Ultralytics Docs are the gateway to understanding and utilizing our cutting-edge machine learning tools. These documents are deployed to [https://docs.ultralytics.com](https://docs.ultralytics.com) for your convenience.
[Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) Docs are the gateway to understanding and utilizing our cutting-edge machine learning tools. These documents are deployed to [https://docs.ultralytics.com](https://docs.ultralytics.com) for your convenience.
@ -99,6 +99,7 @@ Choose a hosting provider and deployment method for your MkDocs documentation:
- Use `mkdocs deploy` to build and deploy your site.
- Use `mkdocs deploy` to build and deploy your site.
* ### GitHub Pages Deployment Example:
* ### GitHub Pages Deployment Example:
```bash
```bash
mkdocs gh-deploy
mkdocs gh-deploy
```
```
@ -113,8 +114,6 @@ Choose a hosting provider and deployment method for your MkDocs documentation:
We cherish the community's input as it drives Ultralytics open-source initiatives. Dive into the [Contributing Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/contributing) and share your thoughts via our [Survey](https://ultralytics.com/survey?utm_source=github&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=Survey). A heartfelt thank you 🙏 to each contributor!
We cherish the community's input as it drives Ultralytics open-source initiatives. Dive into the [Contributing Guide](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/contributing) and share your thoughts via our [Survey](https://ultralytics.com/survey?utm_source=github&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=Survey). A heartfelt thank you 🙏 to each contributor!
<!-- Pictorial representation of our dedicated contributor community -->
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ This guide assumes that you already have a working Raspberry Pi OS install and h
First, we need to install the Edge TPU runtime. There are many different versions available, so you need to choose the right version for your operating system.
First, we need to install the Edge TPU runtime. There are many different versions available, so you need to choose the right version for your operating system.
| Raspberry Pi OS | High frequency mode | Version to download |
| Raspberry Pi OS | High frequency mode | Version to download |
@ -135,6 +135,7 @@ While reviewing, if you find errors, correct them and update the guidelines to a
Here are some questions that might encounter while collecting and annotating data:
Here are some questions that might encounter while collecting and annotating data:
- **Q1:** What is active learning in the context of data annotation?
- **Q1:** What is active learning in the context of data annotation?
- **A1:** Active learning in data annotation is a technique where a machine learning model iteratively selects the most informative data points for labeling. This improves the model's performance with fewer labeled examples. By focusing on the most valuable data, active learning accelerates the training process and improves the model's ability to generalize from limited data.
- **A1:** Active learning in data annotation is a technique where a machine learning model iteratively selects the most informative data points for labeling. This improves the model's performance with fewer labeled examples. By focusing on the most valuable data, active learning accelerates the training process and improves the model's ability to generalize from limited data.
<palign="center">
<palign="center">
@ -142,9 +143,11 @@ Here are some questions that might encounter while collecting and annotating dat
</p>
</p>
- **Q2:** How does automated annotation work?
- **Q2:** How does automated annotation work?
- **A2:** Automated annotation uses pre-trained models and algorithms to label data without needing human effort. These models, which have been trained on large datasets, can identify patterns and features in new data. Techniques like transfer learning adjust these models for specific tasks, and active learning helps by selecting the most useful data points for labeling. However, this approach is only possible in certain cases where the model has been trained on sufficiently similar data and tasks.
- **A2:** Automated annotation uses pre-trained models and algorithms to label data without needing human effort. These models, which have been trained on large datasets, can identify patterns and features in new data. Techniques like transfer learning adjust these models for specific tasks, and active learning helps by selecting the most useful data points for labeling. However, this approach is only possible in certain cases where the model has been trained on sufficiently similar data and tasks.
- **Q3:** How many images do I need to collect for [YOLOv8 custom training](../modes/train.md)?
- **Q3:** How many images do I need to collect for [YOLOv8 custom training](../modes/train.md)?
- **A3:** For transfer learning and object detection, a good general rule of thumb is to have a minimum of a few hundred annotated objects per class. However, when training a model to detect just one class, it is advisable to start with at least 100 annotated images and train for around 100 epochs. For complex tasks, you may need thousands of images per class to achieve reliable model performance.
- **A3:** For transfer learning and object detection, a good general rule of thumb is to have a minimum of a few hundred annotated objects per class. However, when training a model to detect just one class, it is advisable to start with at least 100 annotated images and train for around 100 epochs. For complex tasks, you may need thousands of images per class to achieve reliable model performance.
@ -63,9 +63,11 @@ Other tasks, like [object detection](../tasks/detect.md), are not suitable as th
The order of model selection, dataset preparation, and training approach depends on the specifics of your project. Here are a few tips to help you decide:
The order of model selection, dataset preparation, and training approach depends on the specifics of your project. Here are a few tips to help you decide:
- **Clear Understanding of the Problem**: If your problem and objectives are well-defined, start with model selection. Then, prepare your dataset and decide on the training approach based on the model's requirements.
- **Clear Understanding of the Problem**: If your problem and objectives are well-defined, start with model selection. Then, prepare your dataset and decide on the training approach based on the model's requirements.
- **Example**: Start by selecting a model for a traffic monitoring system that estimates vehicle speeds. Choose an object tracking model, gather and annotate highway videos, and then train the model with techniques for real-time video processing.
- **Example**: Start by selecting a model for a traffic monitoring system that estimates vehicle speeds. Choose an object tracking model, gather and annotate highway videos, and then train the model with techniques for real-time video processing.
- **Unique or Limited Data**: If your project is constrained by unique or limited data, begin with dataset preparation. For instance, if you have a rare dataset of medical images, annotate and prepare the data first. Then, select a model that performs well on such data, followed by choosing a suitable training approach.
- **Unique or Limited Data**: If your project is constrained by unique or limited data, begin with dataset preparation. For instance, if you have a rare dataset of medical images, annotate and prepare the data first. Then, select a model that performs well on such data, followed by choosing a suitable training approach.
- **Example**: Prepare the data first for a facial recognition system with a small dataset. Annotate it, then select a model that works well with limited data, such as a pre-trained model for transfer learning. Finally, decide on a training approach, including data augmentation, to expand the dataset.
- **Example**: Prepare the data first for a facial recognition system with a small dataset. Annotate it, then select a model that works well with limited data, such as a pre-trained model for transfer learning. Finally, decide on a training approach, including data augmentation, to expand the dataset.
- **Need for Experimentation**: In projects where experimentation is crucial, start with the training approach. This is common in research projects where you might initially test different training techniques. Refine your model selection after identifying a promising method and prepare the dataset based on your findings.
- **Need for Experimentation**: In projects where experimentation is crucial, start with the training approach. This is common in research projects where you might initially test different training techniques. Refine your model selection after identifying a promising method and prepare the dataset based on your findings.
@ -118,6 +120,7 @@ Here are some questions that might encounter while defining your computer vision
</p>
</p>
- **Q2:** Can the scope of a computer vision project change after the problem statement is defined?
- **Q2:** Can the scope of a computer vision project change after the problem statement is defined?
- **A2:** Yes, the scope of a computer vision project can change as new information becomes available or as project requirements evolve. It's important to regularly review and adjust the problem statement and objectives to reflect any new insights or changes in project direction.
- **A2:** Yes, the scope of a computer vision project can change as new information becomes available or as project requirements evolve. It's important to regularly review and adjust the problem statement and objectives to reflect any new insights or changes in project direction.
- **Q3:** What are some common challenges in defining the problem for a computer vision project?
- **Q3:** What are some common challenges in defining the problem for a computer vision project?
@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ Here's a compilation of in-depth guides to help you master different aspects of
- [OpenVINO Latency vs Throughput Modes](optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md) - Learn latency and throughput optimization techniques for peak YOLO inference performance.
- [OpenVINO Latency vs Throughput Modes](optimizing-openvino-latency-vs-throughput-modes.md) - Learn latency and throughput optimization techniques for peak YOLO inference performance.
- [Steps of a Computer Vision Project ](steps-of-a-cv-project.md) 🚀 NEW: Learn about the key steps involved in a computer vision project, including defining goals, selecting models, preparing data, and evaluating results.
