Contact
-For YOLOv8 bug reports and feature requests please visit [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues), and join our [Discord](https://discord.gg/7aegy5d8) community for questions and discussions!
+For YOLOv8 bug reports and feature requests please visit [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues), and join our [Discord](https://discord.gg/2wNGbc6g9X) community for questions and discussions!
@@ -259,6 +263,6 @@ For YOLOv8 bug reports and feature requests please visit [GitHub Issues](https:/

 -
+
-
+

diff --git a/README.zh-CN.md b/README.zh-CN.md
index 6e4ca425a..872624907 100644
--- a/README.zh-CN.md
+++ b/README.zh-CN.md
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
[Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) [YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) 是一款前沿、最先进(SOTA)的模型,基于先前 YOLO 版本的成功,引入了新功能和改进,进一步提升性能和灵活性。YOLOv8 设计快速、准确且易于使用,使其成为各种物体检测与跟踪、实例分割、图像分类和姿态估计任务的绝佳选择。
-我们希望这里的资源能帮助您充分利用 YOLOv8。请浏览 YOLOv8 文档 了解详细信息,在 GitHub 上提交问题以获得支持,并加入我们的 Discord 社区进行问题和讨论!
+我们希望这里的资源能帮助您充分利用 YOLOv8。请浏览 YOLOv8 文档 了解详细信息,在 GitHub 上提交问题以获得支持,并加入我们的 Discord 社区进行问题和讨论!
如需申请企业许可,请在 [Ultralytics Licensing](https://ultralytics.com/license) 处填写表格
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@

 -
+
-
+


 -
+
-
+
 @@ -57,12 +57,16 @@
@@ -57,12 +57,16 @@
安装
-在一个 [**Python>=3.7**](https://www.python.org/) 环境中,使用 [**PyTorch>=1.7**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/),通过 pip 安装 ultralytics 软件包以及所有[依赖项](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt)。 +使用Pip在一个[**Python>=3.8**](https://www.python.org/)环境中安装`ultralytics`包,此环境还需包含[**PyTorch>=1.7**](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)。这也会安装所有必要的[依赖项](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt)。 + +[](https://badge.fury.io/py/ultralytics) [](https://pepy.tech/project/ultralytics) ```bash pip install ultralytics ``` +如需使用包括Conda、Docker和Git在内的其他安装方法,请参考[快速入门指南](https://docs.ultralytics.com/quickstart)。 +
@@ -236,7 +240,7 @@ YOLOv8 提供两种不同的许可证:
##
diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile b/docker/Dockerfile index 4fca588d2..2f86bb858 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile +++ b/docker/Dockerfile @@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ RUN pip install --no-cache nvidia-tensorrt --index-url https://pypi.ngc.nvidia.c ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y gcc git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 b/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 index bd5432394..3a91abd47 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 @@ -9,8 +9,9 @@ FROM arm64v8/ubuntu:22.10 ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ - && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop gcc libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev + && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop gcc libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 # Create working directory diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-cpu b/docker/Dockerfile-cpu index c58e4233c..3bf0339c1 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-cpu +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-cpu @@ -3,13 +3,13 @@ # Image is CPU-optimized for ONNX, OpenVINO and PyTorch YOLOv8 deployments # Start FROM Ubuntu image https://hub.docker.com/_/ubuntu -FROM ubuntu:22.10 +FROM ubuntu:lunar-20230615 # Downloads to user config dir ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 @@ -23,6 +23,9 @@ WORKDIR /usr/src/ultralytics RUN git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics /usr/src/ultralytics ADD https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/yolov8n.pt /usr/src/ultralytics/ +# Remove python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED or use 'pip install --break-system-packages' avoid 'externally-managed-environment' Ubuntu nightly error +RUN rm -rf /usr/lib/python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED + # Install pip packages RUN python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel RUN pip install --no-cache -e . thop --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-jetson b/docker/Dockerfile-jetson index 0182f2c26..785ca8938 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-jetson +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-jetson @@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/l4t-pytorch:r35.2.1-pth2.0-py3 ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y gcc git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 diff --git a/docs/datasets/classify/index.md b/docs/datasets/classify/index.md index fd902882d..ab6ca5cff 100644 --- a/docs/datasets/classify/index.md +++ b/docs/datasets/classify/index.md @@ -97,9 +97,24 @@ In this example, the `train` directory contains subdirectories for each class in ```bash # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model - yolo detect train data=path/to/data model=yolov8n-seg.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 + yolo detect train data=path/to/data model=yolov8n-cls.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 ``` ## Supported Datasets -TODO \ No newline at end of file +Ultralytics supports the following datasets with automatic download: + +* [Caltech 101](caltech101.md): A dataset containing images of 101 object categories for image classification tasks. +* [Caltech 256](caltech256.md): An extended version of Caltech 101 with 256 object categories and more challenging images. +* [CIFAR-10](cifar10.md): A dataset of 60K 32x32 color images in 10 classes, with 6K images per class. +* [CIFAR-100](cifar100.md): An extended version of CIFAR-10 with 100 object categories and 600 images per class. +* [Fashion-MNIST](fashion-mnist.md): A dataset consisting of 70,000 grayscale images of 10 fashion categories for image classification tasks. +* [ImageNet](imagenet.md): A large-scale dataset for object detection and image classification with over 14 million images and 20,000 categories. +* [ImageNet-10](imagenet10.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet with 10 categories for faster experimentation and testing. +* [Imagenette](imagenette.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet that contains 10 easily distinguishable classes for quicker training and testing. +* [Imagewoof](imagewoof.md): A more challenging subset of ImageNet containing 10 dog breed categories for image classification tasks. +* [MNIST](mnist.md): A dataset of 70,000 grayscale images of handwritten digits for image classification tasks. + +### Adding your own dataset + +If you have your own dataset and would like to use it for training classification models with Ultralytics, ensure that it follows the format specified above under "Dataset format" and then point your `data` argument to the dataset directory. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/datasets/detect/index.md b/docs/datasets/detect/index.md index 7eec93cd9..6a9cd614d 100644 --- a/docs/datasets/detect/index.md +++ b/docs/datasets/detect/index.md @@ -1,82 +1,53 @@ --- comments: true -description: Learn about supported dataset formats for training YOLO detection models, including Ultralytics YOLO and COCO, in this Object Detection Datasets Overview. -keywords: object detection, datasets, formats, Ultralytics YOLO, label format, dataset file format, dataset definition, YOLO dataset, model configuration +description: Explore supported dataset formats for training YOLO detection models, including Ultralytics YOLO and COCO. This guide covers various dataset formats and their specific configurations for effective object detection training. +keywords: object detection, datasets, formats, Ultralytics YOLO, COCO, label format, dataset file format, dataset definition, YOLO dataset, model configuration --- # Object Detection Datasets Overview +Training a robust and accurate object detection model requires a comprehensive dataset. This guide introduces various formats of datasets that are compatible with the Ultralytics YOLO model and provides insights into their structure, usage, and how to convert between different formats. + ## Supported Dataset Formats ### Ultralytics YOLO format -** Label Format ** - -The dataset format used for training YOLO detection models is as follows: - -1. One text file per image: Each image in the dataset has a corresponding text file with the same name as the image file and the ".txt" extension. -2. One row per object: Each row in the text file corresponds to one object instance in the image. -3. Object information per row: Each row contains the following information about the object instance: - - Object class index: An integer representing the class of the object (e.g., 0 for person, 1 for car, etc.). - - Object center coordinates: The x and y coordinates of the center of the object, normalized to be between 0 and 1. - - Object width and height: The width and height of the object, normalized to be between 0 and 1. - -The format for a single row in the detection dataset file is as follows: - -``` -
-```
-
-Here is an example of the YOLO dataset format for a single image with two object instances:
-
-```
-0 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.6
-1 0.3 0.7 0.4 0.2
-```
-
-In this example, the first object is of class 0 (person), with its center at (0.5, 0.4), width of 0.3, and height of 0.6. The second object is of class 1 (car), with its center at (0.3, 0.7), width of 0.4, and height of 0.2.
-
-** Dataset file format **
-
-The Ultralytics framework uses a YAML file format to define the dataset and model configuration for training Detection Models. Here is an example of the YAML format used for defining a detection dataset:
-
-```
-train:
-val:
-
-nc:
-names: [, , ..., ]
-
-```
-
-The `train` and `val` fields specify the paths to the directories containing the training and validation images, respectively.
-
-The `nc` field specifies the number of object classes in the dataset.
-
-The `names` field is a list of the names of the object classes. The order of the names should match the order of the object class indices in the YOLO dataset files.
-
-NOTE: Either `nc` or `names` must be defined. Defining both are not mandatory
-
-Alternatively, you can directly define class names like this:
+The Ultralytics YOLO format is a dataset configuration format that allows you to define the dataset root directory, the relative paths to training/validation/testing image directories or *.txt files containing image paths, and a dictionary of class names. Here is an example:
```yaml
+# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
+path: ../datasets/coco8 # dataset root dir
+train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+test: # test images (optional)
+
+# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
+ 2: car
+ ...
+ 77: teddy bear
+ 78: hair drier
+ 79: toothbrush
```
-** Example **
+Labels for this format should be exported to YOLO format with one `*.txt` file per image. If there are no objects in an image, no `*.txt` file is required. The `*.txt` file should be formatted with one row per object in `class x_center y_center width height` format. Box coordinates must be in **normalized xywh** format (from 0 - 1). If your boxes are in pixels, you should divide `x_center` and `width` by image width, and `y_center` and `height` by image height. Class numbers should be zero-indexed (start with 0).
-```yaml
-train: data/train/
-val: data/val/
+` is the index of the class for the object,` ` are coordinates of boudning box, and ` ... ` are the pixel coordinates of the keypoints. The coordinates are separated by spaces.
-** Dataset file format **
+### Dataset YAML format
The Ultralytics framework uses a YAML file format to define the dataset and model configuration for training Detection Models. Here is an example of the YAML format used for defining a detection dataset:
```yaml
-train:
-val:
-
-nc:
-names: [, , ..., ]
+# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
+path: ../datasets/coco8-pose # dataset root dir
+train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+test: # test images (optional)
# Keypoints
-kpt_shape: [num_kpts, dim] # number of keypoints, number of dims (2 for x,y or 3 for x,y,visible)
-flip_idx: [n1, n2 ... , n(num_kpts)]
-
-```
-
-The `train` and `val` fields specify the paths to the directories containing the training and validation images, respectively.
-
-The `nc` field specifies the number of object classes in the dataset.
-
-The `names` field is a list of the names of the object classes. The order of the names should match the order of the object class indices in the YOLO dataset files.
-
-NOTE: Either `nc` or `names` must be defined. Defining both are not mandatory
-
-Alternatively, you can directly define class names like this:
+kpt_shape: [17, 3] # number of keypoints, number of dims (2 for x,y or 3 for x,y,visible)
+flip_idx: [0, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 8, 7, 10, 9, 12, 11, 14, 13, 16, 15]
-```
+# Classes dictionary
names:
0: person
- 1: bicycle
```
-(Optional) if the points are symmetric then need flip_idx, like left-right side of human or face.
-For example let's say there're five keypoints of facial landmark: [left eye, right eye, nose, left point of mouth, right point of mouse], and the original index is [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], then flip_idx is [1, 0, 2, 4, 3].(just exchange the left-right index, i.e 0-1 and 3-4, and do not modify others like nose in this example)
-
-** Example **
-
-```yaml
-train: data/train/
-val: data/val/
+The `train` and `val` fields specify the paths to the directories containing the training and validation images, respectively.
-nc: 2
-names: ['person', 'car']
+`names` is a dictionary of class names. The order of the names should match the order of the object class indices in the YOLO dataset files.
-# Keypoints
-kpt_shape: [17, 3] # number of keypoints, number of dims (2 for x,y or 3 for x,y,visible)
-flip_idx: [0, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 8, 7, 10, 9, 12, 11, 14, 13, 16, 15]
-```
+(Optional) if the points are symmetric then need flip_idx, like left-right side of human or face.
+For example if we assume five keypoints of facial landmark: [left eye, right eye, nose, left mouth, right mouth], and the original index is [0, 1, 2, 3, 4], then flip_idx is [1, 0, 2, 4, 3] (just exchange the left-right index, i.e 0-1 and 3-4, and do not modify others like nose in this example).
## Usage
@@ -112,14 +89,40 @@ flip_idx: [0, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 8, 7, 10, 9, 12, 11, 14, 13, 16, 15]
## Supported Datasets
-TODO
+This section outlines the datasets that are compatible with Ultralytics YOLO format and can be used for training pose estimation models:
-## Port or Convert label formats
+### COCO-Pose
-### COCO dataset format to YOLO format
+- **Description**: COCO-Pose is a large-scale object detection, segmentation, and pose estimation dataset. It is a subset of the popular COCO dataset and focuses on human pose estimation. COCO-Pose includes multiple keypoints for each human instance.
+- **Label Format**: Same as Ultralytics YOLO format as described above, with keypoints for human poses.
+- **Number of Classes**: 1 (Human).
+- **Keypoints**: 17 keypoints including nose, eyes, ears, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
+- **Usage**: Suitable for training human pose estimation models.
+- **Additional Notes**: The dataset is rich and diverse, containing over 200k labeled images.
+- [Read more about COCO-Pose](./coco.md)
-```
+### COCO8-Pose
+
+- **Description**: [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) COCO8-Pose is a small, but versatile pose detection dataset composed of the first 8 images of the COCO train 2017 set, 4 for training and 4 for validation.
+- **Label Format**: Same as Ultralytics YOLO format as described above, with keypoints for human poses.
+- **Number of Classes**: 1 (Human).
+- **Keypoints**: 17 keypoints including nose, eyes, ears, shoulders, elbows, wrists, hips, knees, and ankles.
+- **Usage**: Suitable for testing and debugging object detection models, or for experimenting with new detection approaches.
+- **Additional Notes**: COCO8-Pose is ideal for sanity checks and CI checks.
+- [Read more about COCO8-Pose](./coco8-pose.md)
+
+### Adding your own dataset
+
+If you have your own dataset and would like to use it for training pose estimation models with Ultralytics YOLO format, ensure that it follows the format specified above under "Ultralytics YOLO format". Convert your annotations to the required format and specify the paths, number of classes, and class names in the YAML configuration file.
+
+### Conversion Tool
+
+Ultralytics provides a convenient conversion tool to convert labels from the popular COCO dataset format to YOLO format:
+
+```python
from ultralytics.yolo.data.converter import convert_coco
convert_coco(labels_dir='../coco/annotations/', use_keypoints=True)
-```
\ No newline at end of file
+```
+
+This conversion tool can be used to convert the COCO dataset or any dataset in the COCO format to the Ultralytics YOLO format. The `use_keypoints` parameter specifies whether to include keypoints (for pose estimation) in the converted labels.
diff --git a/docs/datasets/segment/index.md b/docs/datasets/segment/index.md
index 7d24e4160..5bafefe6d 100644
--- a/docs/datasets/segment/index.md
+++ b/docs/datasets/segment/index.md
@@ -35,46 +35,36 @@ Here is an example of the YOLO dataset format for a single image with two object
1 0.5046 0.0 0.5015 0.004 0.4984 0.00416 0.4937 0.010 0.492 0.0104
```
-Note: The length of each row does not have to be equal.
+!!! tip "Tip"
-** Dataset file format **
+ - The length of each row does not have to be equal.
+ - Each segmentation label must have a **minimum of 3 xy points**: ` `
+
+### Dataset YAML format
The Ultralytics framework uses a YAML file format to define the dataset and model configuration for training Detection Models. Here is an example of the YAML format used for defining a detection dataset:
```yaml
-train:
-val:
-
-nc:
-names: [ , , ..., ]
-
-```
-
-The `train` and `val` fields specify the paths to the directories containing the training and validation images, respectively.
+# Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..]
+path: ../datasets/coco8-seg # dataset root dir
+train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 4 images
+test: # test images (optional)
-The `nc` field specifies the number of object classes in the dataset.
-
-The `names` field is a list of the names of the object classes. The order of the names should match the order of the object class indices in the YOLO dataset files.
-
-NOTE: Either `nc` or `names` must be defined. Defining both are not mandatory.
