---
comments: true
description: Quick start guide to setting up YOLOv8 on a NVIDIA Jetson device with comprehensive benchmarks.
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, NVIDIA, Jetson, TensorRT, quick start guide, hardware setup, machine learning, AI
---
# Quick Start Guide: NVIDIA Jetson with Ultralytics YOLOv8
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed walkthrough for deploying Ultralytics YOLOv8 on [NVIDIA Jetson](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/) devices. Additionally, it showcases performance benchmarks to demonstrate the capabilities of YOLOv8 on these small and powerful devices.
 !!! Note
This guide has been tested with [Seeed Studio reComputer J4012](https://www.seeedstudio.com/reComputer-J4012-p-5586.html) which is based on NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX 16GB running the latest stable JetPack release of [JP5.1.3](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetpack-sdk-513). Using this guide for older Jetson devices such as the Jetson Nano (this only supports until JP4.6.4) may not be guaranteed to work. However this is expected to work on all Jetson Orin, Xavier NX, AGX Xavier devices running JP5.1.3.
## What is NVIDIA Jetson?
NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring accelerated AI (artificial intelligence) computing to edge devices. These compact and powerful devices are built around NVIDIA's GPU architecture and are capable of running complex AI algorithms and deep learning models directly on the device, without needing to rely on cloud computing resources. Jetson boards are often used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and other applications where AI inference needs to be performed locally with low latency and high efficiency. Additionally, these boards are based on the ARM64 architecture and runs on lower power compared to traditional GPU computing devices.
## NVIDIA Jetson Series Comparison
[Jetson Orin](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-orin/) is the latest iteration of the NVIDIA Jetson family based on NVIDIA Ampere architecture which brings drastically improved AI performance when compared to the previous generations. Below table compared few of the Jetson devices in the ecosystem.
| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano |
| ----------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------- |
| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS |
| GPU | 2048-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 512-core NVIDIA Volta architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 384-core NVIDIA Volta™ architecture GPU with 48 Tensor Cores | 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell™ architecture GPU |
| GPU Max Frequency | 1.3 GHz | 918 MHz | 625 MHz | 1377 MHz | 1100 MHz | 921MHz |
| CPU | 12-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 3MB L2 + 6MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core Arm® Cortex®-A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 1.5MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 8MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 6MB L2 + 4MB L3 | Quad-Core Arm® Cortex®-A57 MPCore processor |
| CPU Max Frequency | 2.2 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 1.43GHz |
| Memory | 64GB 256-bit LPDDR5 204.8GB/s | 16GB 128-bit LPDDR5 102.4GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR5 68 GB/s | 32GB 256-bit LPDDR4x 136.5GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR4x 59.7GB/s | 4GB 64-bit LPDDR4 25.6GB/s" |
For a more detailed comparison table, please visit the **Technical Specifications** section of [official NVIDIA Jetson page](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetson-modules).
## What is NVIDIA JetPack?
[NVIDIA JetPack SDK](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetpack) powering the Jetson modules is the most comprehensive solution and provides full development environment for building end-to-end accelerated AI applications and shortens time to market. JetPack includes Jetson Linux with bootloader, Linux kernel, Ubuntu desktop environment, and a complete set of libraries for acceleration of GPU computing, multimedia, graphics, and computer vision. It also includes samples, documentation, and developer tools for both host computer and developer kit, and supports higher level SDKs such as DeepStream for streaming video analytics, Isaac for robotics, and Riva for conversational AI.
## Flash JetPack to NVIDIA Jetson
The first step after getting your hands on an NVIDIA Jetson device is to flash NVIDIA JetPack to the device. There are several different way of flashing NVIDIA Jetson devices.
1. If you own an official NVIDIA Development Kit such as the Jetson Orin Nano Developer Kit, you can visit [this link](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/learn/get-started-jetson-orin-nano-devkit) to download an image and prepare an SD card with JetPack for booting the device.
2. If you own any other NVIDIA Development Kit, you can visit [this link](https://docs.nvidia.com/sdk-manager/install-with-sdkm-jetson/index.html) to flash JetPack to the device using [SDK Manager](https://developer.nvidia.com/sdk-manager).