- [Steps of a Computer Vision Project ](steps-of-a-cv-project.md) 🚀 NEW: Learn about the key steps involved in a computer vision project, including defining goals, selecting models, preparing data, and evaluating results.
- [Defining A Computer Vision Project's Goals](defining-project-goals.md) 🚀 NEW: Walk through how to effectively define clear and measurable goals for your computer vision project. Learn the importance of a well-defined problem statement and how it creates a roadmap for your project.
- [Defining A Computer Vision Project's Goals](defining-project-goals.md) 🚀 NEW: Walk through how to effectively define clear and measurable goals for your computer vision project. Learn the importance of a well-defined problem statement and how it creates a roadmap for your project.
- - [Data Collection and Annotation](data-collection-and-annotation.md)🚀 NEW: Explore the tools, techniques, and best practices for collecting and annotating data to create high-quality inputs for your computer vision models.
- [Data Collection and Annotation](data-collection-and-annotation.md)🚀 NEW: Explore the tools, techniques, and best practices for collecting and annotating data to create high-quality inputs for your computer vision models.
- [Preprocessing Annotated Data](preprocessing_annotated_data.md)🚀 NEW: Learn about preprocessing and augmenting image data in computer vision projects using YOLOv8, including normalization, dataset augmentation, splitting, and exploratory data analysis (EDA).
- [Preprocessing Annotated Data](preprocessing_annotated_data.md)🚀 NEW: Learn about preprocessing and augmenting image data in computer vision projects using YOLOv8, including normalization, dataset augmentation, splitting, and exploratory data analysis (EDA).
@ -263,7 +263,7 @@ NCNN is a high-performance neural network inference framework optimized for the
The following table provides a snapshot of the various deployment options available for YOLOv8 models, helping you to assess which may best fit your project needs based on several critical criteria. For an in-depth look at each deployment option's format, please see the [Ultralytics documentation page on export formats](../modes/export.md#export-formats).
The following table provides a snapshot of the various deployment options available for YOLOv8 models, helping you to assess which may best fit your project needs based on several critical criteria. For an in-depth look at each deployment option's format, please see the [Ultralytics documentation page on export formats](../modes/export.md#export-formats).
| Deployment Option | Performance Benchmarks | Compatibility and Integration | Community Support and Ecosystem | Case Studies | Maintenance and Updates | Security Considerations | Hardware Acceleration |
| Deployment Option | Performance Benchmarks | Compatibility and Integration | Community Support and Ecosystem | Case Studies | Maintenance and Updates | Security Considerations | Hardware Acceleration |
| PyTorch | Good flexibility; may trade off raw performance | Excellent with Python libraries | Extensive resources and community | Research and prototypes | Regular, active development | Dependent on deployment environment | CUDA support for GPU acceleration |
| PyTorch | Good flexibility; may trade off raw performance | Excellent with Python libraries | Extensive resources and community | Research and prototypes | Regular, active development | Dependent on deployment environment | CUDA support for GPU acceleration |
| TorchScript | Better for production than PyTorch | Smooth transition from PyTorch to C++ | Specialized but narrower than PyTorch | Industry where Python is a bottleneck | Consistent updates with PyTorch | Improved security without full Python | Inherits CUDA support from PyTorch |
| TorchScript | Better for production than PyTorch | Smooth transition from PyTorch to C++ | Specialized but narrower than PyTorch | Industry where Python is a bottleneck | Consistent updates with PyTorch | Improved security without full Python | Inherits CUDA support from PyTorch |
| ONNX | Variable depending on runtime | High across different frameworks | Broad ecosystem, supported by many orgs | Flexibility across ML frameworks | Regular updates for new operations | Ensure secure conversion and deployment practices | Various hardware optimizations |
| ONNX | Variable depending on runtime | High across different frameworks | Broad ecosystem, supported by many orgs | Flexibility across ML frameworks | Regular updates for new operations | Ensure secure conversion and deployment practices | Various hardware optimizations |
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ NVIDIA Jetson is a series of embedded computing boards designed to bring acceler
[Jetson Orin](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-orin/) is the latest iteration of the NVIDIA Jetson family based on NVIDIA Ampere architecture which brings drastically improved AI performance when compared to the previous generations. Below table compared few of the Jetson devices in the ecosystem.
[Jetson Orin](https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/autonomous-machines/embedded-systems/jetson-orin/) is the latest iteration of the NVIDIA Jetson family based on NVIDIA Ampere architecture which brings drastically improved AI performance when compared to the previous generations. Below table compared few of the Jetson devices in the ecosystem.
| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano |
| | Jetson AGX Orin 64GB | Jetson Orin NX 16GB | Jetson Orin Nano 8GB | Jetson AGX Xavier | Jetson Xavier NX | Jetson Nano |
|  | 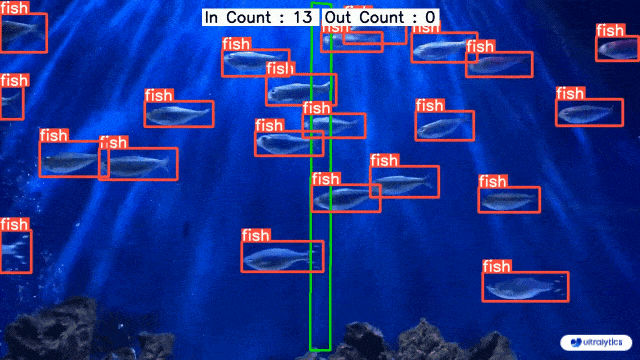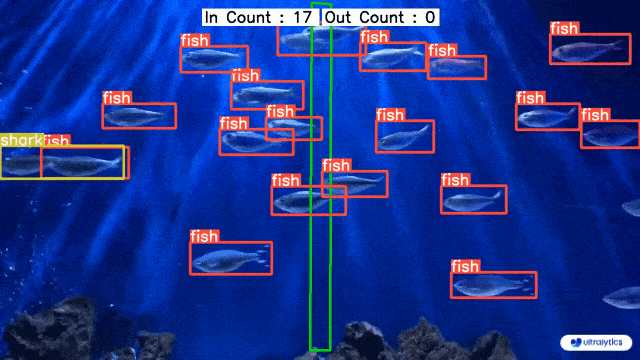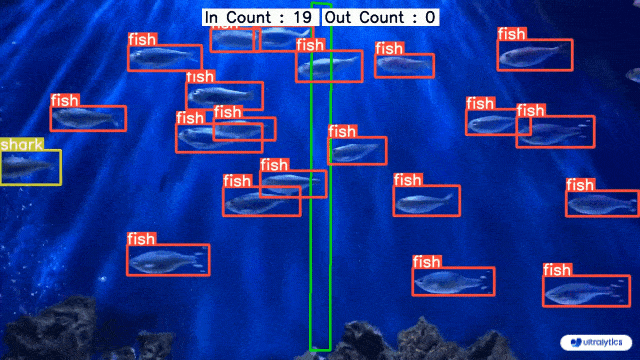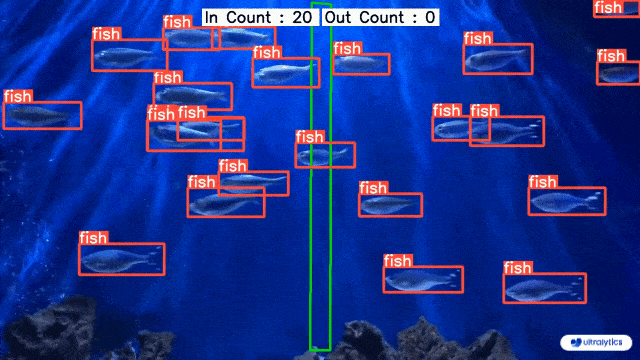 |
|  |  |
| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
| Conveyor Belt Packets Counting Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Fish Counting in Sea using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ Object counting with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
Here's a table with the `ObjectCounter` arguments:
Here's a table with the `ObjectCounter` arguments:
|  |
|  |
| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
| Suitcases Cropping at airport conveyor belt using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ Object cropping with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultraly
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
@ -54,9 +54,9 @@ With respect to YOLOv8, normalization is seamlessly handled as part of its prepr
Once you've cleaned the data, you are ready to split the dataset. Splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets is done to ensure that the model can be evaluated on unseen data to assess its generalization performance. A common split is 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing. There are various tools and libraries that you can use to split your data like scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
Once you've cleaned the data, you are ready to split the dataset. Splitting the data into training, validation, and test sets is done to ensure that the model can be evaluated on unseen data to assess its generalization performance. A common split is 70% for training, 20% for validation, and 10% for testing. There are various tools and libraries that you can use to split your data like scikit-learn or TensorFlow.