-
-Alternatively, you can directly define class names like this:
-
-```yaml
+# Classes (80 COCO classes)
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
+ 2: car
+ ...
+ 77: teddy bear
+ 78: hair drier
+ 79: toothbrush
```
-** Example **
-
-```yaml
-train: data/train/
-val: data/val/
+The `train` and `val` fields specify the paths to the directories containing the training and validation images, respectively.
-nc: 2
-names: [ 'person', 'car' ]
-```
+`names` is a dictionary of class names. The order of the names should match the order of the object class indices in the YOLO dataset files.
## Usage
@@ -100,16 +90,29 @@ names: [ 'person', 'car' ]
## Supported Datasets
-## Port or Convert label formats
+* [COCO](coco.md): A large-scale dataset designed for object detection, segmentation, and captioning tasks with over 200K labeled images.
+* [COCO8-seg](coco8-seg.md): A smaller dataset for instance segmentation tasks, containing a subset of 8 COCO images with segmentation annotations.
-### COCO dataset format to YOLO format
+### Adding your own dataset
-```
+If you have your own dataset and would like to use it for training segmentation models with Ultralytics YOLO format, ensure that it follows the format specified above under "Ultralytics YOLO format". Convert your annotations to the required format and specify the paths, number of classes, and class names in the YAML configuration file.
+
+## Port or Convert Label Formats
+
+### COCO Dataset Format to YOLO Format
+
+You can easily convert labels from the popular COCO dataset format to the YOLO format using the following code snippet:
+
+```python
from ultralytics.yolo.data.converter import convert_coco
convert_coco(labels_dir='../coco/annotations/', use_segments=True)
```
+This conversion tool can be used to convert the COCO dataset or any dataset in the COCO format to the Ultralytics YOLO format.
+
+Remember to double-check if the dataset you want to use is compatible with your model and follows the necessary format conventions. Properly formatted datasets are crucial for training successful object detection models.
+
## Auto-Annotation
Auto-annotation is an essential feature that allows you to generate a segmentation dataset using a pre-trained detection model. It enables you to quickly and accurately annotate a large number of images without the need for manual labeling, saving time and effort.
diff --git a/docs/help/environmental-health-safety.md b/docs/help/environmental-health-safety.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2d072a571
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/help/environmental-health-safety.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+---
+comments: false
+description: Discover Ultralytics' commitment to Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS). Learn about our policy, principles, and strategies for ensuring a sustainable and safe working environment.
+keywords: Ultralytics, Environmental Policy, Health and Safety, EHS, Sustainability, Workplace Safety, Environmental Compliance
+---
+
+# Ultralytics Environmental, Health and Safety (EHS) Policy
+
+At Ultralytics, we recognize that the long-term success of our company relies not only on the products and services we offer, but also the manner in which we conduct our business. We are committed to ensuring the safety and well-being of our employees, stakeholders, and the environment, and we will continuously strive to mitigate our impact on the environment while promoting health and safety.
+
+## Policy Principles
+
+1. **Compliance**: We will comply with all applicable laws, regulations, and standards related to EHS, and we will strive to exceed these standards where possible.
+
+2. **Prevention**: We will work to prevent accidents, injuries, and environmental harm by implementing risk management measures and ensuring all our operations and procedures are safe.
+
+3. **Continuous Improvement**: We will continuously improve our EHS performance by setting measurable objectives, monitoring our performance, auditing our operations, and revising our policies and procedures as needed.
+
+4. **Communication**: We will communicate openly about our EHS performance and will engage with stakeholders to understand and address their concerns and expectations.
+
+5. **Education and Training**: We will educate and train our employees and contractors in appropriate EHS procedures and practices.
+
+## Implementation Measures
+
+1. **Responsibility and Accountability**: Every employee and contractor working at or with Ultralytics is responsible for adhering to this policy. Managers and supervisors are accountable for ensuring this policy is implemented within their areas of control.
+
+2. **Risk Management**: We will identify, assess, and manage EHS risks associated with our operations and activities to prevent accidents, injuries, and environmental harm.
+
+3. **Resource Allocation**: We will allocate the necessary resources to ensure the effective implementation of our EHS policy, including the necessary equipment, personnel, and training.
+
+4. **Emergency Preparedness and Response**: We will develop, maintain, and test emergency preparedness and response plans to ensure we can respond effectively to EHS incidents.
+
+5. **Monitoring and Review**: We will monitor and review our EHS performance regularly to identify opportunities for improvement and ensure we are meeting our objectives.
+
+This policy reflects our commitment to minimizing our environmental footprint, ensuring the safety and well-being of our employees, and continuously improving our performance.
+
+Please remember that the implementation of an effective EHS policy requires the involvement and commitment of everyone working at or with Ultralytics. We encourage you to take personal responsibility for your safety and the safety of others, and to take care of the environment in which we live and work.
diff --git a/docs/help/index.md b/docs/help/index.md
index 9647552b3..ed6b93e6e 100644
--- a/docs/help/index.md
+++ b/docs/help/index.md
@@ -12,6 +12,7 @@ Welcome to the Ultralytics Help page! We are committed to providing you with com
- [Contributor License Agreement (CLA)](CLA.md): Familiarize yourself with our CLA to understand the terms and conditions for contributing to Ultralytics projects.
- [Minimum Reproducible Example (MRE) Guide](minimum_reproducible_example.md): Understand how to create an MRE when submitting bug reports to ensure that our team can quickly and efficiently address the issue.
- [Code of Conduct](code_of_conduct.md): Learn about our community guidelines and expectations to ensure a welcoming and inclusive environment for all participants.
+- [Environmental, Health and Safety (EHS) Policy](environmental-health-safety.md): Explore Ultralytics' dedicated approach towards maintaining a sustainable, safe, and healthy work environment for all our stakeholders.
- [Security Policy](../SECURITY.md): Understand our security practices and how to report security vulnerabilities responsibly.
We highly recommend going through these guides to make the most of your collaboration with the Ultralytics community. Our goal is to maintain a welcoming and supportive environment for all users and contributors. If you need further assistance, don't hesitate to reach out to us through GitHub Issues or the official discussion forum. Happy coding!
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/help/minimum_reproducible_example.md b/docs/help/minimum_reproducible_example.md
index 758287cc0..1a8acd27b 100644
--- a/docs/help/minimum_reproducible_example.md
+++ b/docs/help/minimum_reproducible_example.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, bug report, minimum reproducible example, MRE, isol
# Creating a Minimum Reproducible Example for Bug Reports in Ultralytics YOLO Repositories
-When submitting a bug report for Ultralytics YOLO repositories, it's essential to provide a [minimum reproducible example](https://stackoverflow.com/help/minimal-reproducible-example) (MRE). An MRE is a small, self-contained piece of code that demonstrates the problem you're experiencing. Providing an MRE helps maintainers and contributors understand the issue and work on a fix more efficiently. This guide explains how to create an MRE when submitting bug reports to Ultralytics YOLO repositories.
+When submitting a bug report for Ultralytics YOLO repositories, it's essential to provide a [minimum reproducible example](https://docs.ultralytics.com/help/minimum_reproducible_example/) (MRE). An MRE is a small, self-contained piece of code that demonstrates the problem you're experiencing. Providing an MRE helps maintainers and contributors understand the issue and work on a fix more efficiently. This guide explains how to create an MRE when submitting bug reports to Ultralytics YOLO repositories.
## 1. Isolate the Problem
diff --git a/docs/hub/datasets.md b/docs/hub/datasets.md
index d09f77b32..c1bdc38ef 100644
--- a/docs/hub/datasets.md
+++ b/docs/hub/datasets.md
@@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ Also, you can analyze your dataset by click on the **Overview** tab.

-Next, [train a model](./models.md) on your dataset.
+Next, [train a model](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/models/#train-model) on your dataset.

diff --git a/docs/hub/index.md b/docs/hub/index.md
index 6e25dc278..30f1652b6 100644
--- a/docs/hub/index.md
+++ b/docs/hub/index.md
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ easily upload their data and train new models quickly. It offers a range of pre-
templates to choose from, making it easy for users to get started with training their own models. Once a model is
trained, it can be easily deployed and used for real-time object detection, instance segmentation and classification tasks.
-We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please browse the HUB Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!
+We hope that the resources here will help you get the most out of HUB. Please browse the HUB Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!
- [**Quickstart**](./quickstart.md). Start training and deploying YOLO models with HUB in seconds.
- [**Datasets: Preparing and Uploading**](./datasets.md). Learn how to prepare and upload your datasets to HUB in YOLO format.
diff --git a/docs/hub/models.md b/docs/hub/models.md
index 5ae171f25..31cba2df9 100644
--- a/docs/hub/models.md
+++ b/docs/hub/models.md
@@ -4,18 +4,210 @@ description: Train and Deploy your Model to 13 different formats, including Tens
keywords: Ultralytics, HUB, models, artificial intelligence, APIs, export models, TensorFlow, ONNX, Paddle, OpenVINO, CoreML, iOS, Android
---
-# HUB Models
+# Ultralytics HUB Models
-## Train a Model
+Ultralytics HUB models provide a streamlined solution for training vision AI models on your custom datasets.
-Connect to the Ultralytics HUB notebook and use your model API key to begin training!
+The process is user-friendly and efficient, involving a simple three-step creation and accelerated training powered by Utralytics YOLOv8. During training, real-time updates on model metrics are available so that you can monitor each step of the progress. Once training is completed, you can preview your model and easily deploy it to real-world applications. Therefore, Ultralytics HUB offers a comprehensive yet straightforward system for model creation, training, evaluation, and deployment.
+
+## Train Model
+
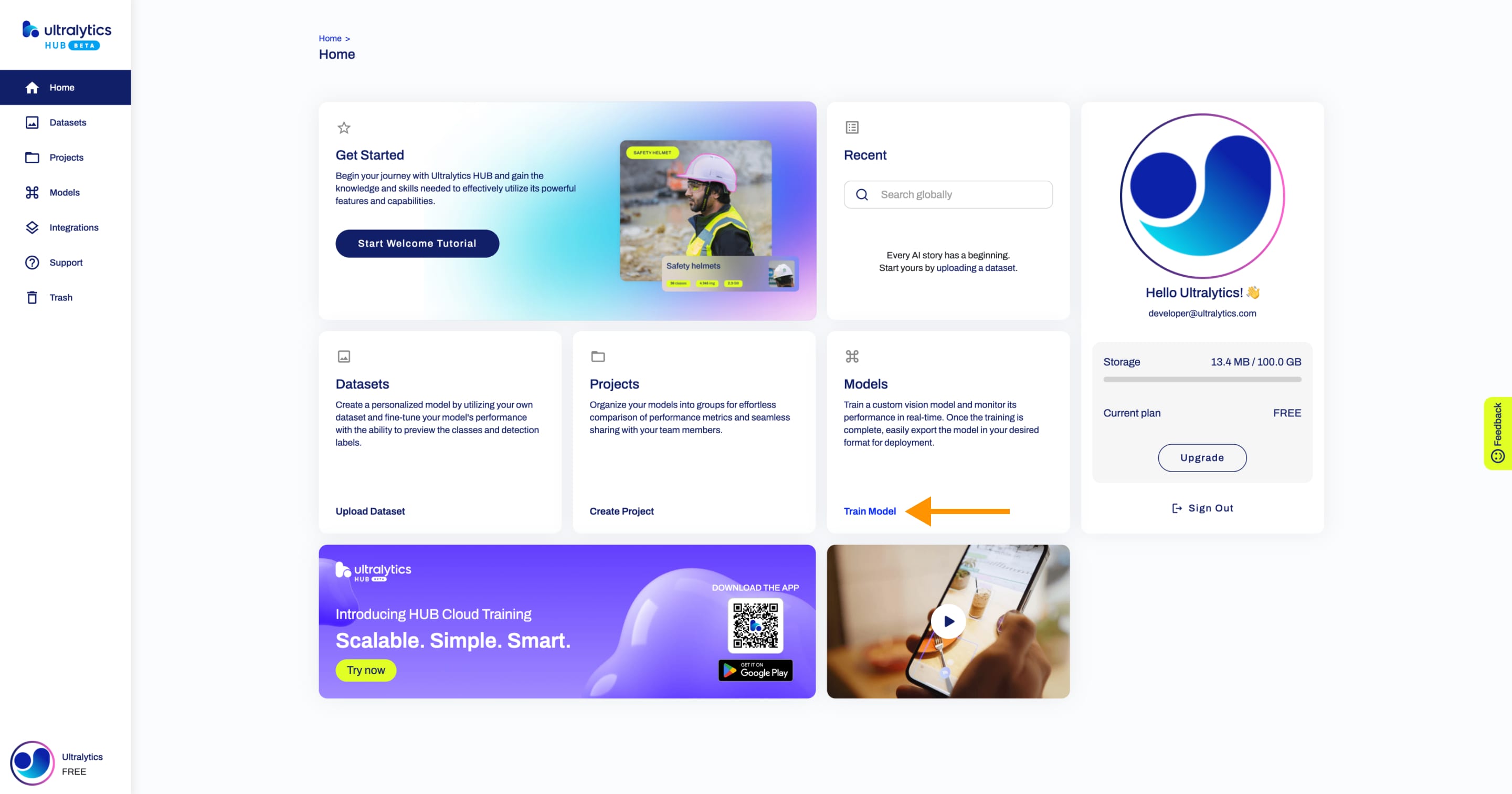
+Navigate to the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page by clicking on the **Models** button in the sidebar.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
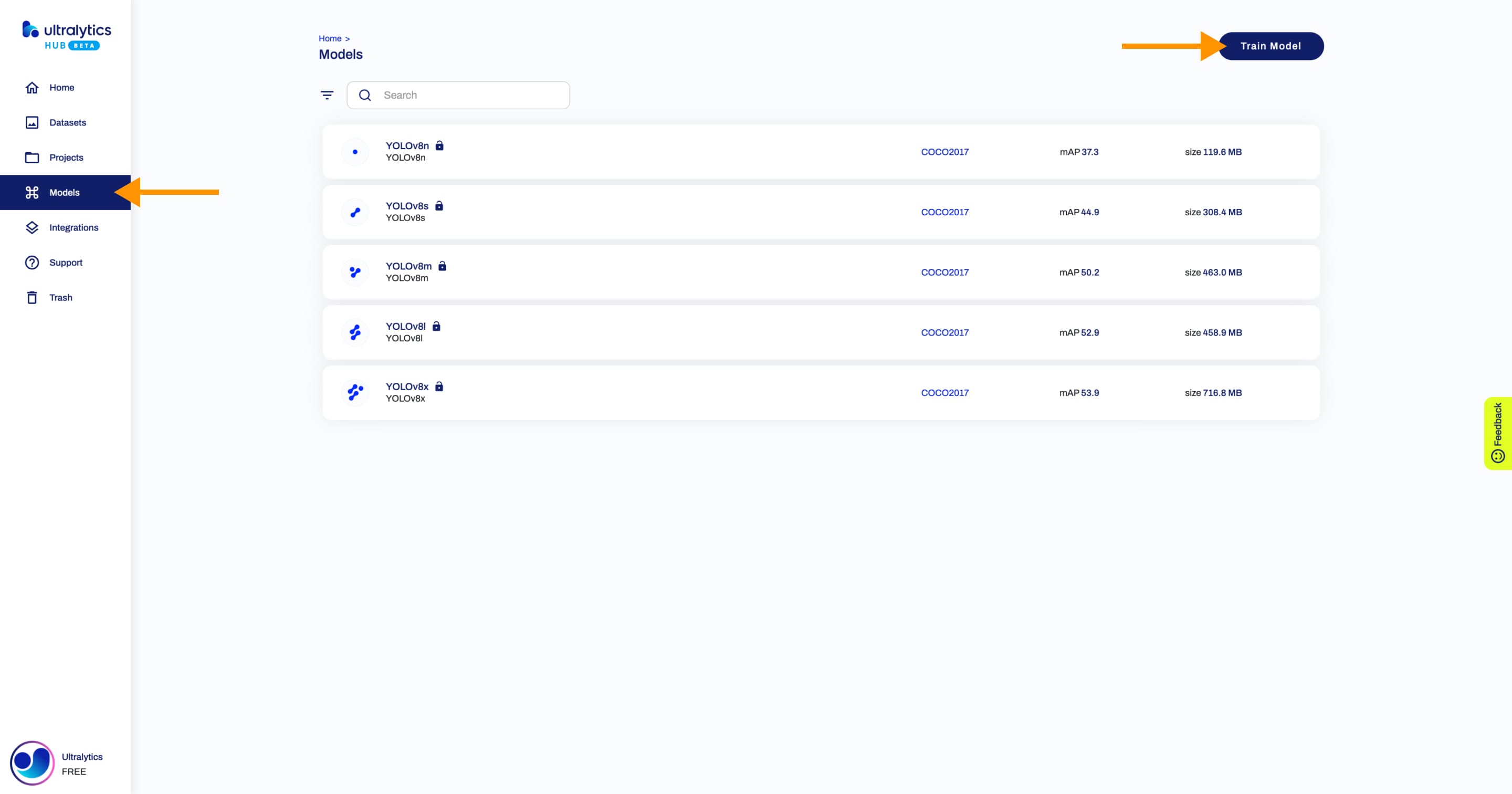
+
+ You can also train a model directly from the [Home](https://hub.ultralytics.com/home) page.