3. If you own a Seeed Studio reComputer J4012 device, you can visit [this link](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/reComputer_J4012_Flash_Jetpack) to flash JetPack to the included SSD.
4. If you own any other third party device powered by the NVIDIA Jetson module, it is recommended to follow command-line flashing by visiting [this link](https://docs.nvidia.com/jetson/archives/r35.5.0/DeveloperGuide/IN/QuickStart.html).
!!! Note
For methods 3 and 4 above, after flashing the system and booting the device, please enter "sudo apt update && sudo apt install nvidia-jetpack -y" on the device terminal to install all the remaining JetPack components needed.
## Set Up Ultralytics
There are two ways of setting up Ultralytics package on NVIDIA Jetson to build your next Computer Vision project. You can use either of them.
- [Start with Docker](#start-with-docker)
- [Start without Docker](#start-without-docker)
### Start with Docker
The fastest way to get started with Ultralytics YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson is to run with pre-built docker image for Jetson.
Execute the below command to pull the Docker container and run on Jetson. This is based on [l4t-pytorch](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/containers/l4t-pytorch) docker image which contains PyTorch and Torchvision in a Python3 environment.
```bash
t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest-jetson && sudo docker pull $t && sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --runtime=nvidia $t
```
After this is done, skip to [Use TensorRT on NVIDIA Jetson section](#use-tensorrt-on-nvidia-jetson).
### Start without Docker
#### Install Ultralytics Package
Here we will install ultralyics package on the Jetson with optional dependencies so that we can export the PyTorch models to other different formats. We will mainly focus on [NVIDIA TensorRT exports](../integrations/tensorrt.md) because TensoRT will make sure we can get the maximum performance out of the Jetson devices.
1. Update packages list, install pip and upgrade to latest
```bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
pip install -U pip
```
2. Install `ultralytics` pip package with optional dependencies
```bash
pip install ultralytics[export]
```
3. Reboot the device
```bash
sudo reboot
```
#### Install PyTorch and Torchvision
The above ultralytics installation will install Torch and Torchvision. However, these 2 packages installed via pip are not compatible to run on Jetson platform which is based on ARM64 architecture. Therefore, we need to manually install pre-built PyTorch pip wheel and compile/ install Torchvision from source.
1. Uninstall currently installed PyTorch and Torchvision
```bash
pip uninstall torch torchvision
```
2. Install PyTorch 2.1.0 according to JP5.1.3
```bash
sudo apt-get install -y libopenblas-base libopenmpi-dev
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/redist/jp/v512/pytorch/torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl -O torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
pip install torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
```
3. Install Torchvision v0.16.2 according to PyTorch v2.1.0
```bash
sudo apt install -y libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision torchvision
cd torchvision
git checkout v0.16.2
python3 setup.py install --user
```
Visit the [PyTorch for Jetson page](https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/pytorch-for-jetson/72048) to access all different versions of PyTorch for different JetPack versions. For a more detailed list on the PyTorch, Torchvision compatibility, visit the [PyTorch and Torchvision compatibility page](https://github.com/pytorch/vision).
#### Install `onnxruntime-gpu`
The [onnxruntime-gpu](https://pypi.org/project/onnxruntime-gpu/) package hosted in PyPI does not have `aarch64` binaries for the Jetson. So we need to manually install this package. This package is needed for some of the exports.
All different `onnxruntime-gpu` packages corresponsing to different JetPack and Python versions are listed [here](https://elinux.org/Jetson_Zoo#ONNX_Runtime). However, here we will download and install `onnxruntime-gpu 1.17.0` with `Python3.8` support for the JetPack we are using for this guide.
```bash
wget https://nvidia.box.com/shared/static/zostg6agm00fb6t5uisw51qi6kpcuwzd.whl -O onnxruntime_gpu-1.17.0-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
pip install onnxruntime_gpu-1.17.0-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
```
!!! Note
`onnxruntime-gpu` will automatically revert back the numpy version to latest. So we need to reinstall numpy to `1.23.5` to fix an issue by executing:
`pip install numpy==1.23.5`
## Use TensorRT on NVIDIA Jetson
Out of all the model export formats supported by Ultralytics, TensorRT delivers the best inference performance when working with NVIDIA Jetson devices and our recommendation is to use TensorRT with Jetson. We also have a detailed document on TensorRT [here](../integrations/tensorrt.md).