Consider the following when splitting your dataset:
Consider the following when splitting your dataset:
- **Maintaining Data Distribution**: Ensure that the data distribution of classes is maintained across training, validation, and test sets.
- **Maintaining Data Distribution**: Ensure that the data distribution of classes is maintained across training, validation, and test sets.
- **Avoiding Data Leakage**: Typically, data augmentation is done after the dataset is split. Data augmentation and any other preprocessing should only be applied to the training set to prevent information from the validation or test sets from influencing the model training.
- **Avoiding Data Leakage**: Typically, data augmentation is done after the dataset is split. Data augmentation and any other preprocessing should only be applied to the training set to prevent information from the validation or test sets from influencing the model training. -**Balancing Classes**: For imbalanced datasets, consider techniques such as oversampling the minority class or under-sampling the majority class within the training set.
-**Balancing Classes**: For imbalanced datasets, consider techniques such as oversampling the minority class or under-sampling the majority class within the training set.
### What is Data Augmentation?
### What is Data Augmentation?
@ -131,9 +131,11 @@ For a more advanced approach to EDA, you can use the Ultralytics Explorer tool.
Here are some questions that might come up while you prepare your dataset:
Here are some questions that might come up while you prepare your dataset:
- **Q1:** How much preprocessing is too much?
- **Q1:** How much preprocessing is too much?
- **A1:** Preprocessing is essential but should be balanced. Overdoing it can lead to loss of critical information, overfitting, increased complexity, and higher computational costs. Focus on necessary steps like resizing, normalization, and basic augmentation, adjusting based on model performance.
- **A1:** Preprocessing is essential but should be balanced. Overdoing it can lead to loss of critical information, overfitting, increased complexity, and higher computational costs. Focus on necessary steps like resizing, normalization, and basic augmentation, adjusting based on model performance.
- **Q2:** What are the common pitfalls in EDA?
- **Q2:** What are the common pitfalls in EDA?