+
+ 
+
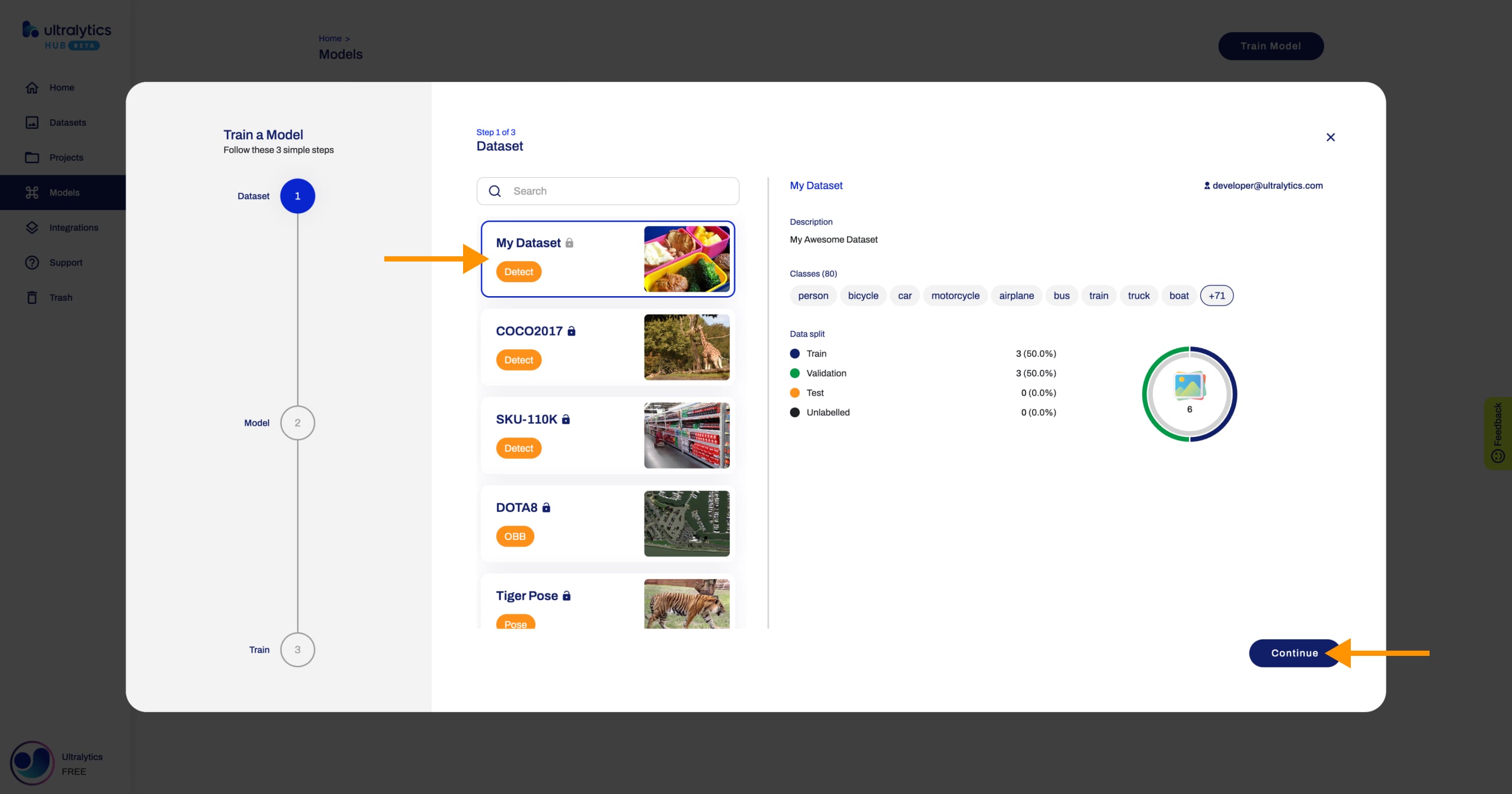
+Click on the **Train Model** button on the top right of the page. This action will trigger the **Train Model** dialog.
+
+
+
+The **Train Model** dialog has three simple steps, explained below.
+
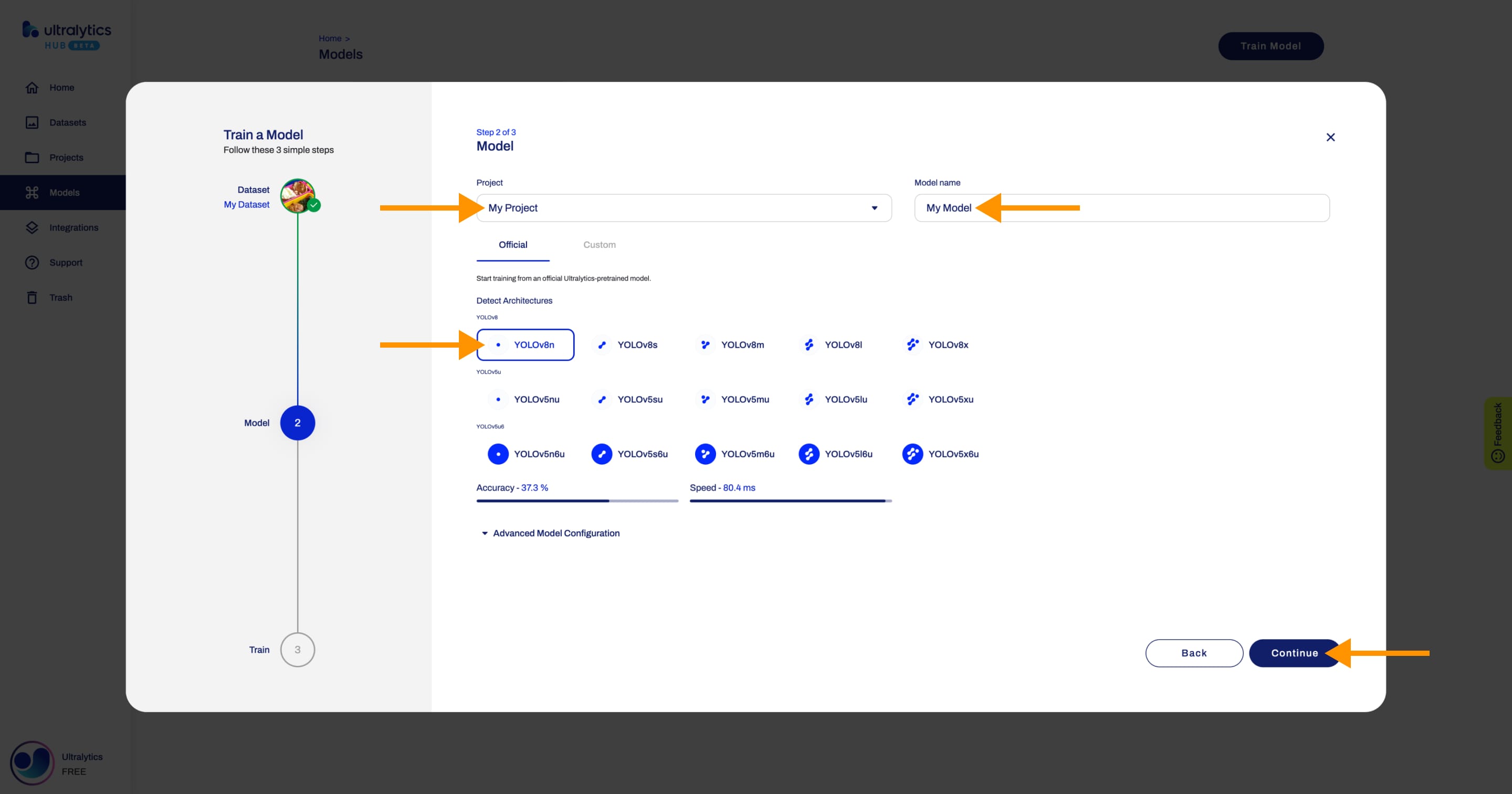
+### 1. Dataset
+
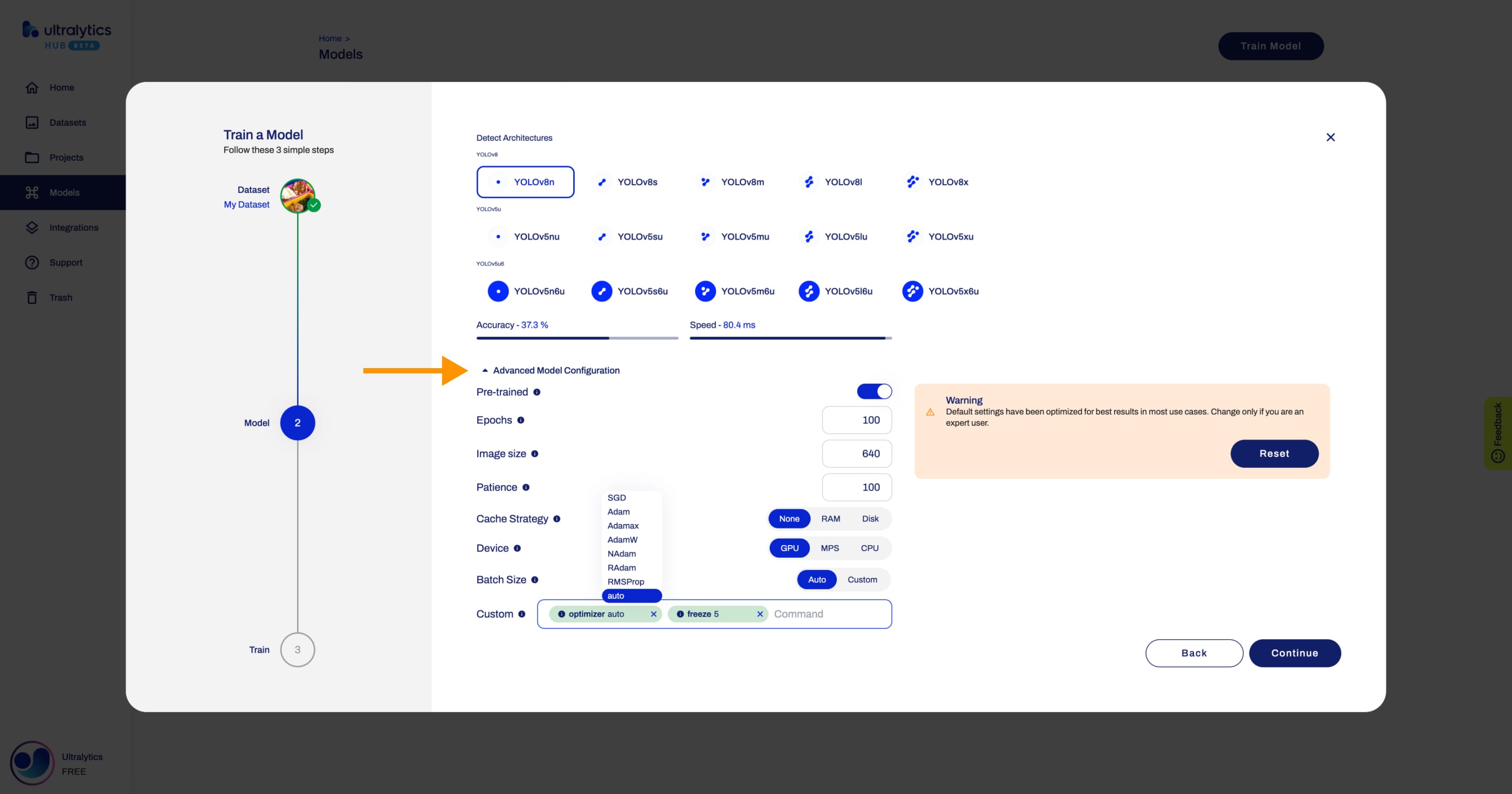
+In this step, you have to select the dataset you want to train your model on. After you selected a dataset, click **Continue**.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can skip this step if you train a model directly from the Dataset page.
+
+ 
+
+### 2. Model
+
+In this step, you have to choose the project in which you want to create your model, the name of your model and your model's architecture.
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ Ultralytics HUB will try to pre-select the project.
+
+ If you opened the **Train Model** dialog as described above, Ultralytics HUB will pre-select the last project you used.
+
+ If you opened the **Train Model** dialog from the Project page, Ultralytics HUB will pre-select the project you were inside of.
+
+ 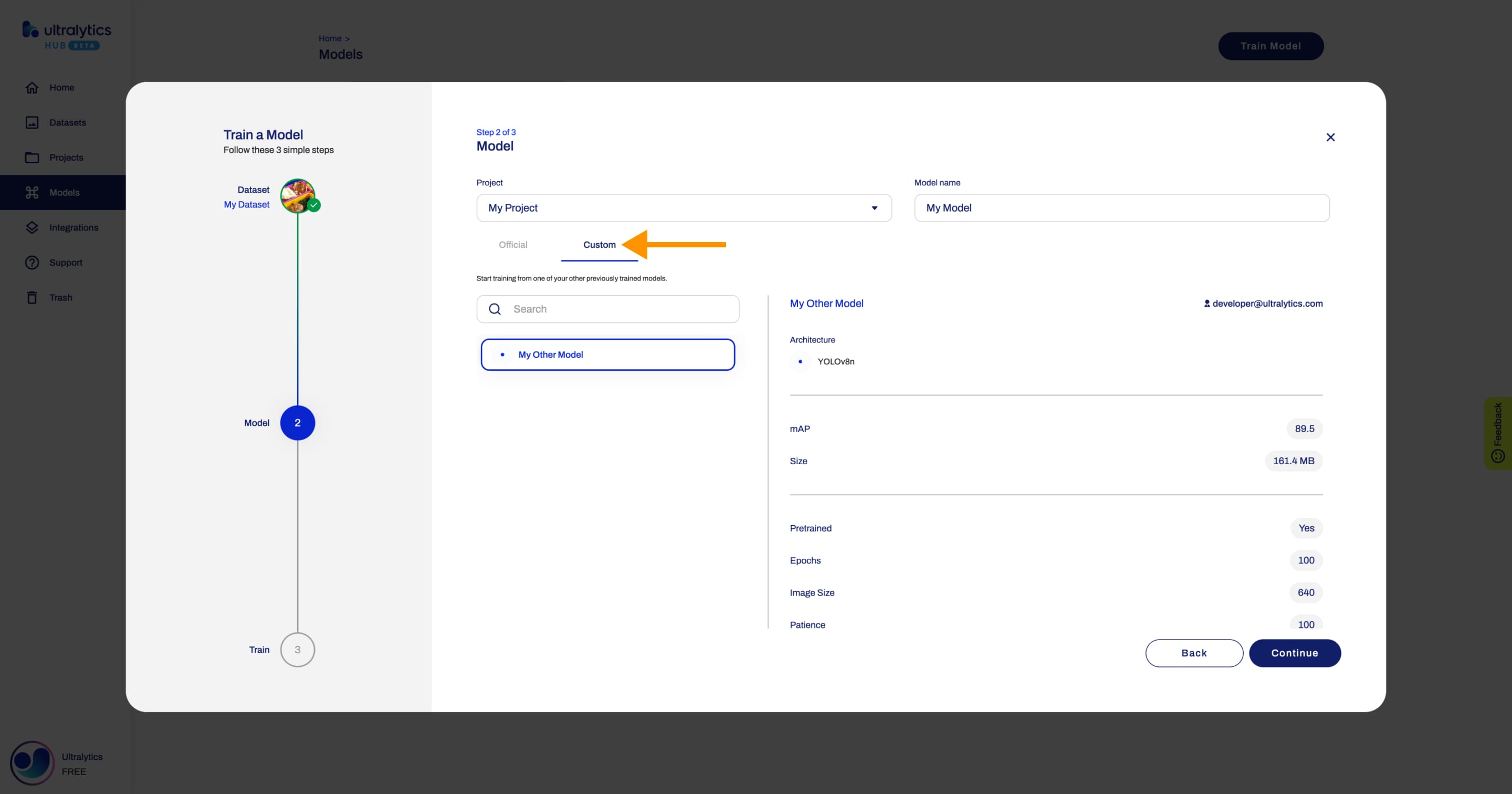
+
+ In case you don't have a project created yet, you can set the name of your project in this step and it will be created together with your model.