## Convert Model to TensorRT and Run Inference
The YOLOv8n model in PyTorch format is converted to TensorRT to run inference with the exported model.
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
# Export the model
model.export(format="engine") # creates 'yolov8n.engine'
# Load the exported TensorRT model
trt_model = YOLO("yolov8n.engine")
# Run inference
results = trt_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TensorRT format
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=engine # creates 'yolov8n.engine'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model=yolov8n.engine source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
```
!!! Note
Visit the [Export page](../modes/export.md#arguments) to access additional arguments when exporting models to different model formats
## NVIDIA Jetson Orin YOLOv8 Benchmarks
YOLOv8 benchmarks were run by the Ultralytics team on 10 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, TF SavedModel, TF Graphdef, TF Lite, PaddlePaddle, NCNN. Benchmarks were run on Seeed Studio reComputer J4012 powered by Jetson Orin NX 16GB device at FP32 precision with default input image size of 640.
### Comparison Chart
Eventhough all model exports are working with NVIDIA Jetson, we have only included **PyTorch, TorchScript, TensorRT** for the comparison chart below because, they make use of the GPU on the Jetson and are guaranteed to produce the best results. All the other exports only utilize the CPU and the performance is not as good as the above three. You can find benchmarks for all exports in the section after this chart.
### Detailed Comparison Table
The below table represents the benchmark results for five different models (YOLOv8n, YOLOv8s, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l, YOLOv8x) across ten different formats (PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, TF SavedModel, TF Graphdef, TF Lite, PaddlePaddle, NCNN), giving us the status, size, mAP50-95(B) metric, and inference time for each combination.
!!! Performance
=== "YOLOv8n"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 6.2 | 0.6381 | 14.3 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 12.4 | 0.6117 | 13.3 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 12.2 | 0.6092 | 70.6 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 104.2 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 13.6 | 0.6117 | 8.9 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 30.6 | 0.6092 | 141.74 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 199.93 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 349.18 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 24.4 | 0.6030 | 555 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 12.2 | 0.6092 | 32 |
=== "YOLOv8s"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 21.5 | 0.6967 | 18 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 43.0 | 0.7136 | 23.81 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 185.55 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 42.9 | 0.7136 | 243.97 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 44.0 | 0.7136 | 14.82 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 107 | 0.7136 | 260.03 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 423.4 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 1046.64 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 85.5 | 0.7140 | 1464 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 42.7 | 0.7200 | 63 |
=== "YOLOv8m"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 49.7 | 0.7370 | 36.4 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 99.2 | 0.7285 | 53.58 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 452.09 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 99.1 | 0.7280 | 544.36 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 100.3 | 0.7285 | 33.21 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 247.5 | 0.7280 | 543.65 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 906.63 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 2758.08 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 197.9 | 0.7280 | 3678 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 98.9 | 0.7260 | 135 |
=== "YOLOv8l"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 83.7 | 0.7768 | 61.3 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 167.2 | 0.7554 | 87.9 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 166.8 | 0.7551 | 852.29 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 167 | 0.7551 | 1012.6 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 168.4 | 0.7554 | 51.23 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 417.2 | 0.7551 | 990.45 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 166.9 | 0.7551 | 1649.86 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 166.9 | 0.7551 | 5652.37 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 333.6 | 0.7551 | 7114.67 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 166.8 | 0.7685 | 231.9 |
=== "YOLOv8x"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 130.5 | 0.7759 | 93 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 260.7 | 0.7472 | 135.1 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7479 | 1296.13 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 260.6 | 0.7479 | 1502.15 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 261.8 | 0.7469 | 84.53 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 651.1 | 0.7479 | 1451.76 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 260.5 | 0.7479 | 4029.36 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7479 | 8772.86 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 520.8 | 0.7479 | 10619.53 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7646 | 376.38 |
Visit [this link](https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2023/03/30/yolov8-performance-benchmarks-on-nvidia-jetson-devices) to explore more benchmarking efforts by Seeed Studio running on different versions of NVIDIA Jetson hardware.