- **A2:** Common pitfalls in Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) include ignoring data quality issues like missing values and outliers, confirmation bias, overfitting visualizations, neglecting data distribution, and overlooking correlations. A systematic approach helps gain accurate and valuable insights.
- **A2:** Common pitfalls in Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) include ignoring data quality issues like missing values and outliers, confirmation bias, overfitting visualizations, neglecting data distribution, and overlooking correlations. A systematic approach helps gain accurate and valuable insights.
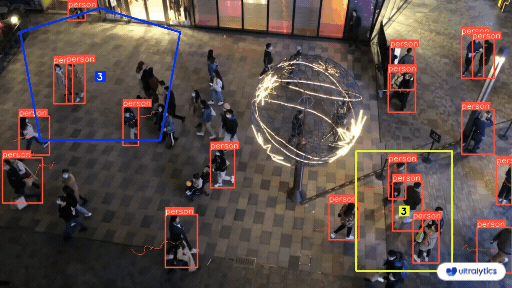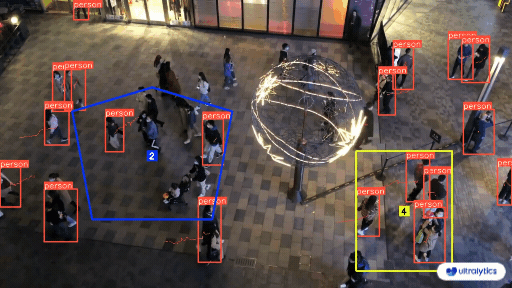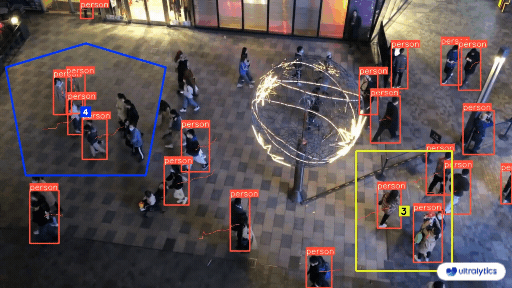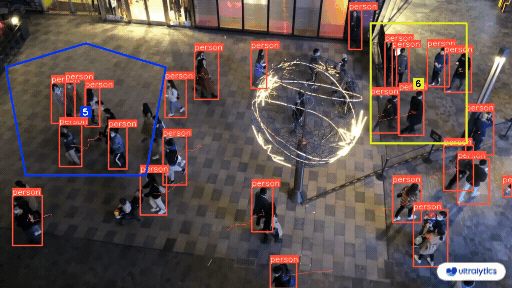
|  |  |
|  |  |
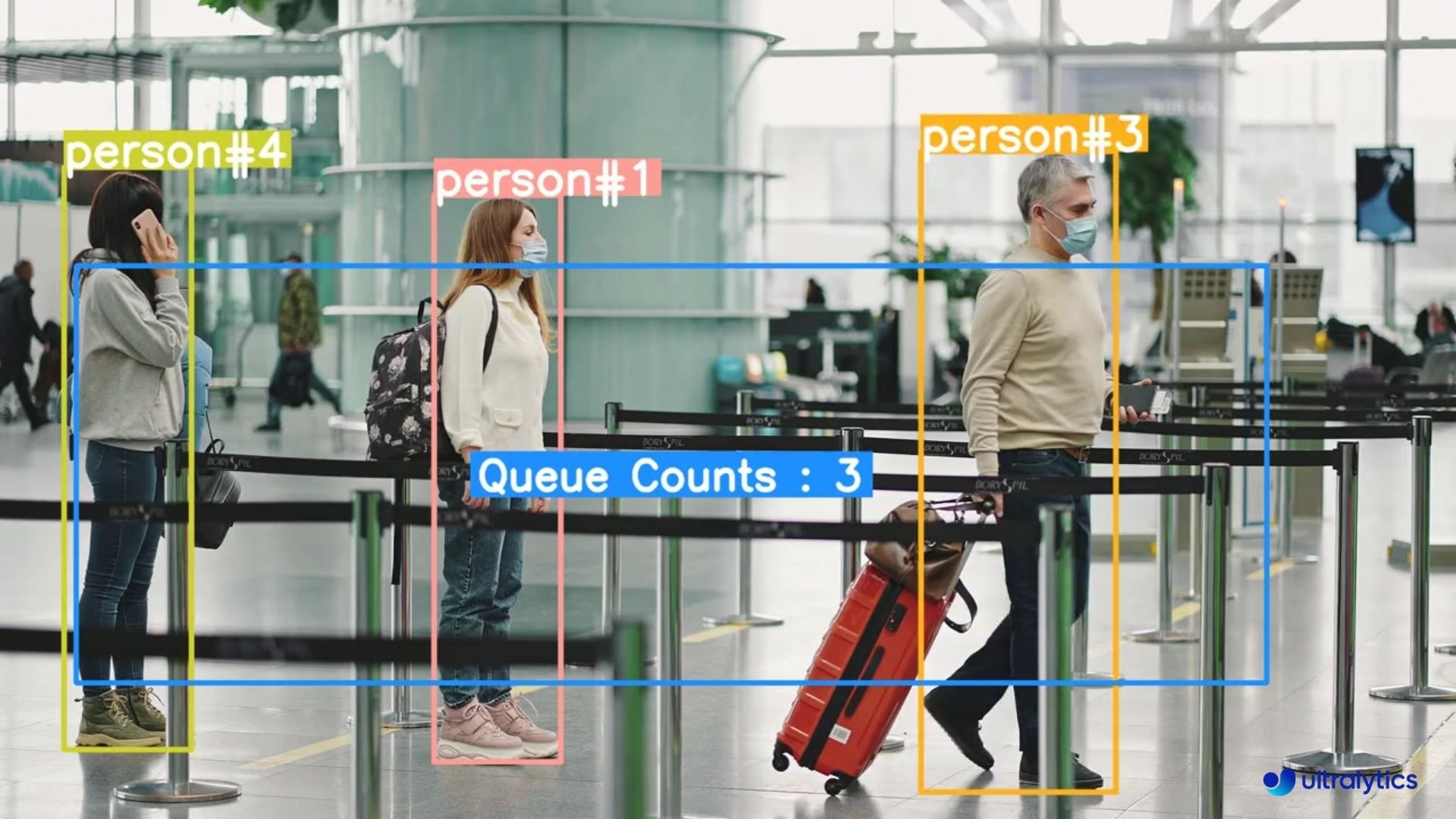
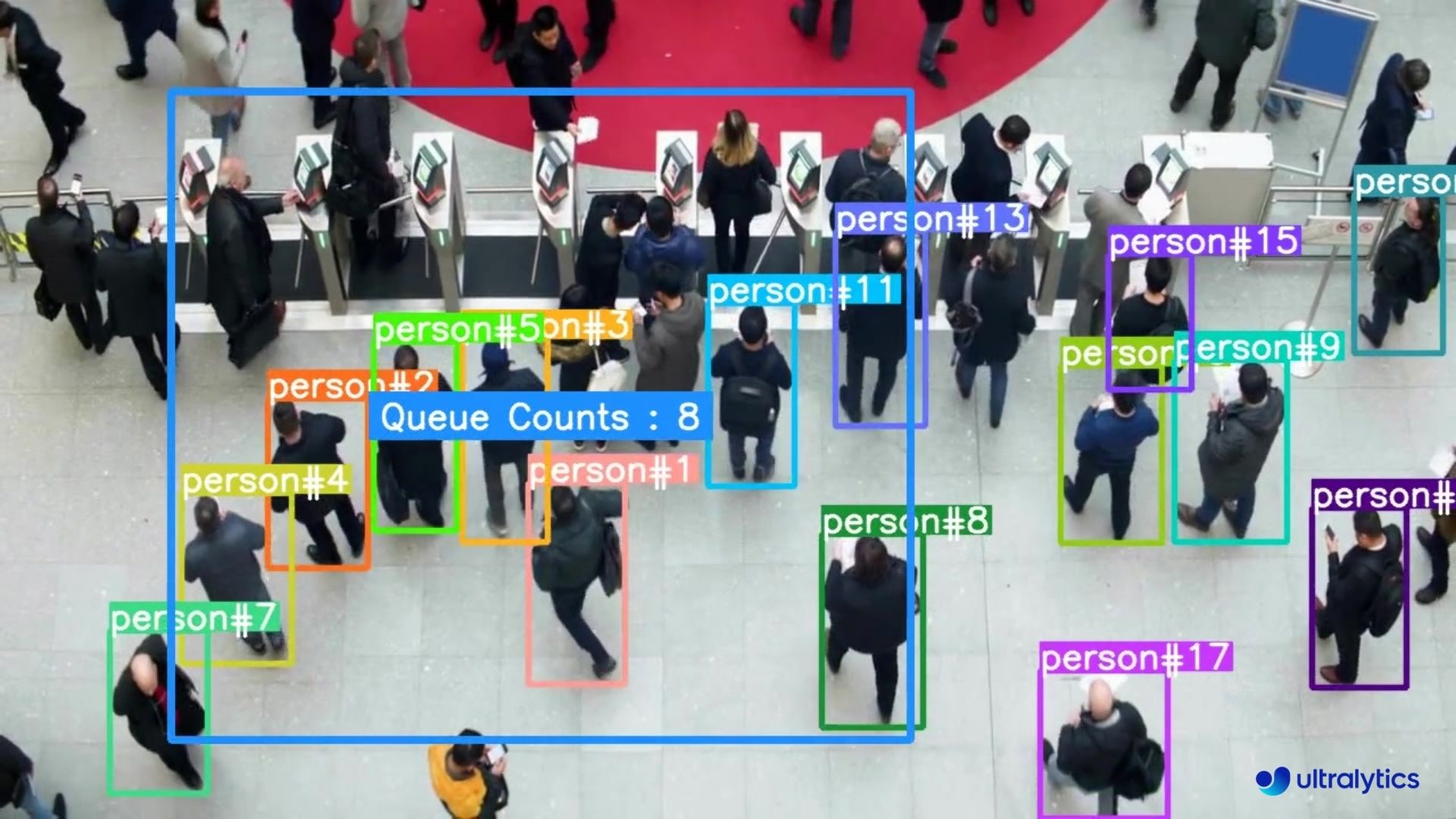
| Queue management at airport ticket counter Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Queue monitoring in crowd Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
| Queue management at airport ticket counter Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Queue monitoring in crowd Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ Queue management using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultra
|  |  |
|  |  |
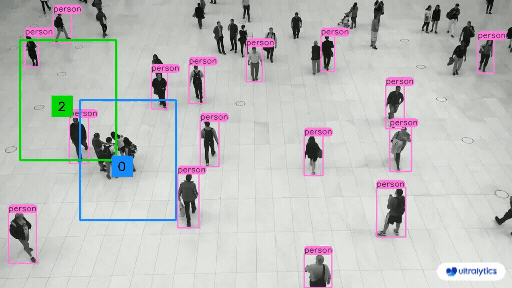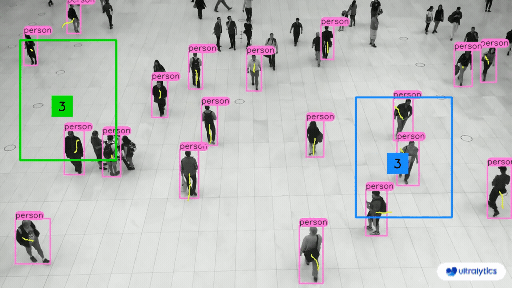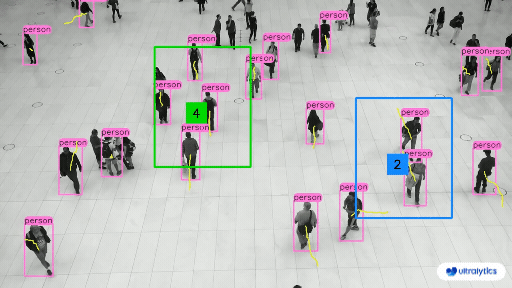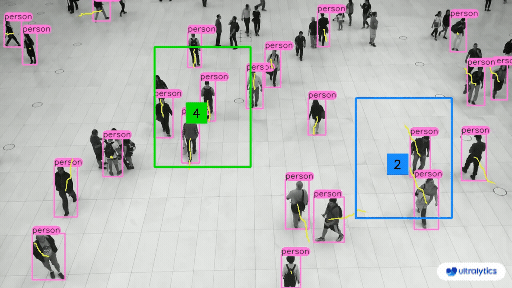
| People Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Crowd Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
| People Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Crowd Counting in Different Region using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
|  | 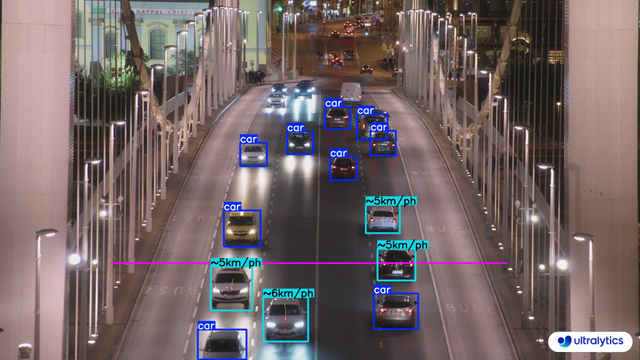 |
|  |  |
| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
@ -41,9 +41,11 @@ The first step in any computer vision project is clearly defining the problem yo
Here are some examples of project objectives and the computer vision tasks that can be used to reach these objectives:
Here are some examples of project objectives and the computer vision tasks that can be used to reach these objectives:
- **Objective:** To develop a system that can monitor and manage the flow of different vehicle types on highways, improving traffic management and safety.