+
+ 
+
+!!! info "Info"
+
+ You can read more about the available [YOLOv8](https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8) (and [YOLOv5](https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov5)) architectures in our documentation.
+
+When you're happy with your model configuration, click **Continue**.
+
+
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ By default, your model will use a pre-trained model (trained on the [COCO](https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/detect/coco) dataset) to reduce training time.
+
+ You can change this behaviour by opening the **Advanced Options** accordion.
+
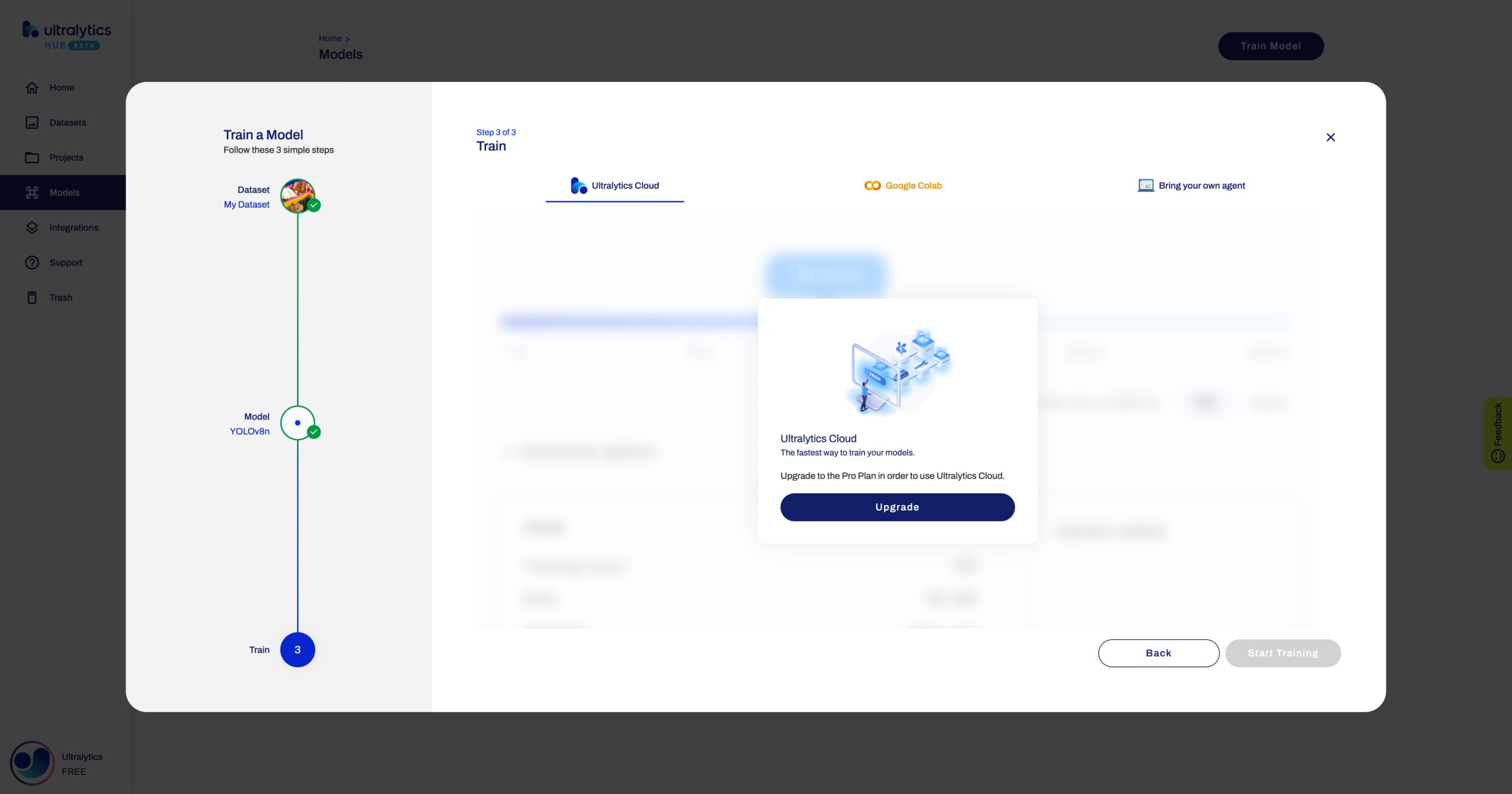
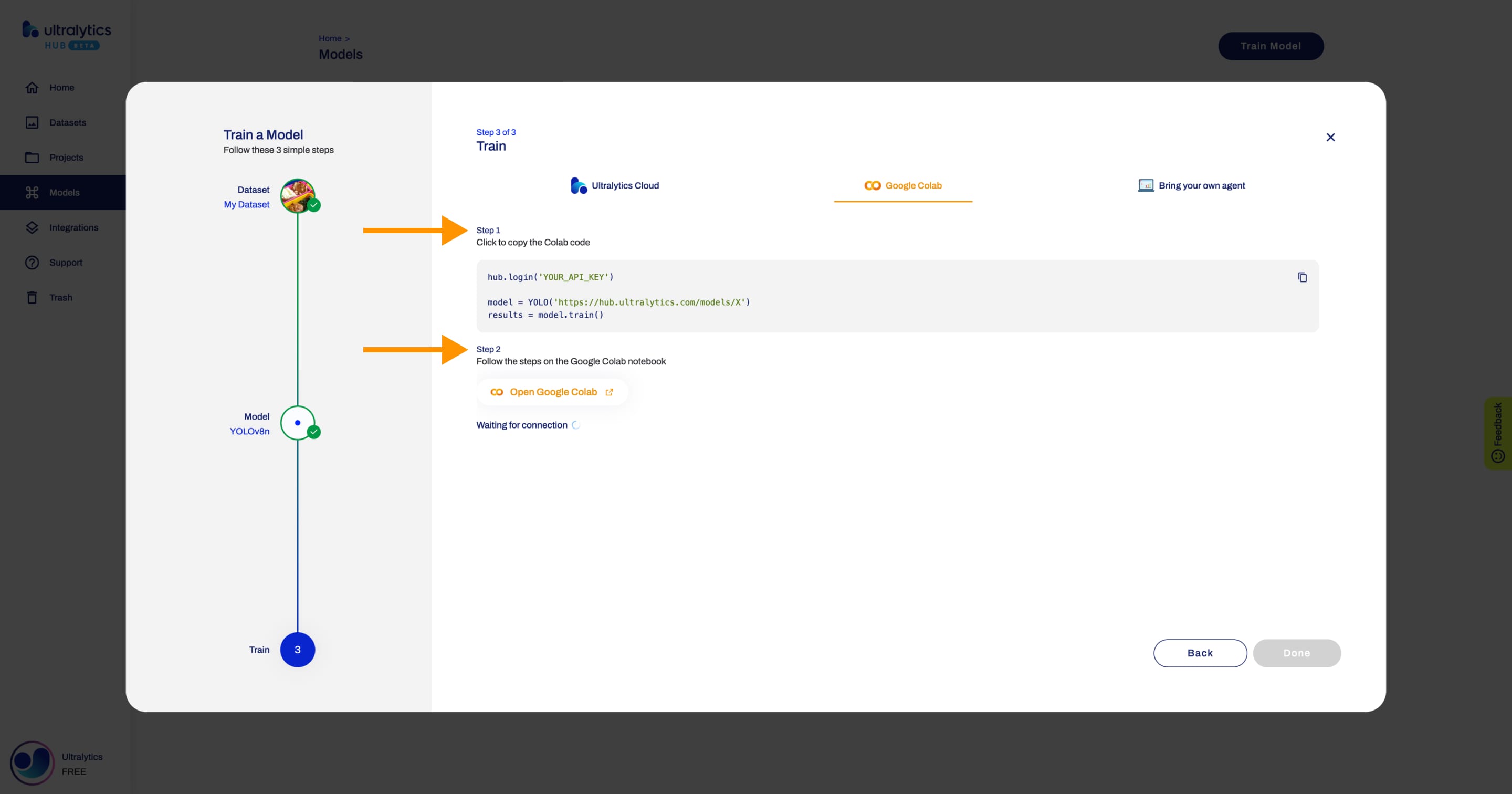
+### 3. Train
+
+In this step, you will start training you model.
+
+Ultralytics HUB offers three training options:
+
+- Ultralytics Cloud **(COMING SOON)**
+- Google Colab
+- Bring your own agent
+
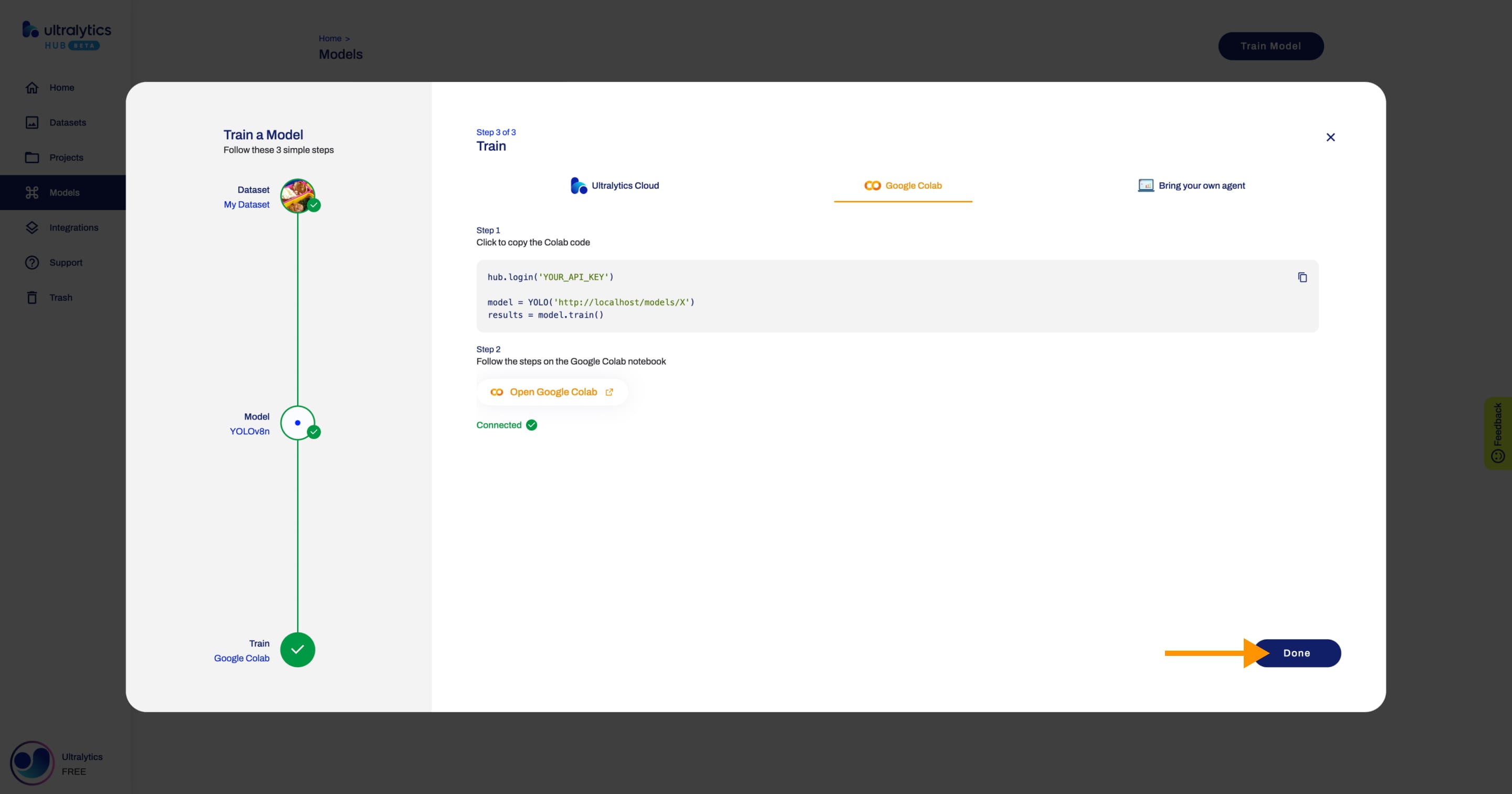
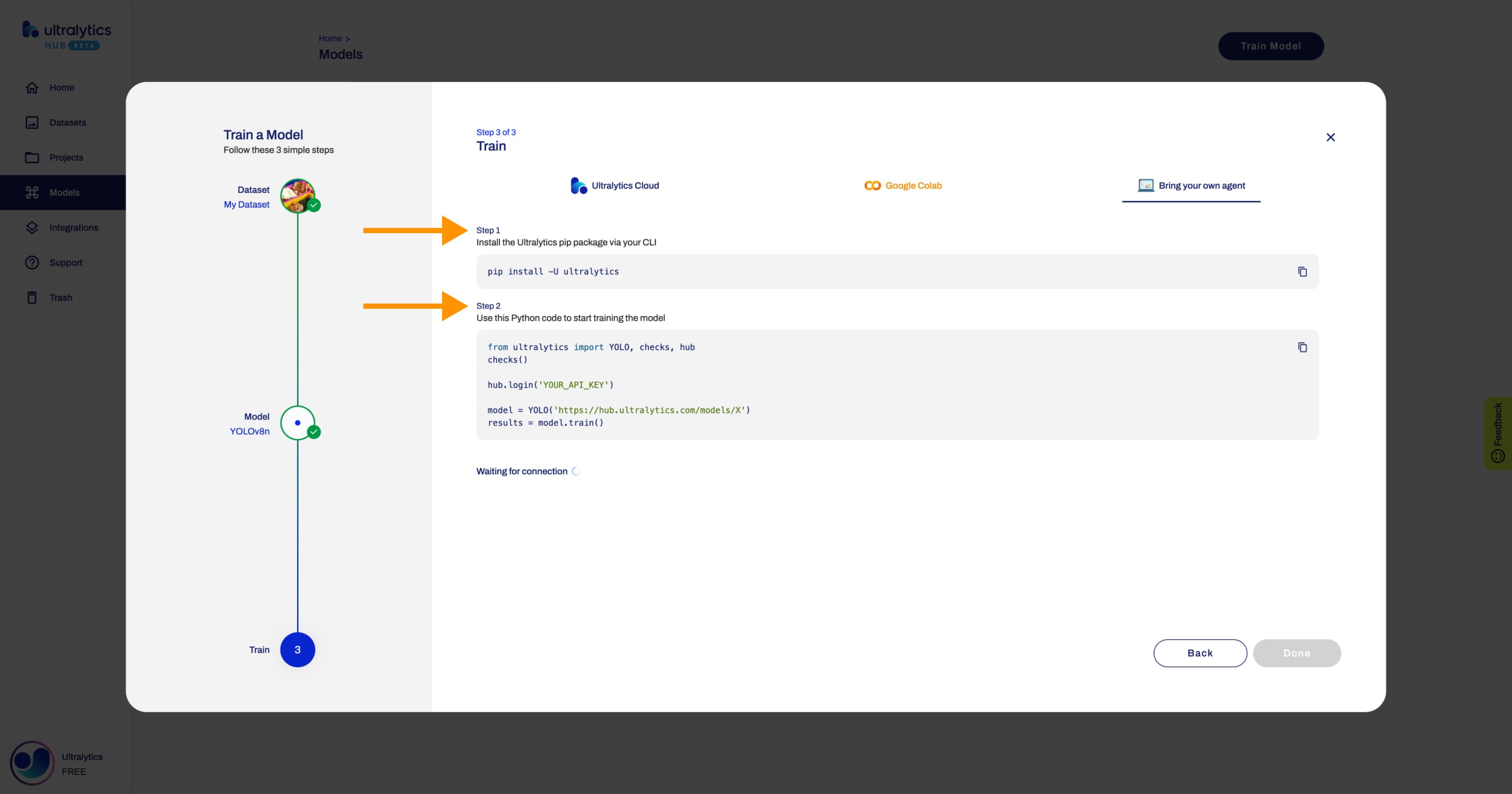
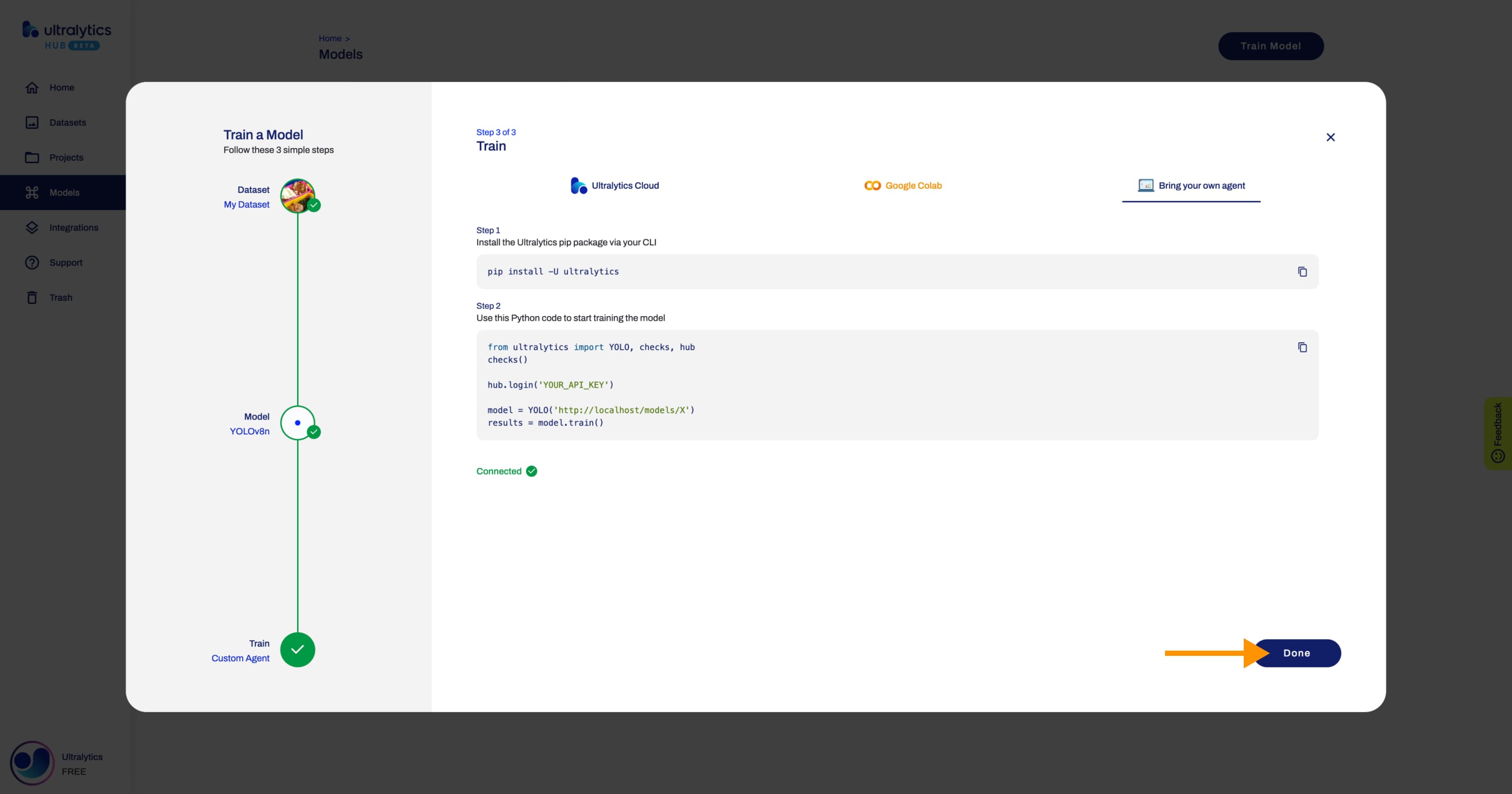