## Reproduce Our Results
To reproduce the above Ultralytics benchmarks on all export [formats](../modes/export.md) run this code:
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all all export formats
results = model.benchmarks(data="coco8.yaml", imgsz=640)
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all all export formats
yolo benchmark model=yolov8n.pt data=coco8.yaml imgsz=640
```
Note that benchmarking results might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run. For the most reliable results use a dataset with a large number of images, i.e. `data='coco8.yaml' (4 val images), or `data='coco.yaml'` (5000 val images).
## Best Practices when using NVIDIA Jetson
When using NVIDIA Jetson, there are a couple of best practices to follow in order to enable maximum performance on the NVIDIA Jetson running YOLOv8.
1. Enable MAX Power Mode
Enabling MAX Power Mode on the Jetson will make sure all CPU, GPU cores are turned on.
```bash
sudo nvpmodel -m 0
```
2. Enable Jetson Clocks
Enabling Jetson Clocks will make sure all CPU, GPU cores are clocked at their maximum frequency.
```bash
sudo jetson_clocks
```
3. Install Jetson Stats Application
We can use jetson stats application to monitor the temperatures of the system components and check other system details such as view CPU, GPU, RAM utilization, change power modes, set to max clocks, check JetPack information
```bash
sudo apt update
sudo pip install jetson-stats
sudo reboot
jtop
```
!!! Note
This guide has been tested with [Seeed Studio reComputer J4012](https://www.seeedstudio.com/reComputer-J4012-p-5586.html) which is based on NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX 16GB running the latest stable JetPack release of [JP5.1.3](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetpack-sdk-513). Using this guide for older Jetson devices such as the Jetson Nano (this only supports until JP4.6.4) may not be guaranteed to work. However this is expected to work on all Jetson Orin, Xavier NX, AGX Xavier devices running JP5.1.3.
## What is NVIDIA Jetson?
NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring accelerated AI (artificial intelligence) computing to edge devices. These compact and powerful devices are built around NVIDIA's GPU architecture and are capable of running complex AI algorithms and deep learning models directly on the device, without needing to rely on cloud computing resources. Jetson boards are often used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and other applications where AI inference needs to be performed locally with low latency and high efficiency. Additionally, these boards are based on the ARM64 architecture and runs on lower power compared to traditional GPU computing devices.
## NVIDIA Jetson Series Comparison
[Jetson Orin](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-orin/) is the latest iteration of the NVIDIA Jetson family based on NVIDIA Ampere architecture which brings drastically improved AI performance when compared to the previous generations. Below table compared few of the Jetson devices in the ecosystem.
| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano |
| ----------------- | ---------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------------------------------------------- |
| AI Performance | 275 TOPS | 100 TOPS | 40 TOPs | 32 TOPS | 21 TOPS | 472 GFLOPS |
| GPU | 2048-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 1024-core NVIDIA Ampere architecture GPU with 32 Tensor Cores | 512-core NVIDIA Volta architecture GPU with 64 Tensor Cores | 384-core NVIDIA Volta™ architecture GPU with 48 Tensor Cores | 128-core NVIDIA Maxwell™ architecture GPU |
| GPU Max Frequency | 1.3 GHz | 918 MHz | 625 MHz | 1377 MHz | 1100 MHz | 921MHz |
| CPU | 12-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 3MB L2 + 6MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Arm® Cortex A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 2MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core Arm® Cortex®-A78AE v8.2 64-bit CPU 1.5MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 8-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 8MB L2 + 4MB L3 | 6-core NVIDIA Carmel Arm®v8.2 64-bit CPU 6MB L2 + 4MB L3 | Quad-Core Arm® Cortex®-A57 MPCore processor |
| CPU Max Frequency | 2.2 GHz | 2.0 GHz | 1.5 GHz | 2.2 GHz | 1.9 GHz | 1.43GHz |
| Memory | 64GB 256-bit LPDDR5 204.8GB/s | 16GB 128-bit LPDDR5 102.4GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR5 68 GB/s | 32GB 256-bit LPDDR4x 136.5GB/s | 8GB 128-bit LPDDR4x 59.7GB/s | 4GB 64-bit LPDDR4 25.6GB/s" |
For a more detailed comparison table, please visit the **Technical Specifications** section of [official NVIDIA Jetson page](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetson-modules).