- **Objective:** To develop a system that can monitor and manage the flow of different vehicle types on highways, improving traffic management and safety.
- **Computer Vision Task:** Object detection is ideal for traffic monitoring because it efficiently locates and identifies multiple vehicles. It is less computationally demanding than image segmentation, which provides unnecessary detail for this task, ensuring faster, real-time analysis.
- **Computer Vision Task:** Object detection is ideal for traffic monitoring because it efficiently locates and identifies multiple vehicles. It is less computationally demanding than image segmentation, which provides unnecessary detail for this task, ensuring faster, real-time analysis.
- **Objective:** To develop a tool that assists radiologists by providing precise, pixel-level outlines of tumors in medical imaging scans.
- **Objective:** To develop a tool that assists radiologists by providing precise, pixel-level outlines of tumors in medical imaging scans.
- **Computer Vision Task:** Image segmentation is suitable for medical imaging because it provides accurate and detailed boundaries of tumors that are crucial for assessing size, shape, and treatment planning.
- **Computer Vision Task:** Image segmentation is suitable for medical imaging because it provides accurate and detailed boundaries of tumors that are crucial for assessing size, shape, and treatment planning.
- **Objective:** To create a digital system that categorizes various documents (e.g., invoices, receipts, legal paperwork) to improve organizational efficiency and document retrieval.
- **Objective:** To create a digital system that categorizes various documents (e.g., invoices, receipts, legal paperwork) to improve organizational efficiency and document retrieval.
@ -174,15 +176,19 @@ In addition to monitoring and maintenance, documentation is also key. Thoroughly
Here are some common questions that might arise during a computer vision project:
Here are some common questions that might arise during a computer vision project:
- **Q1:** How do the steps change if I already have a dataset or data when starting a computer vision project?
- **Q1:** How do the steps change if I already have a dataset or data when starting a computer vision project?
- **A1:** Starting with a pre-existing dataset or data affects the initial steps of your project. In Step 1, along with deciding the computer vision task and model, you'll also need to explore your dataset thoroughly. Understanding its quality, variety, and limitations will guide your choice of model and training approach. Your approach should align closely with the data's characteristics for more effective outcomes. Depending on your data or dataset, you may be able to skip Step 2 as well.
- **A1:** Starting with a pre-existing dataset or data affects the initial steps of your project. In Step 1, along with deciding the computer vision task and model, you'll also need to explore your dataset thoroughly. Understanding its quality, variety, and limitations will guide your choice of model and training approach. Your approach should align closely with the data's characteristics for more effective outcomes. Depending on your data or dataset, you may be able to skip Step 2 as well.
- **Q2:** I'm not sure what computer vision project to start my AI learning journey with.
- **Q2:** I'm not sure what computer vision project to start my AI learning journey with.
- **A2:** Check out our [guides on Real-World Projects](./index.md) for inspiration and guidance.
- **A2:** Check out our [guides on Real-World Projects](./index.md) for inspiration and guidance.
- **Q3:** I don't want to train a model. I just want to try running a model on an image. How can I do that?
- **Q3:** I don't want to train a model. I just want to try running a model on an image. How can I do that?
- **A3:** You can use a pre-trained model to run predictions on an image without training a new model. Check out the [YOLOv8 predict docs page](../modes/predict.md) for instructions on how to use a pre-trained YOLOv8 model to make predictions on your images.
- **A3:** You can use a pre-trained model to run predictions on an image without training a new model. Check out the [YOLOv8 predict docs page](../modes/predict.md) for instructions on how to use a pre-trained YOLOv8 model to make predictions on your images.
- **Q4:** Where can I find more detailed articles and updates about computer vision applications and YOLOv8?
- **Q4:** Where can I find more detailed articles and updates about computer vision applications and YOLOv8?
- **A4:** For more detailed articles, updates, and insights about computer vision applications and YOLOv8, visit the [Ultralytics blog page](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog). The blog covers a wide range of topics and provides valuable information to help you stay updated and improve your projects.
- **A4:** For more detailed articles, updates, and insights about computer vision applications and YOLOv8, visit the [Ultralytics blog page](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog). The blog covers a wide range of topics and provides valuable information to help you stay updated and improve your projects.
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ By integrating with Codecov, we aim to maintain and improve the quality of our c
To quickly get a glimpse of the code coverage status of the `ultralytics` python package, we have included a badge and sunburst visual of the `ultralytics` coverage results. These images show the percentage of code covered by our tests, offering an at-a-glance metric of our testing efforts. For full details please see https://codecov.io/github/ultralytics/ultralytics.
To quickly get a glimpse of the code coverage status of the `ultralytics` python package, we have included a badge and sunburst visual of the `ultralytics` coverage results. These images show the percentage of code covered by our tests, offering an at-a-glance metric of our testing efforts. For full details please see https://codecov.io/github/ultralytics/ultralytics.
In the sunburst graphic below, the innermost circle is the entire project, moving away from the center are folders then, finally, a single file. The size and color of each slice is representing the number of statements and the coverage, respectively.
In the sunburst graphic below, the innermost circle is the entire project, moving away from the center are folders then, finally, a single file. The size and color of each slice is representing the number of statements and the coverage, respectively.
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ The Apple Neural Engine (ANE) is a dedicated hardware component integrated into
By combining quantized YOLO models with the Apple Neural Engine, the Ultralytics iOS App achieves real-time object detection on your iOS device without compromising on accuracy or performance.
By combining quantized YOLO models with the Apple Neural Engine, the Ultralytics iOS App achieves real-time object detection on your iOS device without compromising on accuracy or performance.
| Release Year | iPhone Name | Chipset Name | Node Size | ANE TOPs |
| Release Year | iPhone Name | Chipset Name | Node Size | ANE TOPs |
<ahref="https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml"><imgsrc="https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml/badge.svg"alt="CI CPU"></a><ahref="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/hub/blob/main/hub.ipynb"><imgsrc="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg"alt="Open In Colab"></a><ahref="https://ultralytics.com/discord"><imgalt="Discord"src="https://img.shields.io/discord/1089800235347353640?logo=discord&logoColor=white&label=Discord&color=blue"></a>
<ahref="https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml"><imgsrc="https://github.com/ultralytics/hub/actions/workflows/ci.yaml/badge.svg"alt="CI CPU"></a><ahref="https://colab.research.google.com/github/ultralytics/hub/blob/main/hub.ipynb"><imgsrc="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg"alt="Open In Colab"></a><ahref="https://ultralytics.com/discord"><imgalt="Discord"src="https://img.shields.io/discord/1089800235347353640?logo=discord&logoColor=white&label=Discord&color=blue"></a>
</div>
</div>
👋 Hello from the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) Team! We've been working hard these last few months to launch [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub), a new web tool for training and deploying all your YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 🚀 models from one spot!
👋 Hello from the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) Team! We've been working hard these last few months to launch [Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub), a new web tool for training and deploying all your YOLOv5 and YOLOv8 🚀 models from one spot!
@ -47,7 +48,6 @@ We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please br
[Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing users to quickly upload their datasets and train new YOLO models. It also offers a range of pre-trained models to choose from, making it extremely easy for users to get started. Once a model is trained, it can be effortlessly previewed in the [Ultralytics HUB App](app/index.md) before being deployed for real-time classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks.
[Ultralytics HUB](https://bit.ly/ultralytics_hub) is designed to be user-friendly and intuitive, allowing users to quickly upload their datasets and train new YOLO models. It also offers a range of pre-trained models to choose from, making it extremely easy for users to get started. Once a model is trained, it can be effortlessly previewed in the [Ultralytics HUB App](app/index.md) before being deployed for real-time classification, object detection, and instance segmentation tasks.