+In order to start training your model, follow the instructions presented in this step.
+
+
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ When you are on this step, before the training starts, you can change the default training configuration by opening the **Advanced Options** accordion.
+
+ 
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ When you are on this step, you have the option to close the **Train Model** dialog and start training your model from the Model page later.
+
+ 
+
+To start training your model using Google Colab, simply follow the instructions shown above or on the Google Colab notebook.
- +
+  +
+
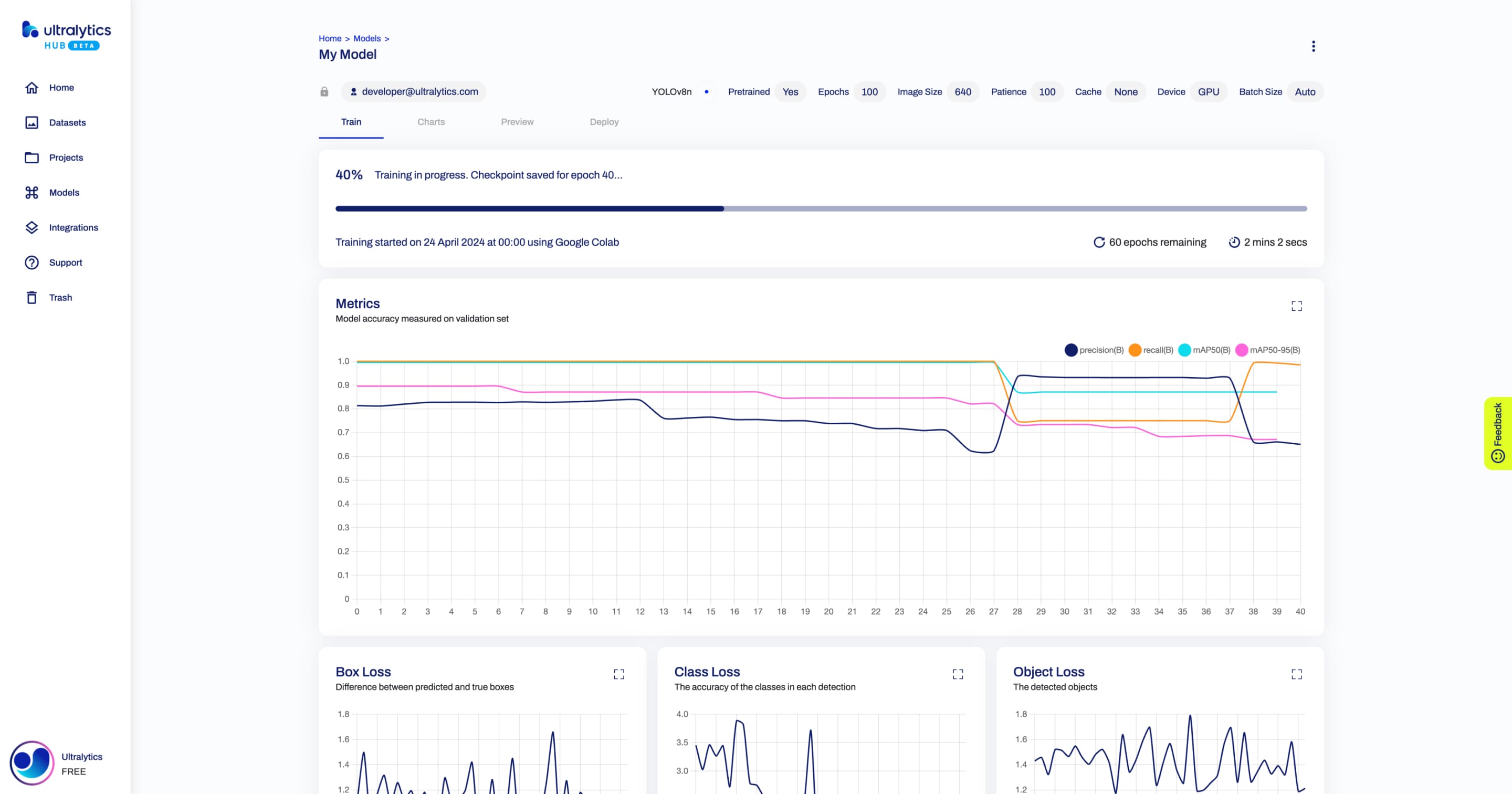
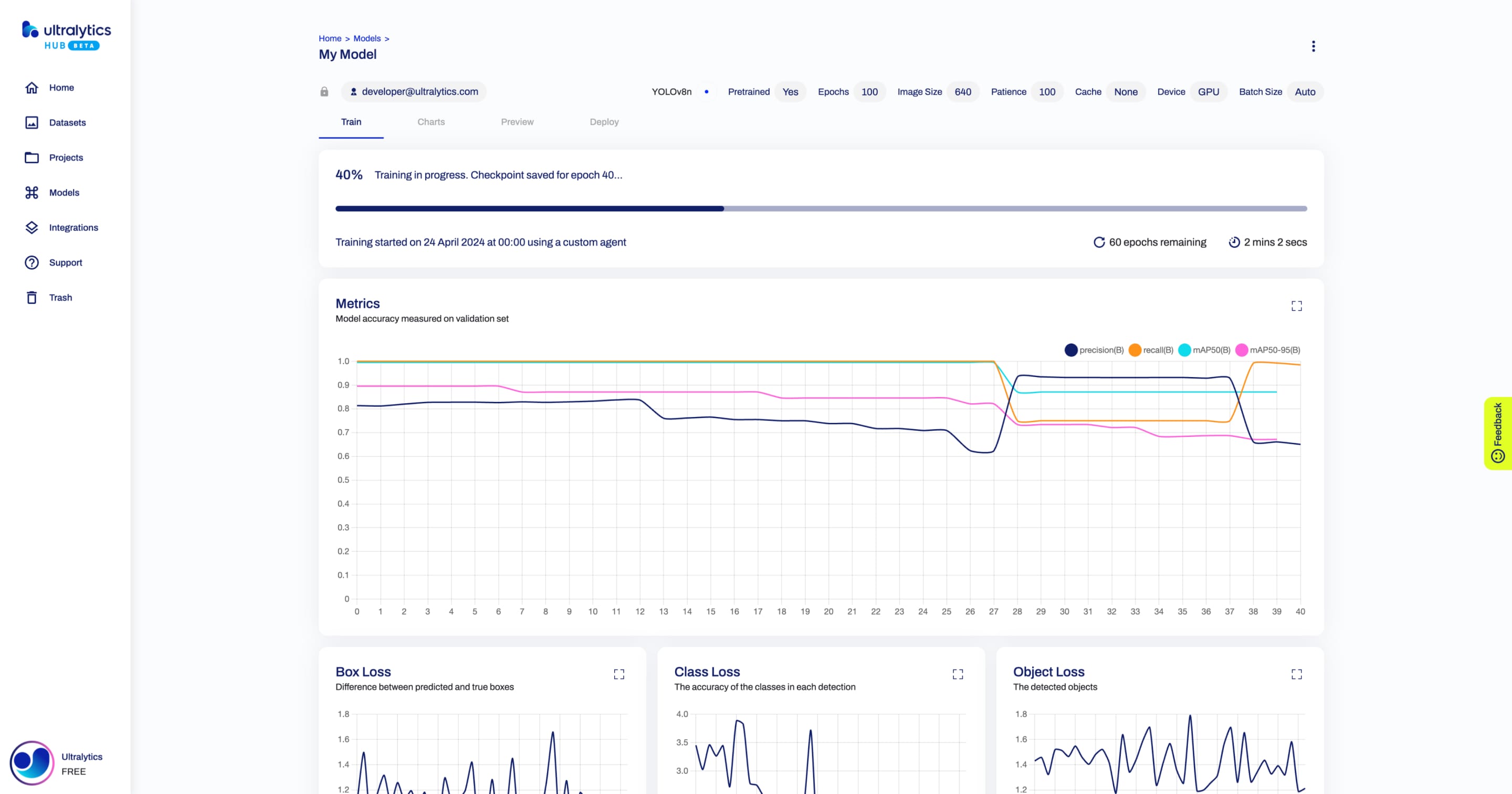
+When the training starts, you can click **Done** and monitor the training progress on the Model page.
+
+
+
+
+
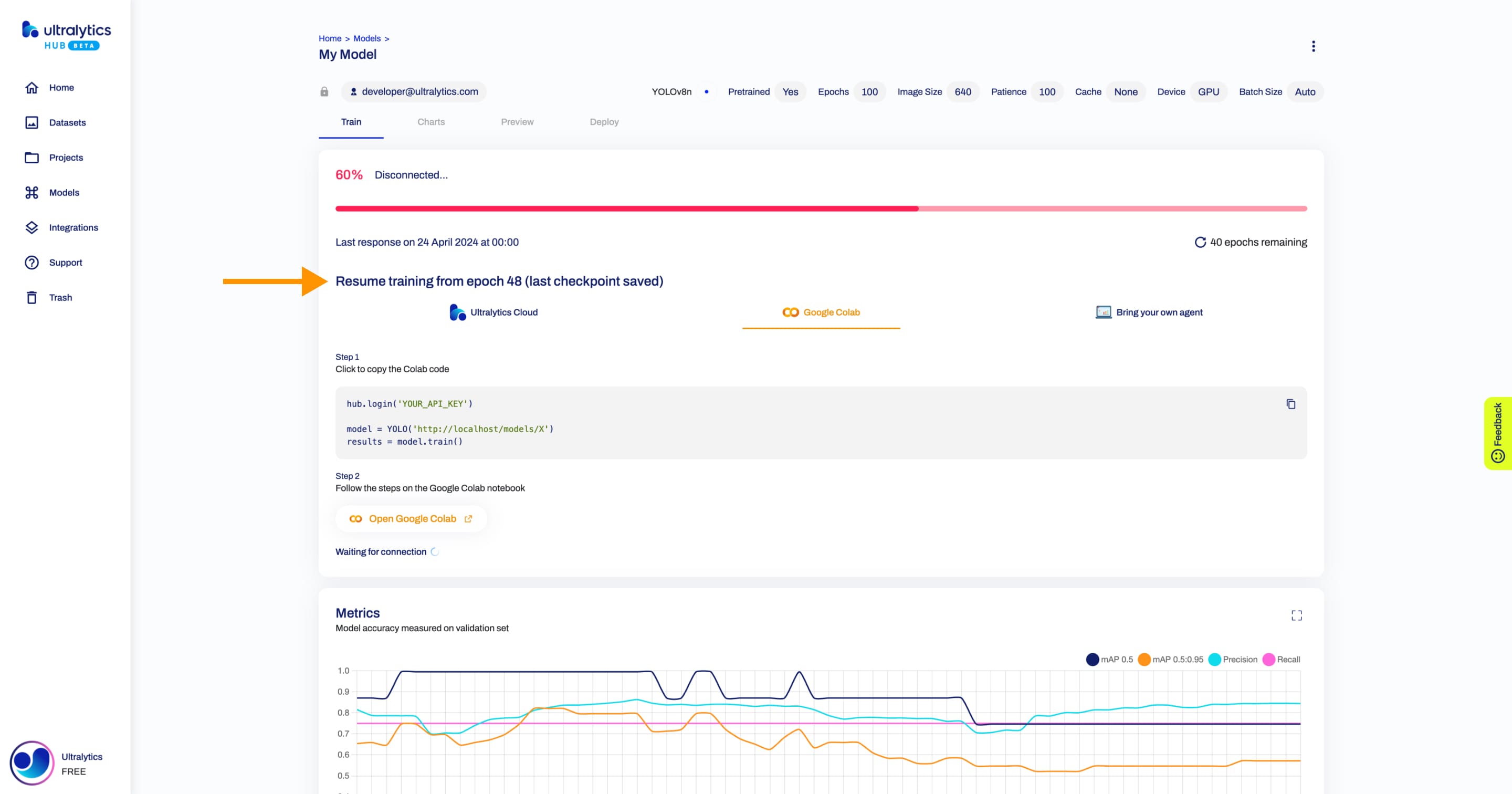
+??? note "Note"
+
+ In case the training stops and a checkpoint was saved, you can resume training your model from the Model page.