## What is NVIDIA JetPack?
[NVIDIA JetPack SDK](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/jetpack) powering the Jetson modules is the most comprehensive solution and provides full development environment for building end-to-end accelerated AI applications and shortens time to market. JetPack includes Jetson Linux with bootloader, Linux kernel, Ubuntu desktop environment, and a complete set of libraries for acceleration of GPU computing, multimedia, graphics, and computer vision. It also includes samples, documentation, and developer tools for both host computer and developer kit, and supports higher level SDKs such as DeepStream for streaming video analytics, Isaac for robotics, and Riva for conversational AI.
## Flash JetPack to NVIDIA Jetson
The first step after getting your hands on an NVIDIA Jetson device is to flash NVIDIA JetPack to the device. There are several different way of flashing NVIDIA Jetson devices.
1. If you own an official NVIDIA Development Kit such as the Jetson Orin Nano Developer Kit, you can visit [this link](https://developer.nvidia.com/embedded/learn/get-started-jetson-orin-nano-devkit) to download an image and prepare an SD card with JetPack for booting the device.
2. If you own any other NVIDIA Development Kit, you can visit [this link](https://docs.nvidia.com/sdk-manager/install-with-sdkm-jetson/index.html) to flash JetPack to the device using [SDK Manager](https://developer.nvidia.com/sdk-manager).
3. If you own a Seeed Studio reComputer J4012 device, you can visit [this link](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/reComputer_J4012_Flash_Jetpack) to flash JetPack to the included SSD.
4. If you own any other third party device powered by the NVIDIA Jetson module, it is recommended to follow command-line flashing by visiting [this link](https://docs.nvidia.com/jetson/archives/r35.5.0/DeveloperGuide/IN/QuickStart.html).
!!! Note
For methods 3 and 4 above, after flashing the system and booting the device, please enter "sudo apt update && sudo apt install nvidia-jetpack -y" on the device terminal to install all the remaining JetPack components needed.
## Set Up Ultralytics
There are two ways of setting up Ultralytics package on NVIDIA Jetson to build your next Computer Vision project. You can use either of them.
- [Start with Docker](#start-with-docker)
- [Start without Docker](#start-without-docker)
### Start with Docker
The fastest way to get started with Ultralytics YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson is to run with pre-built docker image for Jetson.
Execute the below command to pull the Docker container and run on Jetson. This is based on [l4t-pytorch](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/containers/l4t-pytorch) docker image which contains PyTorch and Torchvision in a Python3 environment.
```bash
t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest-jetson && sudo docker pull $t && sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --runtime=nvidia $t
```
After this is done, skip to [Use TensorRT on NVIDIA Jetson section](#use-tensorrt-on-nvidia-jetson).
### Start without Docker
#### Install Ultralytics Package
Here we will install ultralyics package on the Jetson with optional dependencies so that we can export the PyTorch models to other different formats. We will mainly focus on [NVIDIA TensorRT exports](../integrations/tensorrt.md) because TensoRT will make sure we can get the maximum performance out of the Jetson devices.
1. Update packages list, install pip and upgrade to latest
```bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
pip install -U pip
```
2. Install `ultralytics` pip package with optional dependencies
```bash
pip install ultralytics[export]
```
3. Reboot the device
```bash
sudo reboot
```
#### Install PyTorch and Torchvision
The above ultralytics installation will install Torch and Torchvision. However, these 2 packages installed via pip are not compatible to run on Jetson platform which is based on ARM64 architecture. Therefore, we need to manually install pre-built PyTorch pip wheel and compile/ install Torchvision from source.