@ -23,9 +23,9 @@ This Gradio interface provides an easy and interactive way to perform object det
## Why Use Gradio for Object Detection?
## Why Use Gradio for Object Detection?
***User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
-**User-Friendly Interface:** Gradio offers a straightforward platform for users to upload images and visualize detection results without any coding requirement.
***Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
-**Real-Time Adjustments:** Parameters such as confidence and IoU thresholds can be adjusted on the fly, allowing for immediate feedback and optimization of detection results.
***Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
-**Broad Accessibility:** The Gradio web interface can be accessed by anyone, making it an excellent tool for demonstrations, educational purposes, and quick experiments.
<palign="center">
<palign="center">
<imgwidth="800"alt="Gradio example screenshot"src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/26833433/52ee3cd2-ac59-4c27-9084-0fd05c6c33be">
<imgwidth="800"alt="Gradio example screenshot"src="https://github.com/RizwanMunawar/ultralytics/assets/26833433/52ee3cd2-ac59-4c27-9084-0fd05c6c33be">
@ -41,14 +41,14 @@ pip install gradio
1. **Upload Image:** Click on 'Upload Image' to choose an image file for object detection.
1. **Upload Image:** Click on 'Upload Image' to choose an image file for object detection.
2. **Adjust Parameters:**
2. **Adjust Parameters:**
* **Confidence Threshold:** Slider to set the minimum confidence level for detecting objects.
- **Confidence Threshold:** Slider to set the minimum confidence level for detecting objects.
* **IoU Threshold:** Slider to set the IoU threshold for distinguishing different objects.
- **IoU Threshold:** Slider to set the IoU threshold for distinguishing different objects.
3. **View Results:** The processed image with detected objects and their labels will be displayed.
3. **View Results:** The processed image with detected objects and their labels will be displayed.
## Example Use Cases
## Example Use Cases
***Sample Image 1:** Bus detection with default thresholds.
-**Sample Image 1:** Bus detection with default thresholds.
***Sample Image 2:** Detection on a sports image with default thresholds.
-**Sample Image 2:** Detection on a sports image with default thresholds.
Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PArallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
Developed by Baidu, [PaddlePaddle](https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/en) (**PA**rallel **D**istributed **D**eep **LE**arning) is China's first open-source deep learning platform. Unlike some frameworks built mainly for research, PaddlePaddle prioritizes ease of use and smooth integration across industries.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
It offers tools and resources similar to popular frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, making it accessible for developers of all experience levels. From farming and factories to service businesses, PaddlePaddle's large developer community of over 4.77 million is helping create and deploy AI applications.
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ To install the required packages, run:
The `tune()` method in YOLOv8 provides an easy-to-use interface for hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune. It accepts several arguments that allow you to customize the tuning process. Below is a detailed explanation of each parameter:
The `tune()` method in YOLOv8 provides an easy-to-use interface for hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune. It accepts several arguments that allow you to customize the tuning process. Below is a detailed explanation of each parameter:
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
| `data` | `str` | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
| `data` | `str` | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
| `space` | `dict, optional` | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
| `space` | `dict, optional` | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
| `grace_period` | `int, optional` | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api/schedulers.html) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
| `grace_period` | `int, optional` | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api/schedulers.html) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ By customizing these parameters, you can fine-tune the hyperparameter optimizati
The following table lists the default search space parameters for hyperparameter tuning in YOLOv8 with Ray Tune. Each parameter has a specific value range defined by `tune.uniform()`.
The following table lists the default search space parameters for hyperparameter tuning in YOLOv8 with Ray Tune. Each parameter has a specific value range defined by `tune.uniform()`.
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ FastSAM is designed to address the limitations of the [Segment Anything Model (S
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ MobileSAM is trained on a single GPU with a 100k dataset (1% of the original ima
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
# Baidu's RT-DETR: A Vision Transformer-Based Real-Time Object Detector
# Baidu's RT-DETR: A Vision Transformer-Based Real-Time Object Detector
## Overview
## Overview
Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR), developed by Baidu, is a cutting-edge end-to-end object detector that provides real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy. It is based on the idea of DETR (the NMS-free framework), meanwhile introducing conv-based backbone and an efficient hybrid encoder to gain real-time speed. RT-DETR efficiently processes multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. The model is highly adaptable, supporting flexible adjustment of inference speed using different decoder layers without retraining. RT-DETR excels on accelerated backends like CUDA with TensorRT, outperforming many other real-time object detectors.
Real-Time Detection Transformer (RT-DETR), developed by Baidu, is a cutting-edge end-to-end object detector that provides real-time performance while maintaining high accuracy. It is based on the idea of DETR (the NMS-free framework), meanwhile introducing conv-based backbone and an efficient hybrid encoder to gain real-time speed. RT-DETR efficiently processes multiscale features by decoupling intra-scale interaction and cross-scale fusion. The model is highly adaptable, supporting flexible adjustment of inference speed using different decoder layers without retraining. RT-DETR excels on accelerated backends like CUDA with TensorRT, outperforming many other real-time object detectors.
<palign="center">
<palign="center">
@ -74,7 +75,7 @@ This example provides simple RT-DETR training and inference examples. For full d
This table presents the model types, the specific pre-trained weights, the tasks supported by each model, and the various modes ([Train](../modes/train.md) , [Val](../modes/val.md), [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Export](../modes/export.md)) that are supported, indicated by ✅ emojis.
This table presents the model types, the specific pre-trained weights, the tasks supported by each model, and the various modes ([Train](../modes/train.md) , [Val](../modes/val.md), [Predict](../modes/predict.md), [Export](../modes/export.md)) that are supported, indicated by ✅ emojis.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ For an in-depth look at the Segment Anything Model and the SA-1B dataset, please
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
This table presents the available models with their specific pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes like [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), indicated by ✅ emojis for supported modes and ❌ emojis for unsupported modes.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Developed by Deci AI, YOLO-NAS is a groundbreaking object detection foundational
Experience the power of next-generation object detection with the pre-trained YOLO-NAS models provided by Ultralytics. These models are designed to deliver top-notch performance in terms of both speed and accuracy. Choose from a variety of options tailored to your specific needs:
Experience the power of next-generation object detection with the pre-trained YOLO-NAS models provided by Ultralytics. These models are designed to deliver top-notch performance in terms of both speed and accuracy. Choose from a variety of options tailored to your specific needs:
| Model | mAP | Latency (ms) |
| Model | mAP | Latency (ms) |
|------------------|-------|--------------|
| ---------------- | ----- | ------------ |
| YOLO-NAS S | 47.5 | 3.21 |
| YOLO-NAS S | 47.5 | 3.21 |
| YOLO-NAS M | 51.55 | 5.85 |
| YOLO-NAS M | 51.55 | 5.85 |
| YOLO-NAS L | 52.22 | 7.87 |
| YOLO-NAS L | 52.22 | 7.87 |
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ We offer three variants of the YOLO-NAS models: Small (s), Medium (m), and Large
Below is a detailed overview of each model, including links to their pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes.
Below is a detailed overview of each model, including links to their pre-trained weights, the tasks they support, and their compatibility with different operating modes.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ This section details the models available with their specific pre-trained weight
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
All the YOLOv8-World weights have been directly migrated from the official [YOLO-World](https://github.com/AILab-CVC/YOLO-World) repository, highlighting their excellent contributions.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ YOLOv10 comes in various model scales to cater to different application needs:
YOLOv10 outperforms previous YOLO versions and other state-of-the-art models in terms of accuracy and efficiency. For example, YOLOv10-S is 1.8x faster than RT-DETR-R18 with similar AP on the COCO dataset, and YOLOv10-B has 46% less latency and 25% fewer parameters than YOLOv9-C with the same performance.
YOLOv10 outperforms previous YOLO versions and other state-of-the-art models in terms of accuracy and efficiency. For example, YOLOv10-S is 1.8x faster than RT-DETR-R18 with similar AP on the COCO dataset, and YOLOv10-B has 46% less latency and 25% fewer parameters than YOLOv9-C with the same performance.