+
+ 
+
+## Preview Model
+
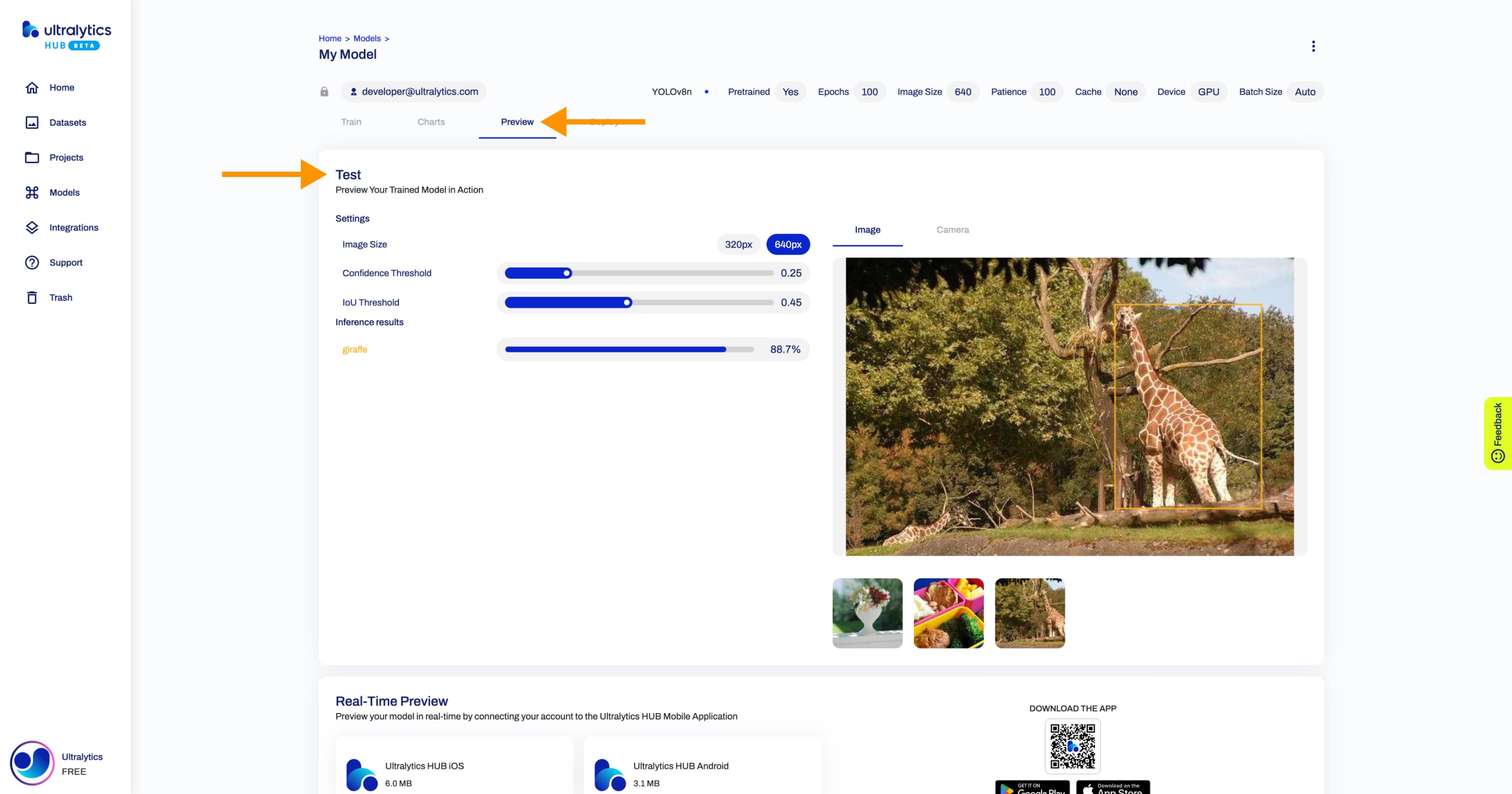
+Ultralytics HUB offers a variety of ways to preview your trained model.
+
+You can preview your model if you click on the **Preview** tab and upload an image in the **Test** card.
+
+
+
+You can also use our Ultralytics Cloud API to effortlessly [run inference](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/inference_api) with your custom model.
+
+
+
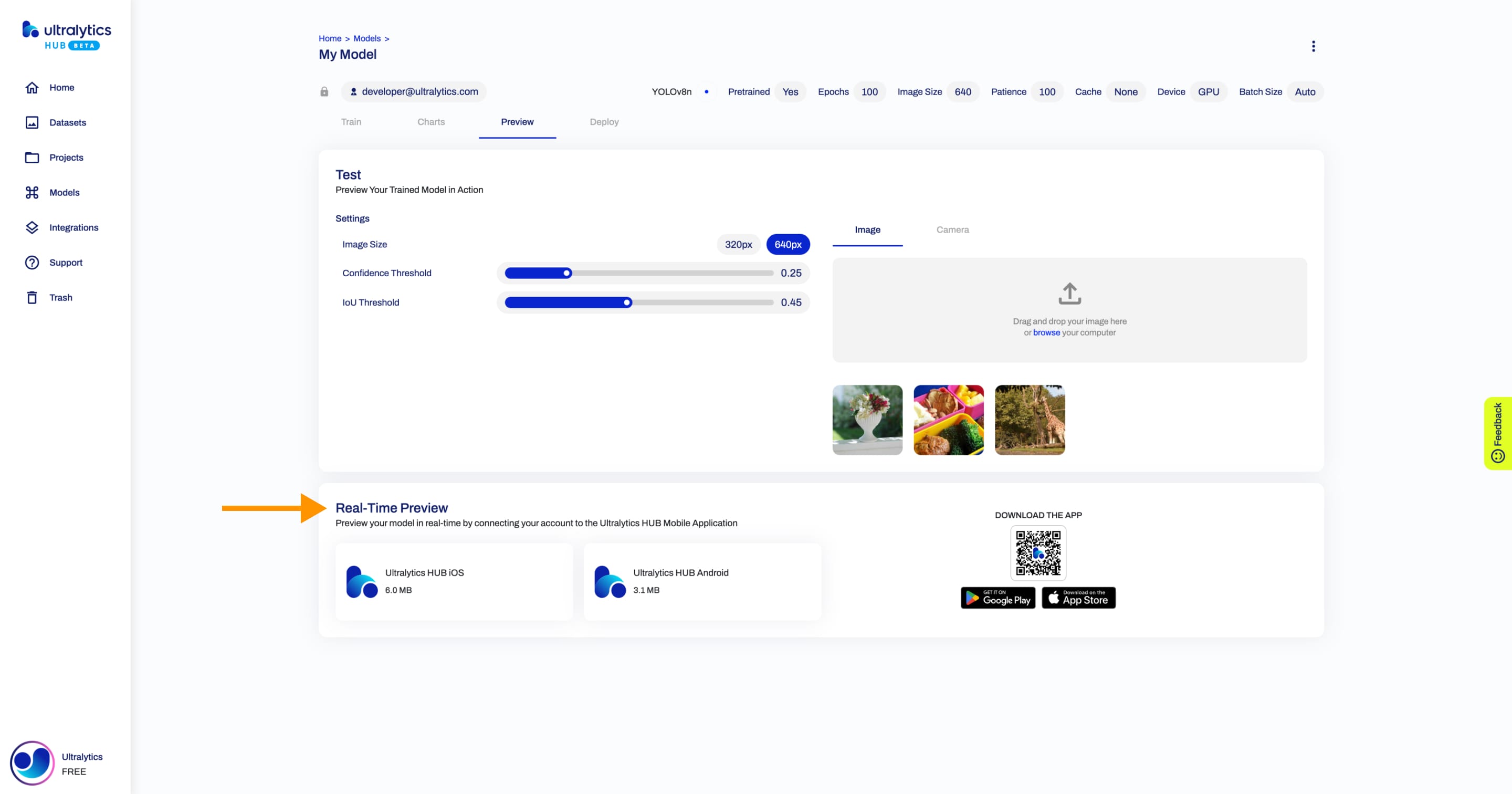
+Furthermore, you can preview your model in real-time directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by [downloading](https://ultralytics.com/app_install) our [Ultralytics HUB Mobile Application](./app/index.md).
+
+
+
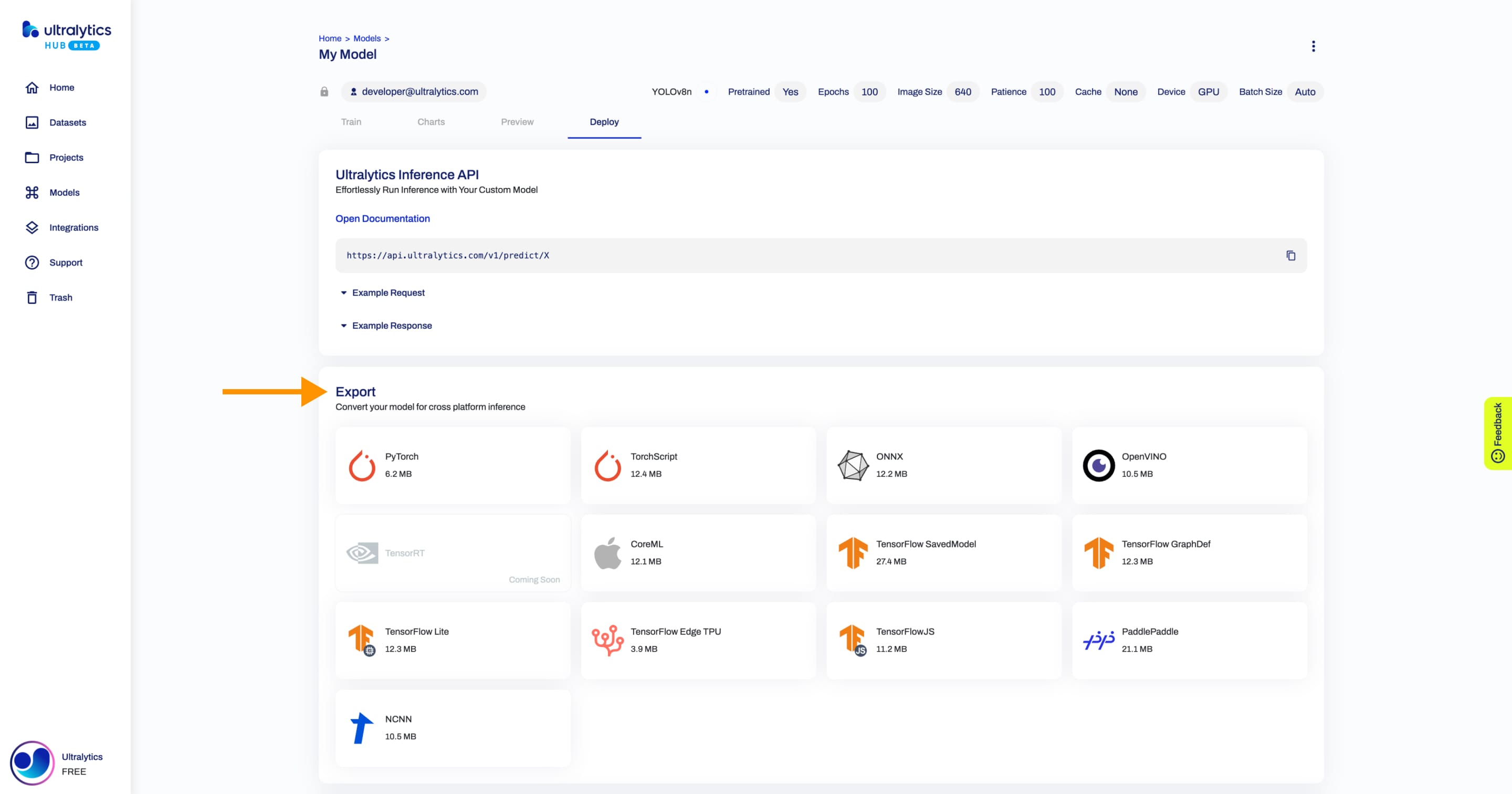
+## Deploy Model
+
+You can export your model to 13 different formats, including ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, TensorFlow, Paddle and many others.
+
+
+
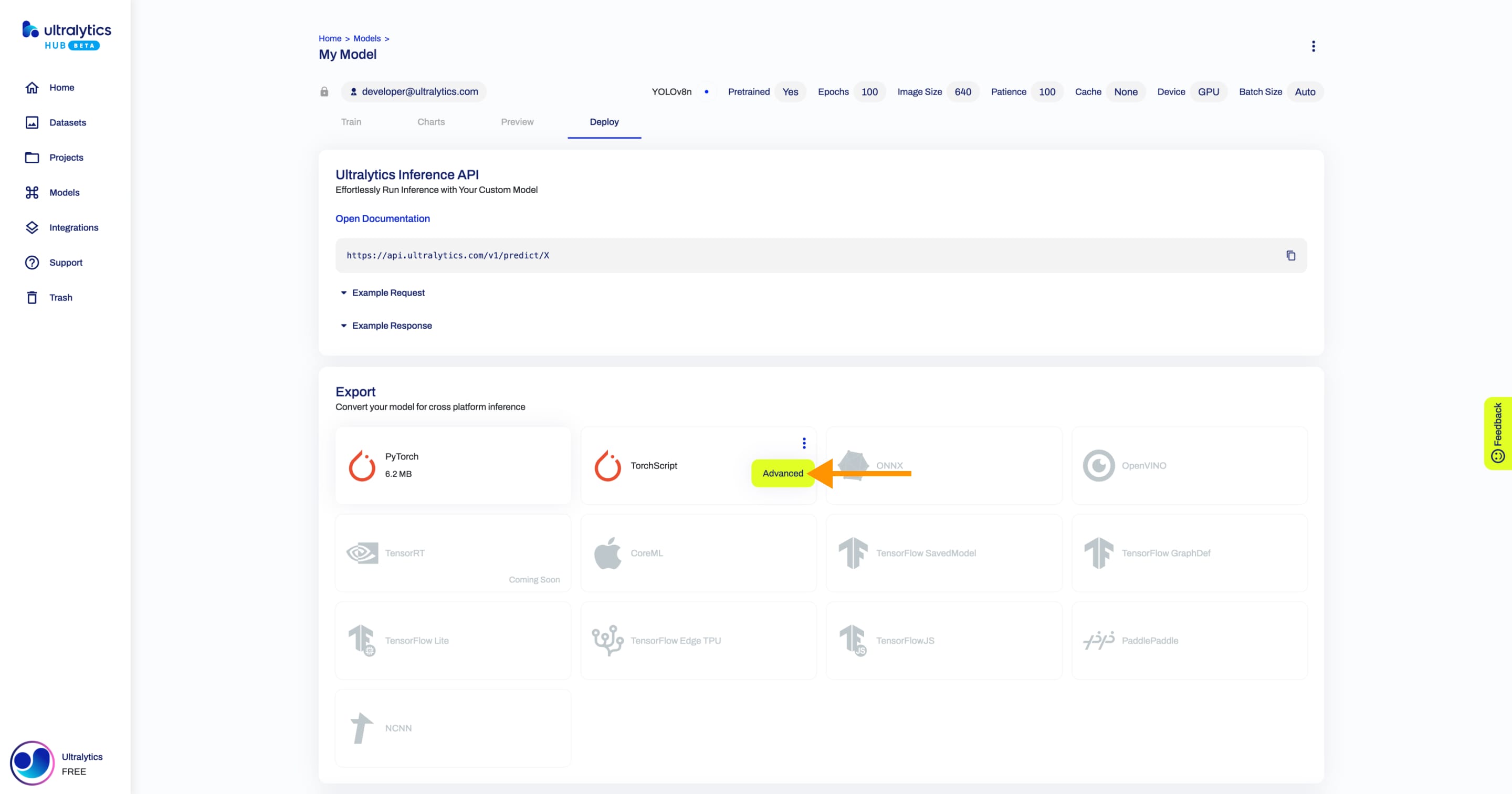
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can customize the export options of each format if you open the export actions dropdown and click on the **Advanced** option.