1. Uninstall currently installed PyTorch and Torchvision
```bash
pip uninstall torch torchvision
```
2. Install PyTorch 2.1.0 according to JP5.1.3
```bash
sudo apt-get install -y libopenblas-base libopenmpi-dev
wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/redist/jp/v512/pytorch/torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl -O torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
pip install torch-2.1.0a0+41361538.nv23.06-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
```
3. Install Torchvision v0.16.2 according to PyTorch v2.1.0
```bash
sudo apt install -y libjpeg-dev zlib1g-dev
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision torchvision
cd torchvision
git checkout v0.16.2
python3 setup.py install --user
```
Visit the [PyTorch for Jetson page](https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/pytorch-for-jetson/72048) to access all different versions of PyTorch for different JetPack versions. For a more detailed list on the PyTorch, Torchvision compatibility, visit the [PyTorch and Torchvision compatibility page](https://github.com/pytorch/vision).
#### Install `onnxruntime-gpu`
The [onnxruntime-gpu](https://pypi.org/project/onnxruntime-gpu/) package hosted in PyPI does not have `aarch64` binaries for the Jetson. So we need to manually install this package. This package is needed for some of the exports.
All different `onnxruntime-gpu` packages corresponsing to different JetPack and Python versions are listed [here](https://elinux.org/Jetson_Zoo#ONNX_Runtime). However, here we will download and install `onnxruntime-gpu 1.17.0` with `Python3.8` support for the JetPack we are using for this guide.
```bash
wget https://nvidia.box.com/shared/static/zostg6agm00fb6t5uisw51qi6kpcuwzd.whl -O onnxruntime_gpu-1.17.0-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
pip install onnxruntime_gpu-1.17.0-cp38-cp38-linux_aarch64.whl
```
!!! Note
`onnxruntime-gpu` will automatically revert back the numpy version to latest. So we need to reinstall numpy to `1.23.5` to fix an issue by executing:
`pip install numpy==1.23.5`
## Use TensorRT on NVIDIA Jetson
Out of all the model export formats supported by Ultralytics, TensorRT delivers the best inference performance when working with NVIDIA Jetson devices and our recommendation is to use TensorRT with Jetson. We also have a detailed document on TensorRT [here](../integrations/tensorrt.md).
## Convert Model to TensorRT and Run Inference
The YOLOv8n model in PyTorch format is converted to TensorRT to run inference with the exported model.
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
# Export the model
model.export(format="engine") # creates 'yolov8n.engine'
# Load the exported TensorRT model
trt_model = YOLO("yolov8n.engine")
# Run inference
results = trt_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Export a YOLOv8n PyTorch model to TensorRT format
yolo export model=yolov8n.pt format=engine # creates 'yolov8n.engine'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model=yolov8n.engine source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
```
!!! Note
Visit the [Export page](../modes/export.md#arguments) to access additional arguments when exporting models to different model formats
## NVIDIA Jetson Orin YOLOv8 Benchmarks
YOLOv8 benchmarks were run by the Ultralytics team on 10 different model formats measuring speed and accuracy: PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, TF SavedModel, TF Graphdef, TF Lite, PaddlePaddle, NCNN. Benchmarks were run on Seeed Studio reComputer J4012 powered by Jetson Orin NX 16GB device at FP32 precision with default input image size of 640.
### Comparison Chart
Eventhough all model exports are working with NVIDIA Jetson, we have only included **PyTorch, TorchScript, TensorRT** for the comparison chart below because, they make use of the GPU on the Jetson and are guaranteed to produce the best results. All the other exports only utilize the CPU and the performance is not as good as the above three. You can find benchmarks for all exports in the section after this chart.
### Detailed Comparison Table
The below table represents the benchmark results for five different models (YOLOv8n, YOLOv8s, YOLOv8m, YOLOv8l, YOLOv8x) across ten different formats (PyTorch, TorchScript, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, TF SavedModel, TF Graphdef, TF Lite, PaddlePaddle, NCNN), giving us the status, size, mAP50-95(B) metric, and inference time for each combination.