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The YOLOv3 series, including YOLOv3, YOLOv3-Ultralytics, and YOLOv3u, are design
All three models support a comprehensive set of modes, ensuring versatility in various stages of model deployment and development. These modes include [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), providing users with a complete toolkit for effective object detection.
All three models support a comprehensive set of modes, ensuring versatility in various stages of model deployment and development. These modes include [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), providing users with a complete toolkit for effective object detection.
| Model Type | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ YOLOv5u represents an advancement in object detection methodologies. Originating
The YOLOv5u models, with various pre-trained weights, excel in [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) tasks. They support a comprehensive range of modes, making them suitable for diverse applications, from development to deployment.
The YOLOv5u models, with various pre-trained weights, excel in [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md) tasks. They support a comprehensive range of modes, making them suitable for diverse applications, from development to deployment.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv5u model variants, highlighting their applicability in object detection tasks and support for various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv5u models in a wide range of object detection scenarios.
This table provides a detailed overview of the YOLOv5u model variants, highlighting their applicability in object detection tasks and support for various operational modes such as [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md). This comprehensive support ensures that users can fully leverage the capabilities of YOLOv5u models in a wide range of object detection scenarios.
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ This example provides simple YOLOv6 training and inference examples. For full do
The YOLOv6 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
The YOLOv6 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model Type | Pre-trained Weights | Tasks Supported | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ The YOLOv8 series offers a diverse range of models, each specialized for specifi
Each variant of the YOLOv8 series is optimized for its respective task, ensuring high performance and accuracy. Additionally, these models are compatible with various operational modes including [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), facilitating their use in different stages of deployment and development.
Each variant of the YOLOv8 series is optimized for its respective task, ensuring high performance and accuracy. Additionally, these models are compatible with various operational modes including [Inference](../modes/predict.md), [Validation](../modes/val.md), [Training](../modes/train.md), and [Export](../modes/export.md), facilitating their use in different stages of deployment and development.
| Model | Filenames | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model | Filenames | Task | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ This example provides simple YOLOv9 training and inference examples. For full do
The YOLOv9 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
The YOLOv9 series offers a range of models, each optimized for high-performance [Object Detection](../tasks/detect.md). These models cater to varying computational needs and accuracy requirements, making them versatile for a wide array of applications.
| Model | Filenames | Tasks | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
| Model | Filenames | Tasks | Inference | Validation | Training | Export |
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ Run YOLOv8n benchmarks on all supported export formats including ONNX, TensorRT
Arguments such as `model`, `data`, `imgsz`, `half`, `device`, and `verbose` provide users with the flexibility to fine-tune the benchmarks to their specific needs and compare the performance of different export formats with ease.
Arguments such as `model`, `data`, `imgsz`, `half`, `device`, and `verbose` provide users with the flexibility to fine-tune the benchmarks to their specific needs and compare the performance of different export formats with ease.
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the path to the model file. Accepts both `.pt` and `.yaml` formats, e.g., `"yolov8n.pt"` for pre-trained models or configuration files. |
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the path to the model file. Accepts both `.pt` and `.yaml` formats, e.g., `"yolov8n.pt"` for pre-trained models or configuration files. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to a YAML file defining the dataset for benchmarking, typically including paths and settings for validation data. Example: `"coco8.yaml"`. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to a YAML file defining the dataset for benchmarking, typically including paths and settings for validation data. Example: `"coco8.yaml"`. |
| `imgsz` | `640` | The input image size for the model. Can be a single integer for square images or a tuple `(width, height)` for non-square, e.g., `(640, 480)`. |
| `imgsz` | `640` | The input image size for the model. Can be a single integer for square images or a tuple `(width, height)` for non-square, e.g., `(640, 480)`. |
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ Arguments such as `model`, `data`, `imgsz`, `half`, `device`, and `verbose` prov
Benchmarks will attempt to run automatically on all possible export formats below.
Benchmarks will attempt to run automatically on all possible export formats below.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX or TensorRT. See Argument
This table details the configurations and options available for exporting YOLO models to different formats. These settings are critical for optimizing the exported model's performance, size, and compatibility across various platforms and environments. Proper configuration ensures that the model is ready for deployment in the intended application with optimal efficiency.
This table details the configurations and options available for exporting YOLO models to different formats. These settings are critical for optimizing the exported model's performance, size, and compatibility across various platforms and environments. Proper configuration ensures that the model is ready for deployment in the intended application with optimal efficiency.
| `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
| `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
| `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. |
| `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. |
| `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
| `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
@ -96,7 +96,7 @@ Adjusting these parameters allows for customization of the export process to fit
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| ![Vehicle Spare Parts Detection][car spare parts] | ![Football Player Detection][football player detect] | ![People Fall Detection][human fall detect] |
| ![Vehicle Spare Parts Detection][car spare parts] | ![Football Player Detection][football player detect] | ![People Fall Detection][human fall detect] |
| Vehicle Spare Parts Detection | Football Player Detection | People Fall Detection |
| Vehicle Spare Parts Detection | Football Player Detection | People Fall Detection |
@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in t
Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. |
| `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. |
| `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. |
| `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. |
| `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. |
| `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. |
@ -409,7 +409,7 @@ YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [ultralytics/da
The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
| `line_width` | `float` | Line width of bounding boxes. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` |
| `line_width` | `float` | Line width of bounding boxes. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` |
| `font_size` | `float` | Text font size. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` |
| `font_size` | `float` | Text font size. Scales with image size if `None`. | `None` |
@ -800,7 +800,5 @@ Here's a Python script using OpenCV (`cv2`) and YOLOv8 to run inference on video
This script will run predictions on each frame of the video, visualize the results, and display them in a window. The loop can be exited by pressing 'q'.
This script will run predictions on each frame of the video, visualize the results, and display them in a window. The loop can be exited by pressing 'q'.
@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at
The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance.
The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance.
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
| `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and conf
Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument:
Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument:
| Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description |
| Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description |
| `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. |
| `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. |
| `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. |
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO8 dataset. No argument need t
When validating YOLO models, several arguments can be fine-tuned to optimize the evaluation process. These arguments control aspects such as input image size, batch processing, and performance thresholds. Below is a detailed breakdown of each argument to help you customize your validation settings effectively.
When validating YOLO models, several arguments can be fine-tuned to optimize the evaluation process. These arguments control aspects such as input image size, batch processing, and performance thresholds. Below is a detailed breakdown of each argument to help you customize your validation settings effectively.
| `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. |
| `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. |
| `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. |
| `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. |
@ -318,7 +318,7 @@ Ultralytics allows users to easily modify their settings. Changes can be perform
The table below provides an overview of the settings available for adjustment within Ultralytics. Each setting is outlined along with an example value, the data type, and a brief description.
The table below provides an overview of the settings available for adjustment within Ultralytics. Each setting is outlined along with an example value, the data type, and a brief description.
| Name | Example Value | Data Type | Description |
| Name | Example Value | Data Type | Description |
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Classify models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose model
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
@ -163,7 +163,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-cls model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-cls export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-cls.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8-cls export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-cls.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Detect models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained OBB models are shown here, which are pretrained on the [DOTAv1
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
@ -185,7 +185,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-obb model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-obb export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-obb.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8-obb export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-obb.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Pose models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models ar
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n Pose model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-pose export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-pose.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8-pose export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-pose.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ YOLOv8 pretrained Segment models are shown here. Detect, Segment and Pose models
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
[Models](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models) download automatically from the latest Ultralytics [release](https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases) on first use.
