
- **Ultralytics YOLOv8 Documentation:** Refer to the [official YOLOv8 documentation](./index.md) for thorough guides and valuable insights on numerous computer vision tasks and projects.
## Your Dataset Is Ready!
Properly resized, normalized, and augmented data improves model performance by reducing noise and improving generalization. By following the preprocessing techniques and best practices outlined in this guide, you can create a solid dataset. With your preprocessed dataset ready, you can confidently proceed to the next steps in your project.