!!! Performance
=== "YOLOv8n"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 6.2 | 0.6381 | 14.3 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 12.4 | 0.6117 | 13.3 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 12.2 | 0.6092 | 70.6 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 104.2 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 13.6 | 0.6117 | 8.9 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 30.6 | 0.6092 | 141.74 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 199.93 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 12.3 | 0.6092 | 349.18 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 24.4 | 0.6030 | 555 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 12.2 | 0.6092 | 32 |
=== "YOLOv8s"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 21.5 | 0.6967 | 18 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 43.0 | 0.7136 | 23.81 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 185.55 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 42.9 | 0.7136 | 243.97 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 44.0 | 0.7136 | 14.82 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 107 | 0.7136 | 260.03 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 423.4 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 42.8 | 0.7136 | 1046.64 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 85.5 | 0.7140 | 1464 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 42.7 | 0.7200 | 63 |
=== "YOLOv8m"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 49.7 | 0.7370 | 36.4 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 99.2 | 0.7285 | 53.58 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 452.09 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 99.1 | 0.7280 | 544.36 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 100.3 | 0.7285 | 33.21 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 247.5 | 0.7280 | 543.65 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 906.63 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 99 | 0.7280 | 2758.08 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 197.9 | 0.7280 | 3678 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 98.9 | 0.7260 | 135 |
=== "YOLOv8l"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 83.7 | 0.7768 | 61.3 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 167.2 | 0.7554 | 87.9 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 166.8 | 0.7551 | 852.29 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 167 | 0.7551 | 1012.6 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 168.4 | 0.7554 | 51.23 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 417.2 | 0.7551 | 990.45 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 166.9 | 0.7551 | 1649.86 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 166.9 | 0.7551 | 5652.37 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 333.6 | 0.7551 | 7114.67 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 166.8 | 0.7685 | 231.9 |
=== "YOLOv8x"
| Format | Status | Size on disk (MB) | mAP50-95(B) | Inference time (ms/im) |
|---------------|--------|-----------|-------------|------------------------|
| PyTorch | ✅ | 130.5 | 0.7759 | 93 |
| TorchScript | ✅ | 260.7 | 0.7472 | 135.1 |
| ONNX | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7479 | 1296.13 |
| OpenVINO | ✅ | 260.6 | 0.7479 | 1502.15 |
| TensorRT | ✅ | 261.8 | 0.7469 | 84.53 |
| TF SavedModel | ✅ | 651.1 | 0.7479 | 1451.76 |
| TF GraphDef | ✅ | 260.5 | 0.7479 | 4029.36 |
| TF Lite | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7479 | 8772.86 |
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | 520.8 | 0.7479 | 10619.53 |
| NCNN | ✅ | 260.4 | 0.7646 | 376.38 |
Visit [this link](https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2023/03/30/yolov8-performance-benchmarks-on-nvidia-jetson-devices) to explore more benchmarking efforts by Seeed Studio running on different versions of NVIDIA Jetson hardware.
## Reproduce Our Results
To reproduce the above Ultralytics benchmarks on all export [formats](../modes/export.md) run this code:
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a YOLOv8n PyTorch model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all all export formats
results = model.benchmarks(data="coco8.yaml", imgsz=640)
```
=== "CLI"
```bash
# Benchmark YOLOv8n speed and accuracy on the COCO8 dataset for all all export formats
yolo benchmark model=yolov8n.pt data=coco8.yaml imgsz=640
```
Note that benchmarking results might vary based on the exact hardware and software configuration of a system, as well as the current workload of the system at the time the benchmarks are run. For the most reliable results use a dataset with a large number of images, i.e. `data='coco8.yaml' (4 val images), or `data='coco.yaml'` (5000 val images).
## Best Practices when using NVIDIA Jetson
When using NVIDIA Jetson, there are a couple of best practices to follow in order to enable maximum performance on the NVIDIA Jetson running YOLOv8.
1. Enable MAX Power Mode
Enabling MAX Power Mode on the Jetson will make sure all CPU, GPU cores are turned on.
```bash
sudo nvpmodel -m 0
```
2. Enable Jetson Clocks
Enabling Jetson Clocks will make sure all CPU, GPU cores are clocked at their maximum frequency.