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n-seg model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8-seg export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
Available YOLOv8-seg export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`. You can predict or validate directly on exported models, i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your model after export completes.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| `task` | `'detect'` | Specifies the YOLO task to be executed. Options include `detect` for object detection, `segment` for segmentation, `classify` for classification, `pose` for pose estimation and `OBB` for oriented bounding boxes. Each task is tailored to specific types of output and problems within image and video analysis. |
| `task` | `'detect'` | Specifies the YOLO task to be executed. Options include `detect` for object detection, `segment` for segmentation, `classify` for classification, `pose` for pose estimation and `OBB` for oriented bounding boxes. Each task is tailored to specific types of output and problems within image and video analysis. |
[Tasks Guide](../tasks/index.md){ .md-button }
[Tasks Guide](../tasks/index.md){ .md-button }
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ YOLO models can be used in different modes depending on the specific problem you
- **Benchmark**: For benchmarking YOLOv8 exports (ONNX, TensorRT, etc.) speed and accuracy.
- **Benchmark**: For benchmarking YOLOv8 exports (ONNX, TensorRT, etc.) speed and accuracy.
| `mode` | `'train'` | Specifies the mode in which the YOLO model operates. Options are `train` for model training, `val` for validation, `predict` for inference on new data, `export` for model conversion to deployment formats, `track` for object tracking, and `benchmark` for performance evaluation. Each mode is designed for different stages of the model lifecycle, from development through deployment. |
| `mode` | `'train'` | Specifies the mode in which the YOLO model operates. Options are `train` for model training, `val` for validation, `predict` for inference on new data, `export` for model conversion to deployment formats, `track` for object tracking, and `benchmark` for performance evaluation. Each mode is designed for different stages of the model lifecycle, from development through deployment. |
[Modes Guide](../modes/index.md){ .md-button }
[Modes Guide](../modes/index.md){ .md-button }
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ YOLO models can be used in different modes depending on the specific problem you
The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance.
The training settings for YOLO models encompass various hyperparameters and configurations used during the training process. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Key training settings include batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Additionally, the choice of optimizer, loss function, and training dataset composition can impact the training process. Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial for optimizing performance.
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
| `model` | `None` | Specifies the model file for training. Accepts a path to either a `.pt` pretrained model or a `.yaml` configuration file. Essential for defining the model structure or initializing weights. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `data` | `None` | Path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file contains dataset-specific parameters, including paths to training and validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
| `epochs` | `100` | Total number of training epochs. Each epoch represents a full pass over the entire dataset. Adjusting this value can affect training duration and model performance. |
@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ The prediction settings for YOLO models encompass a range of hyperparameters and
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `source` | `str` | `'ultralytics/assets'` | Specifies the data source for inference. Can be an image path, video file, directory, URL, or device ID for live feeds. Supports a wide range of formats and sources, enabling flexible application across different types of input. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `conf` | `float` | `0.25` | Sets the minimum confidence threshold for detections. Objects detected with confidence below this threshold will be disregarded. Adjusting this value can help reduce false positives. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `iou` | `float` | `0.7` | Intersection Over Union (IoU) threshold for Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Lower values result in fewer detections by eliminating overlapping boxes, useful for reducing duplicates. |
| `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. |
| `show` | `bool` | `False` | If `True`, displays the annotated images or videos in a window. Useful for immediate visual feedback during development or testing. |
| `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. |
| `save` | `bool` | `False` | Enables saving of the annotated images or videos to file. Useful for documentation, further analysis, or sharing results. |
| `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. |
| `save_frames` | `bool` | `False` | When processing videos, saves individual frames as images. Useful for extracting specific frames or for detailed frame-by-frame analysis. |
@ -191,7 +191,7 @@ Visualization arguments:
The val (validation) settings for YOLO models involve various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Common YOLO validation settings include batch size, validation frequency during training, and performance evaluation metrics. Other factors affecting the validation process include the validation dataset's size and composition, as well as the specific task the model is employed for.
The val (validation) settings for YOLO models involve various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings influence the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Common YOLO validation settings include batch size, validation frequency during training, and performance evaluation metrics. Other factors affecting the validation process include the validation dataset's size and composition, as well as the specific task the model is employed for.
| `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `data` | `str` | `None` | Specifies the path to the dataset configuration file (e.g., `coco8.yaml`). This file includes paths to validation data, class names, and number of classes. |
| `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. |
| `imgsz` | `int` | `640` | Defines the size of input images. All images are resized to this dimension before processing. |
| `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. |
| `batch` | `int` | `16` | Sets the number of images per batch. Use `-1` for AutoBatch, which automatically adjusts based on GPU memory availability. |
@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ Careful tuning and experimentation with these settings are crucial to ensure opt
Export settings for YOLO models encompass configurations and options related to saving or exporting the model for use in different environments or platforms. These settings can impact the model's performance, size, and compatibility with various systems. Key export settings include the exported model file format (e.g., ONNX, TensorFlow SavedModel), the target device (e.g., CPU, GPU), and additional features such as masks or multiple labels per box. The export process may also be affected by the model's specific task and the requirements or constraints of the destination environment or platform.
Export settings for YOLO models encompass configurations and options related to saving or exporting the model for use in different environments or platforms. These settings can impact the model's performance, size, and compatibility with various systems. Key export settings include the exported model file format (e.g., ONNX, TensorFlow SavedModel), the target device (e.g., CPU, GPU), and additional features such as masks or multiple labels per box. The export process may also be affected by the model's specific task and the requirements or constraints of the destination environment or platform.
| `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
| `format` | `str` | `'torchscript'` | Target format for the exported model, such as `'onnx'`, `'torchscript'`, `'tensorflow'`, or others, defining compatibility with various deployment environments. |
| `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. |
| `imgsz` | `int` or `tuple` | `640` | Desired image size for the model input. Can be an integer for square images or a tuple `(height, width)` for specific dimensions. |
| `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
| `keras` | `bool` | `False` | Enables export to Keras format for TensorFlow SavedModel, providing compatibility with TensorFlow serving and APIs. |
@ -238,7 +238,7 @@ It is crucial to thoughtfully configure these settings to ensure the exported mo
Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument:
Augmentation techniques are essential for improving the robustness and performance of YOLO models by introducing variability into the training data, helping the model generalize better to unseen data. The following table outlines the purpose and effect of each augmentation argument:
| Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description |
| Argument | Type | Default | Range | Description |
| `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_h` | `float` | `0.015` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Adjusts the hue of the image by a fraction of the color wheel, introducing color variability. Helps the model generalize across different lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. |
| `hsv_s` | `float` | `0.7` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Alters the saturation of the image by a fraction, affecting the intensity of colors. Useful for simulating different environmental conditions. |
| `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. |
| `hsv_v` | `float` | `0.4` | `0.0 - 1.0` | Modifies the value (brightness) of the image by a fraction, helping the model to perform well under various lighting conditions. |
@ -271,7 +271,7 @@ Logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management are important considerations
Effective logging, checkpointing, plotting, and file management can help you keep track of the model's progress and make it easier to debug and optimize the training process.
Effective logging, checkpointing, plotting, and file management can help you keep track of the model's progress and make it easier to debug and optimize the training process.
| `project` | `'runs'` | Specifies the root directory for saving training runs. Each run will be saved in a separate subdirectory within this directory. |
| `project` | `'runs'` | Specifies the root directory for saving training runs. Each run will be saved in a separate subdirectory within this directory. |
| `name` | `'exp'` | Defines the name of the experiment. If not specified, YOLO automatically increments this name for each run, e.g., `exp`, `exp2`, etc., to avoid overwriting previous experiments. |
| `name` | `'exp'` | Defines the name of the experiment. If not specified, YOLO automatically increments this name for each run, e.g., `exp`, `exp2`, etc., to avoid overwriting previous experiments. |
| `exist_ok` | `False` | Determines whether to overwrite an existing experiment directory if one with the same name already exists. Setting this to `True` allows overwriting, while `False` prevents it. |
| `exist_ok` | `False` | Determines whether to overwrite an existing experiment directory if one with the same name already exists. Setting this to `True` allows overwriting, while `False` prevents it. |
@ -171,7 +171,7 @@ Export a YOLOv8n model to a different format like ONNX, CoreML, etc.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument, i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ YOLOv5 inference is officially supported in 11 formats:
💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613). 💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).
💡 ProTip: Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup. See [CPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6613). 💡 ProTip: Export to TensorRT for up to 5x GPU speedup. See [GPU Benchmarks](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/6963).