+
+ 
+
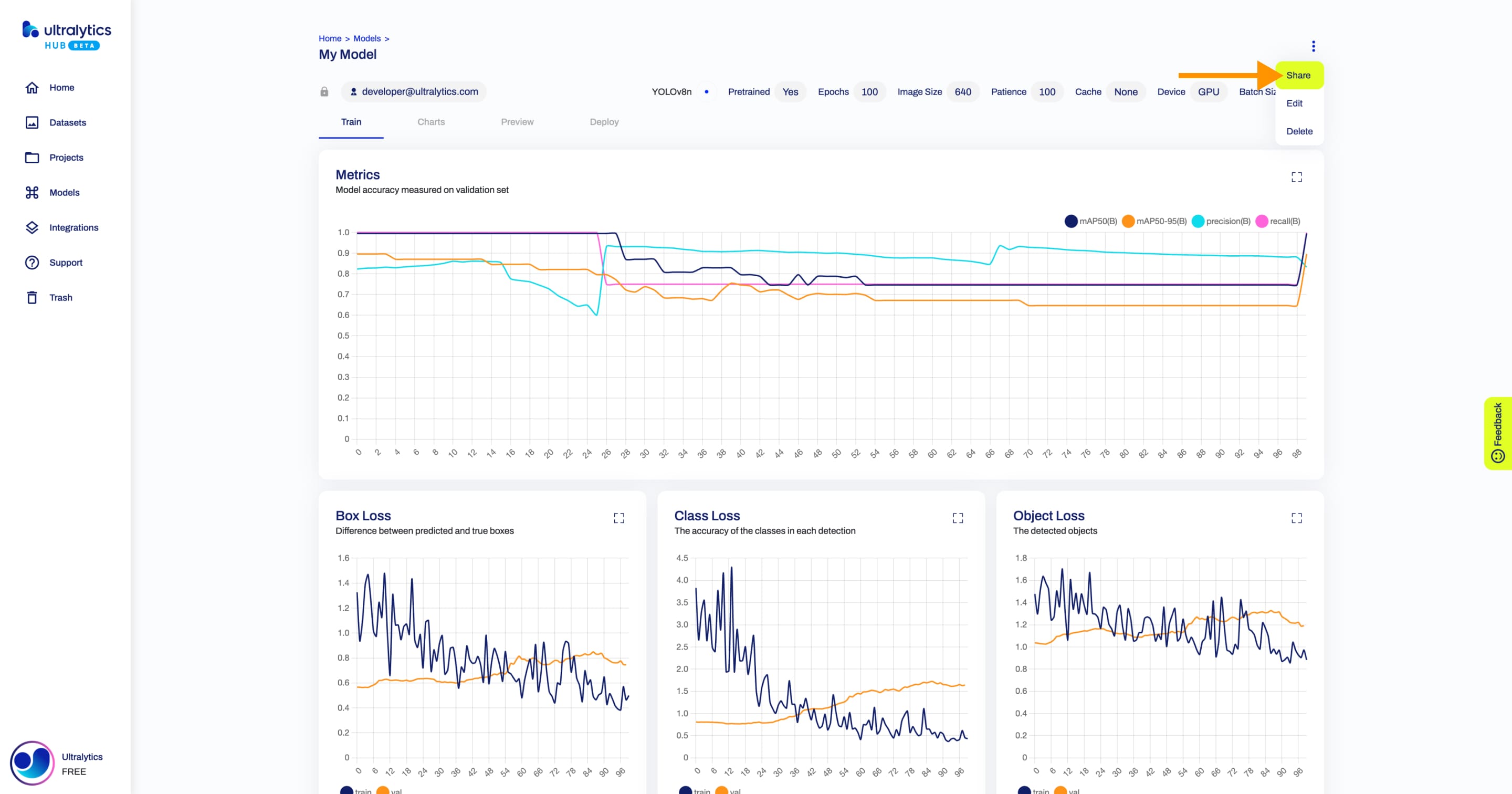
+## Share Model
+
+!!! info "Info"
+
+ Ultralytics HUB's sharing functionality provides a convenient way to share models with others. This feature is designed to accommodate both existing Ultralytics HUB users and those who have yet to create an account.
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ You have control over the general access of your models.
+
+ You can choose to set the general access to "Private", in which case, only you will have access to it. Alternatively, you can set the general access to "Unlisted" which grants viewing access to anyone who has the direct link to the model, regardless of whether they have an Ultralytics HUB account or not.
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to share, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Share** option. This action will trigger the **Share Model** dialog.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also share a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 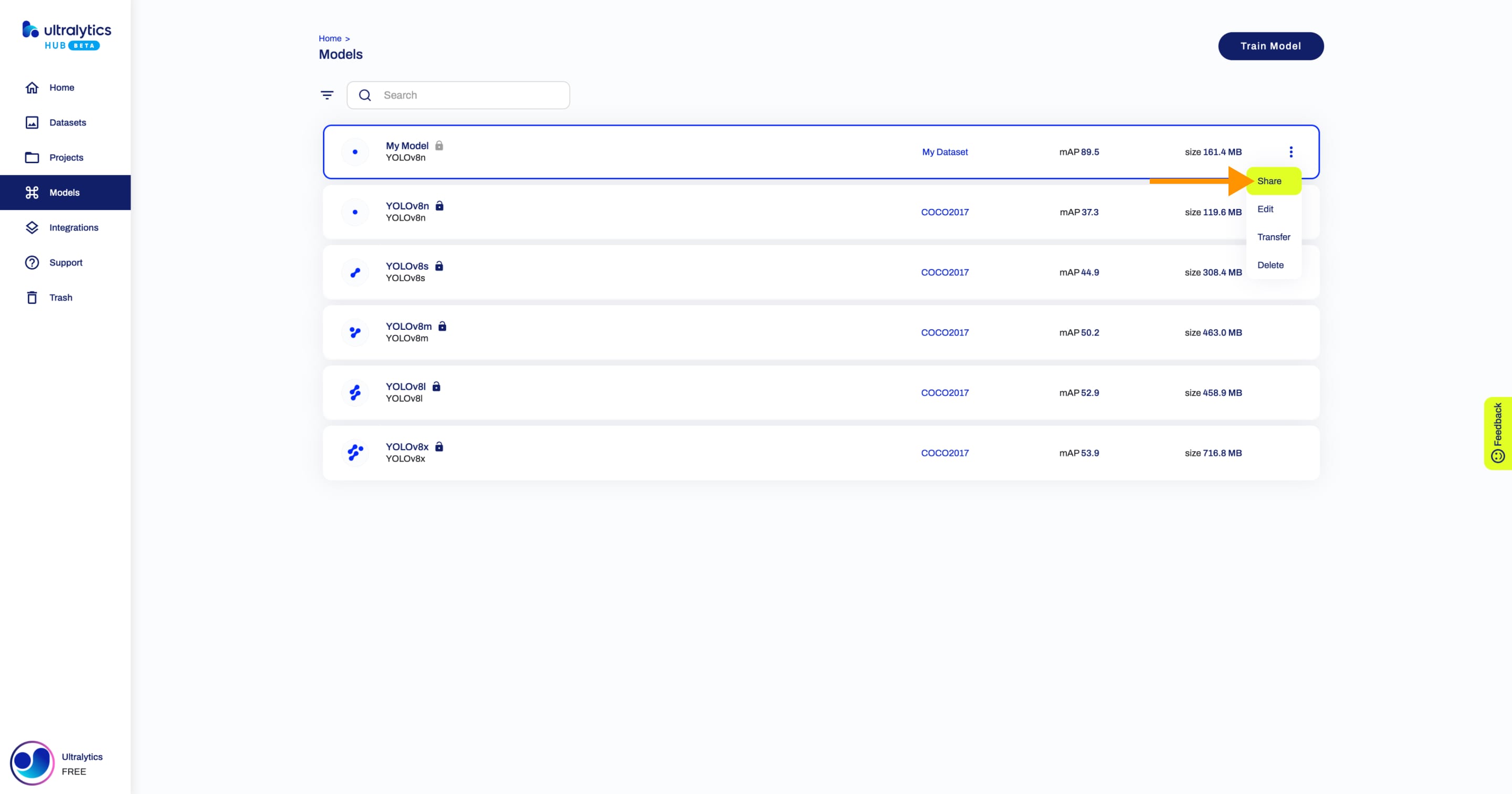
+
+Set the general access to "Unlisted" and click **Save**.
+
+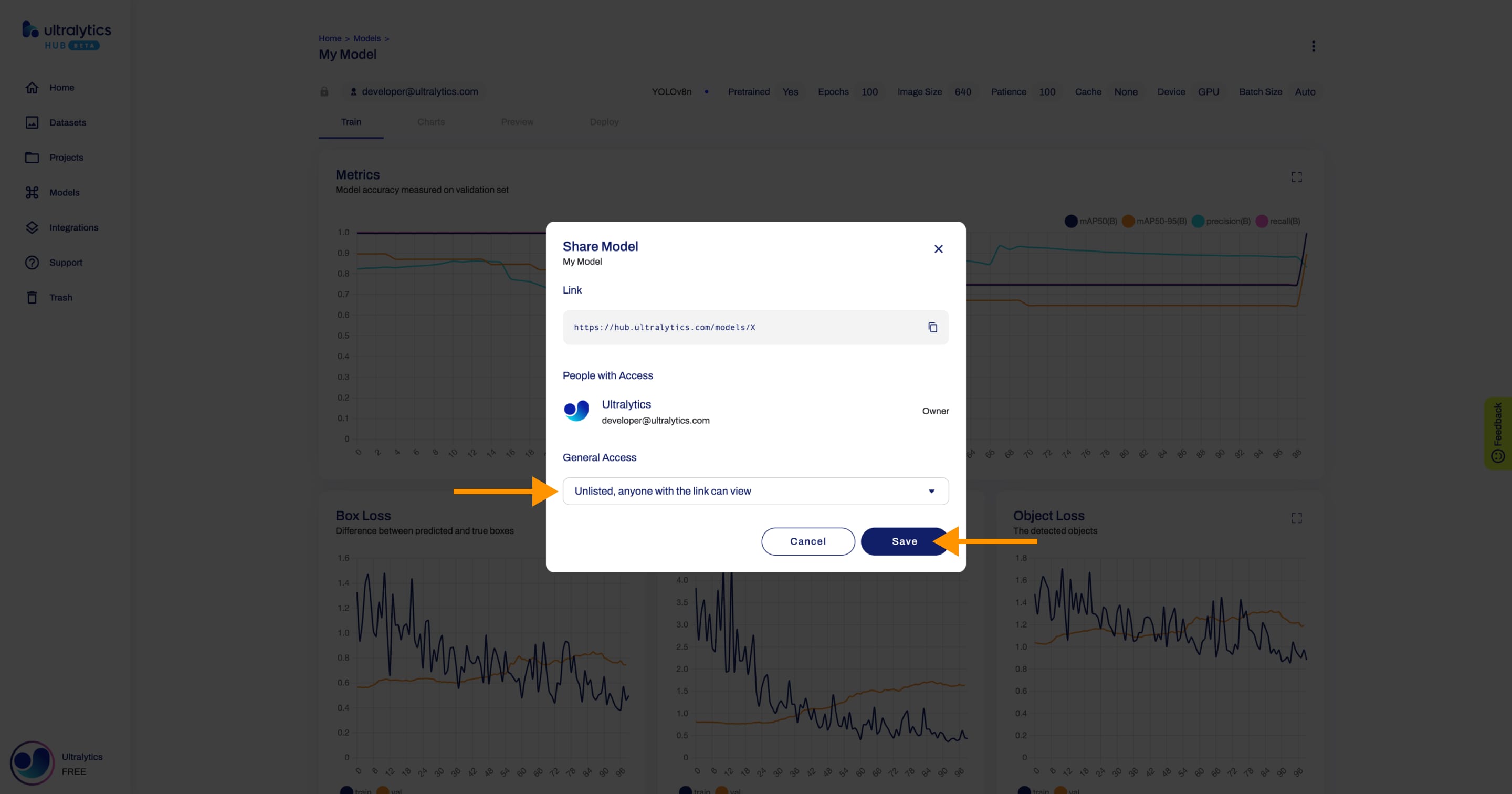
+
+Now, anyone who has the direct link to your model can view it.
+
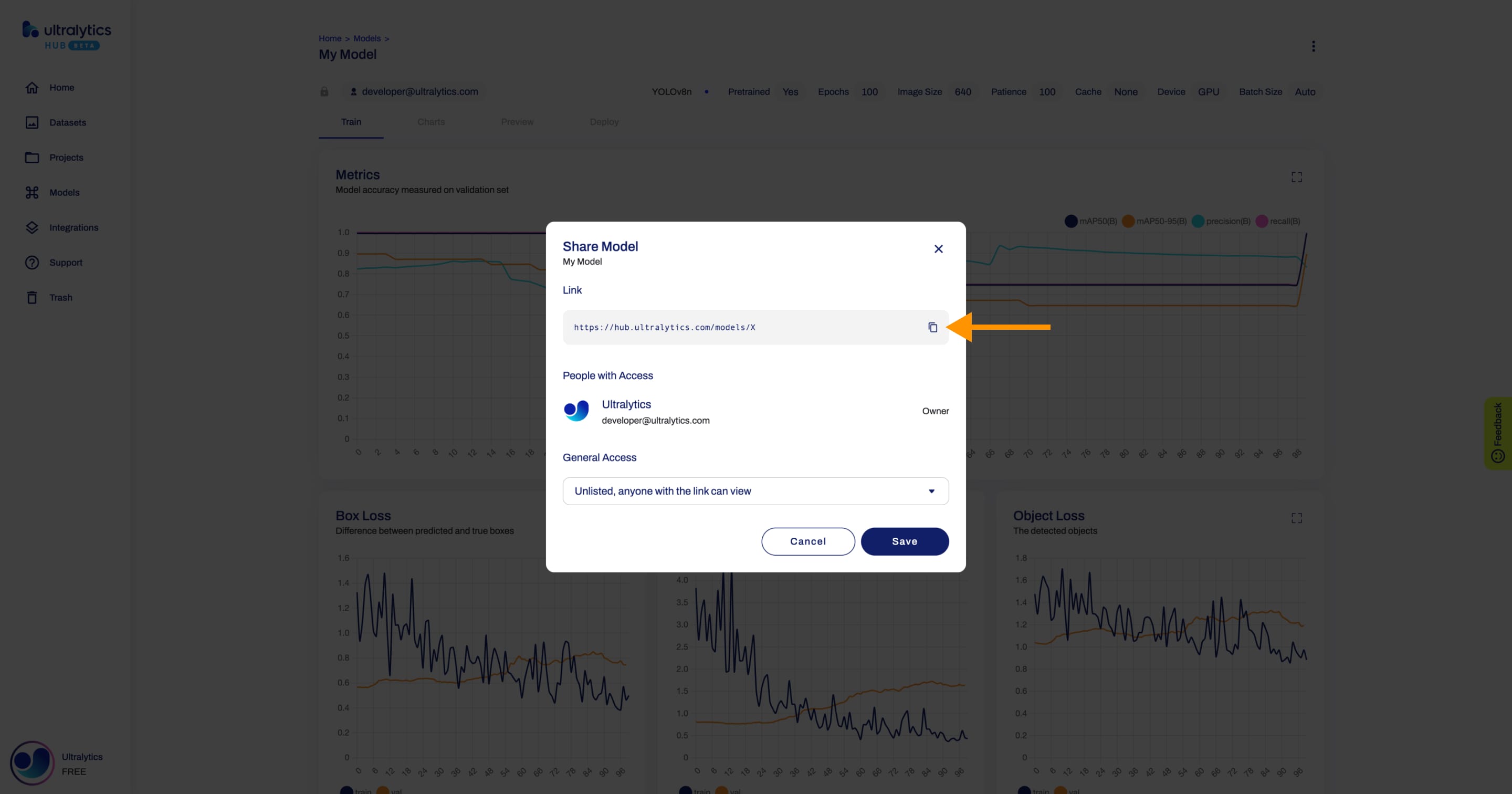
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can easily click on the models's link shown in the **Share Model** dialog to copy it.