```bash
sudo jetson_clocks
```
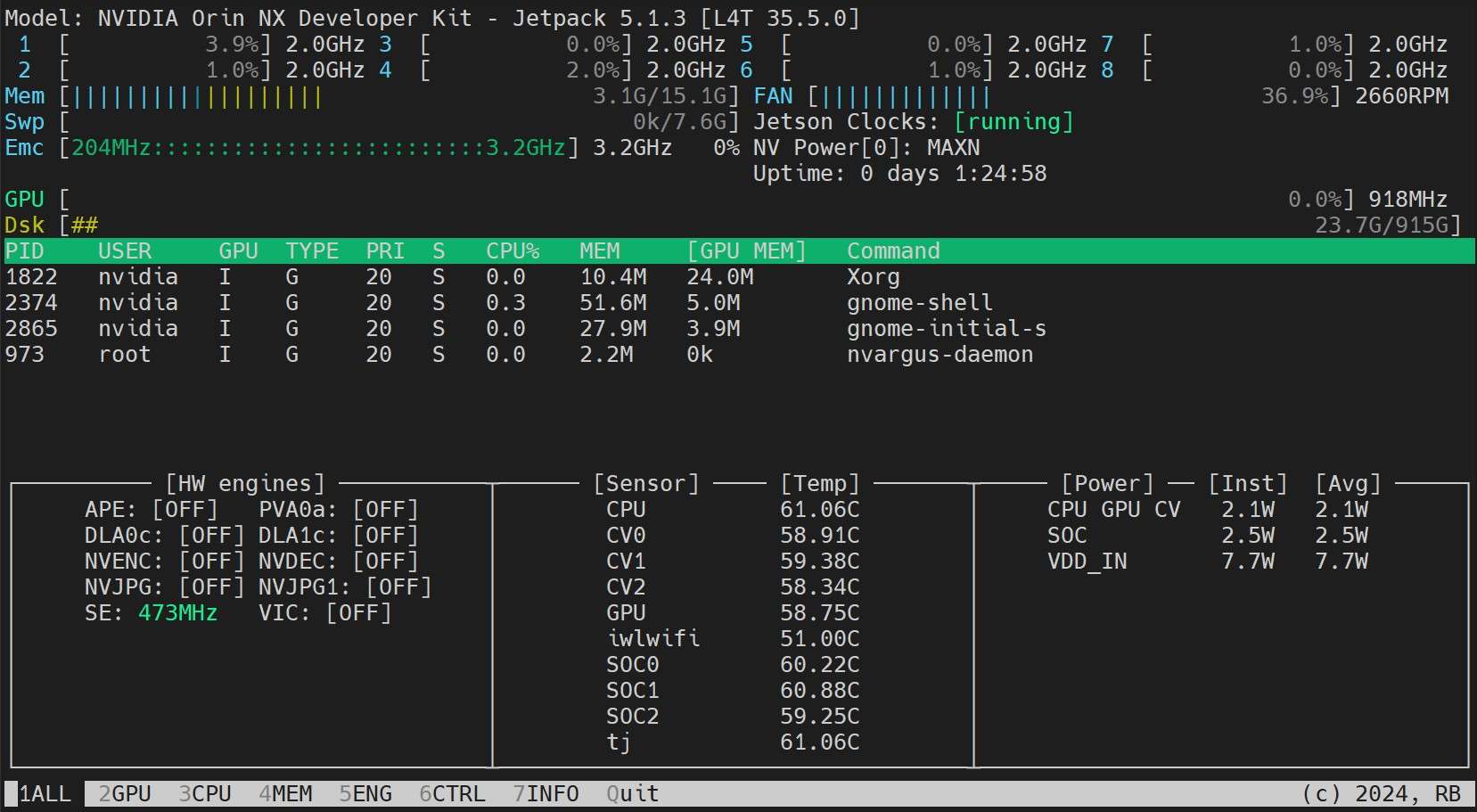
3. Install Jetson Stats Application
We can use jetson stats application to monitor the temperatures of the system components and check other system details such as view CPU, GPU, RAM utilization, change power modes, set to max clocks, check JetPack information
```bash
sudo apt update
sudo pip install jetson-stats
sudo reboot
jtop
```
 ## Next Steps
Congratulations on successfully setting up YOLOv8 on your NVIDIA Jetson! For further learning and support, visit more guide at [Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs](../index.md)!
## Next Steps
Congratulations on successfully setting up YOLOv8 on your NVIDIA Jetson! For further learning and support, visit more guide at [Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs](../index.md)!