+
+ 
+
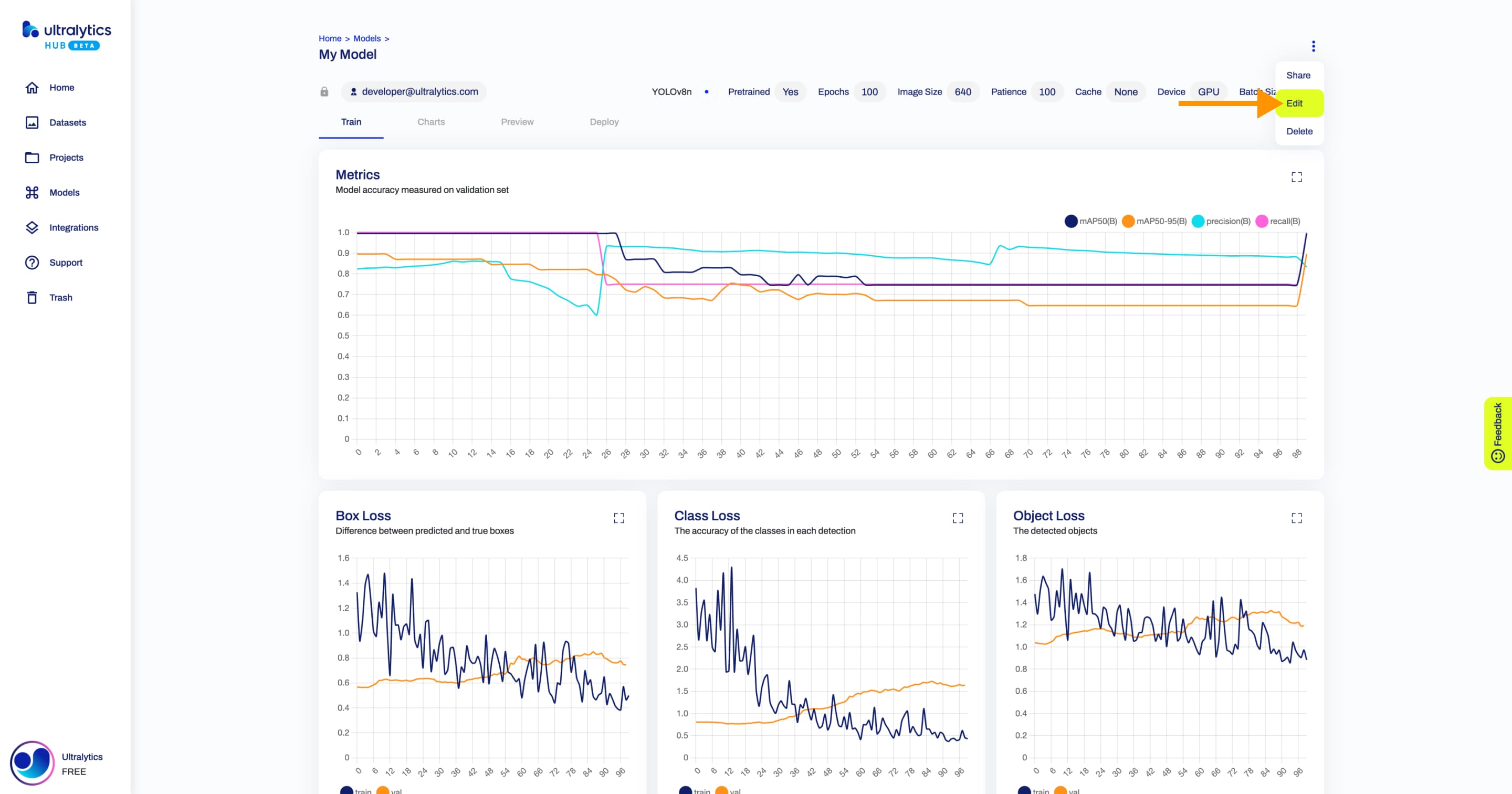
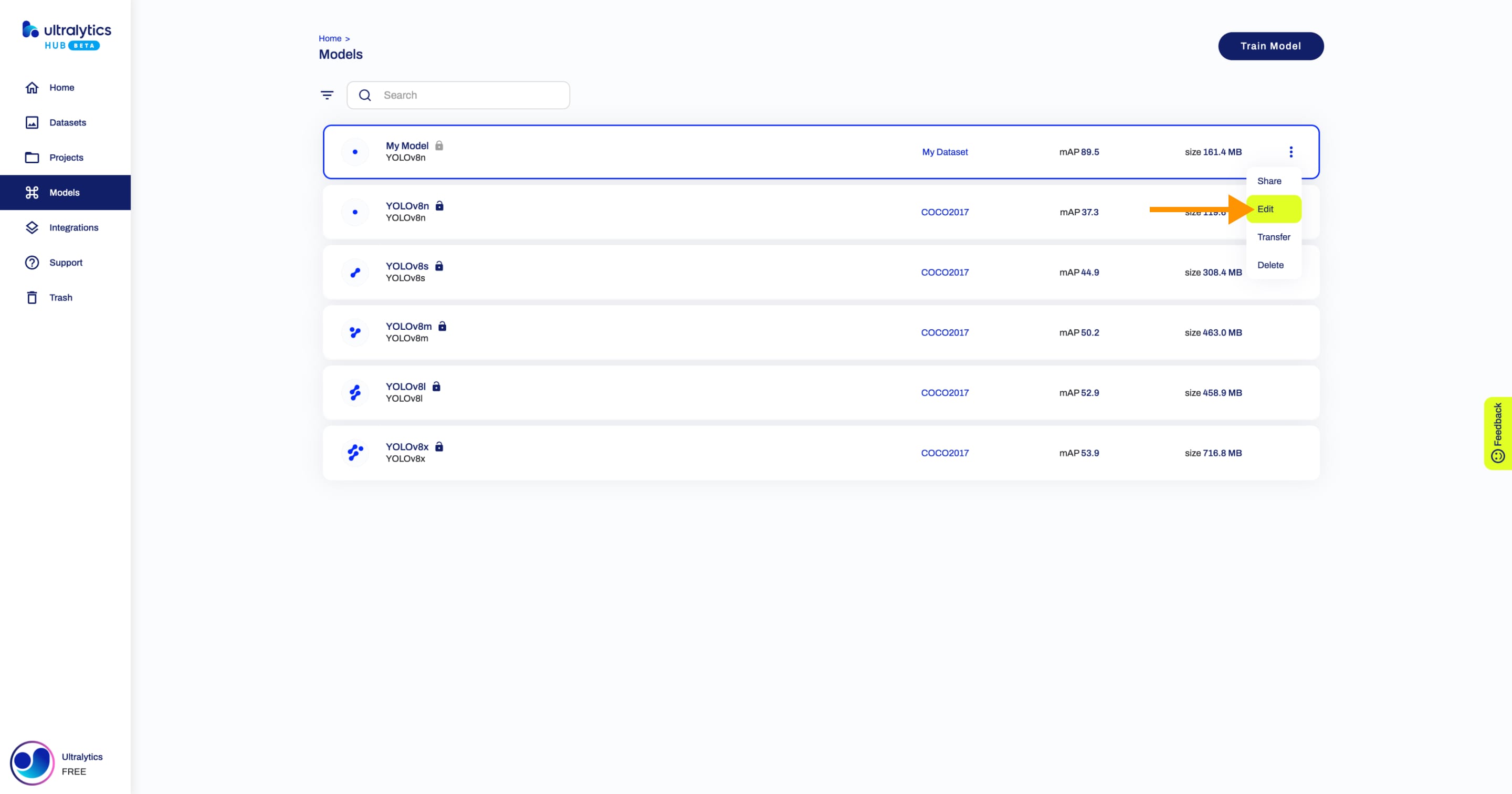
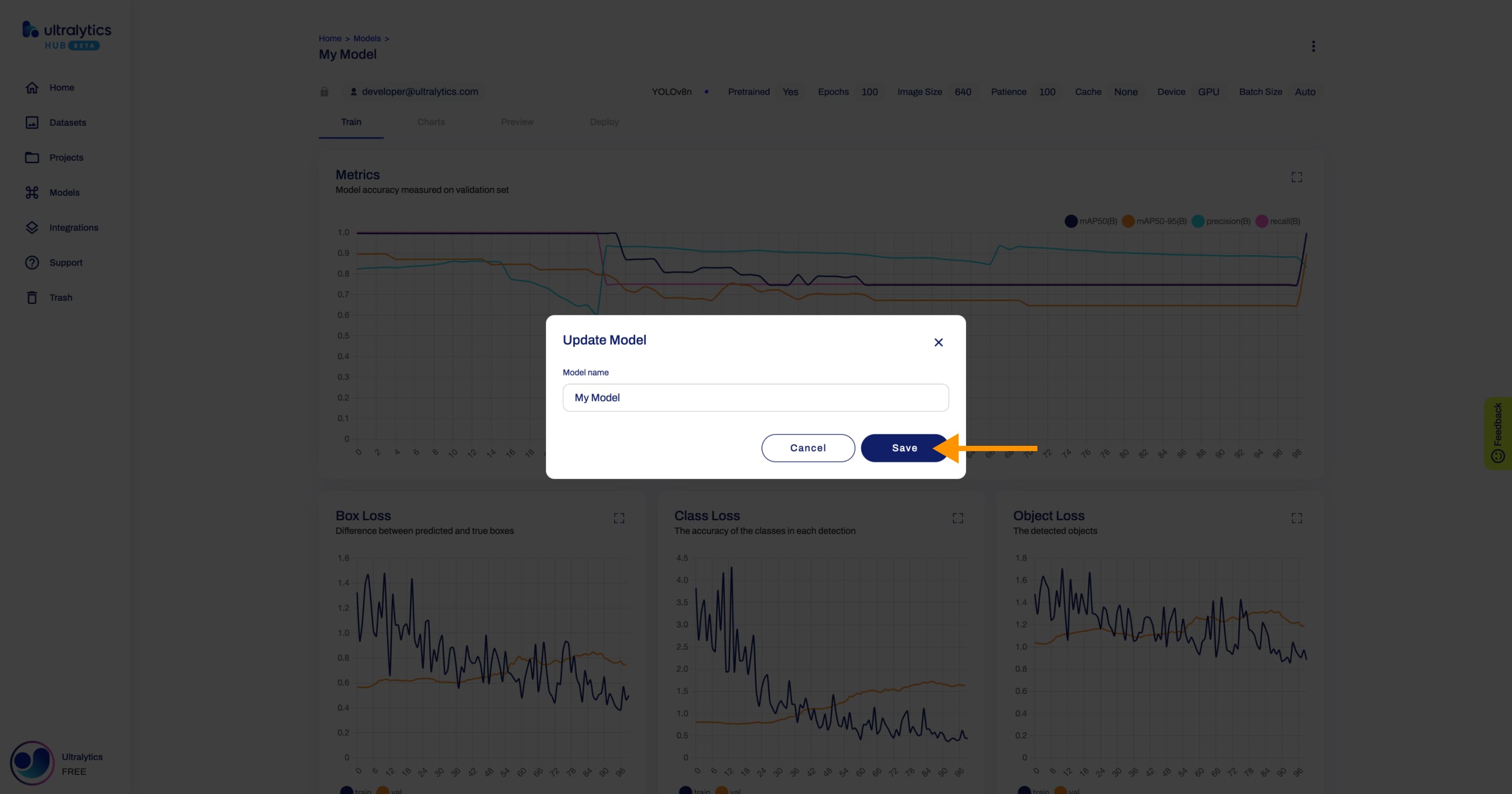
+## Edit Model
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to edit, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Edit** option. This action will trigger the **Update Model** dialog.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also edit a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 
+
+Apply the desired modifications to your model and then confirm the changes by clicking **Save**.
+
+
+
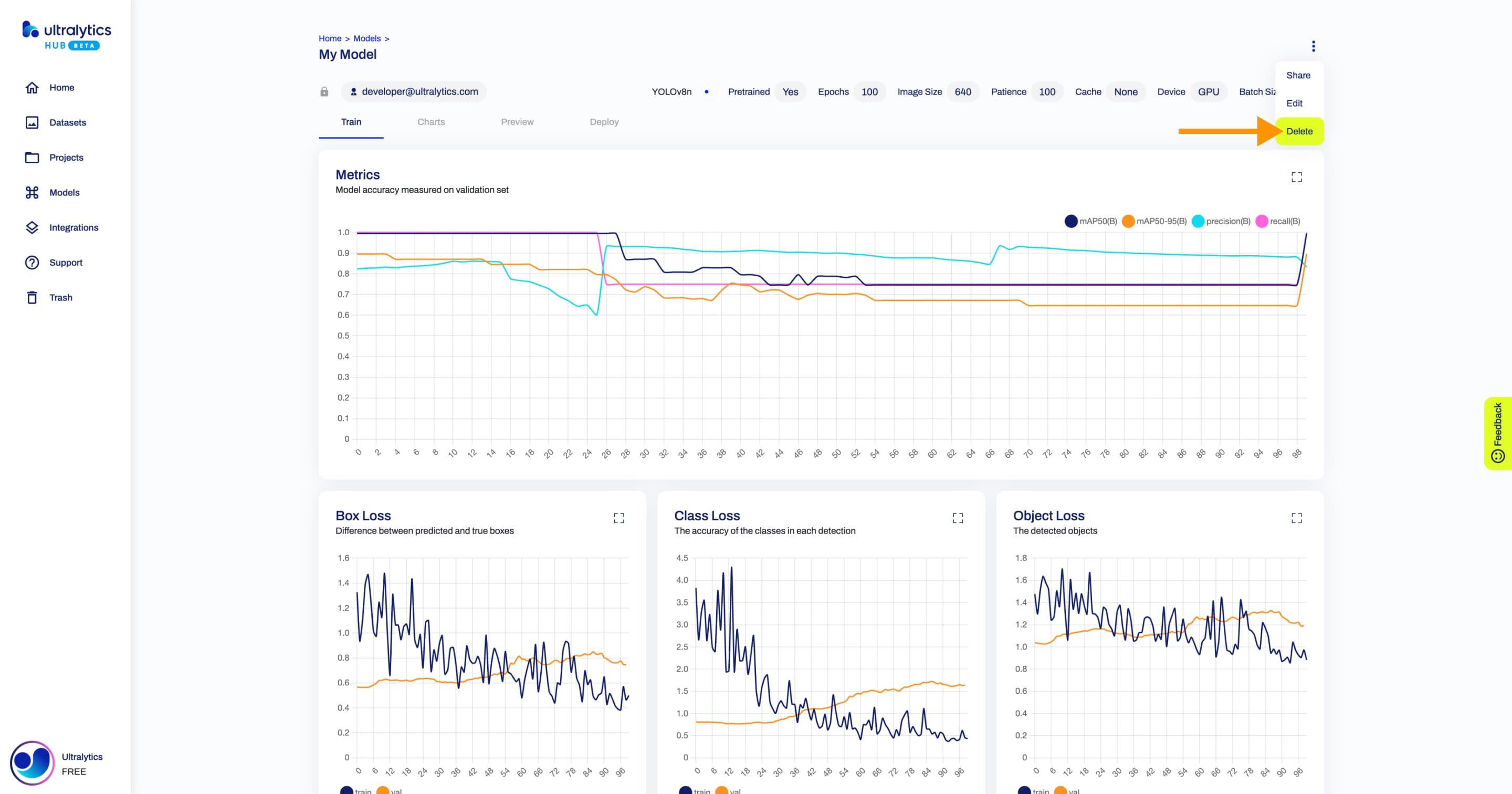
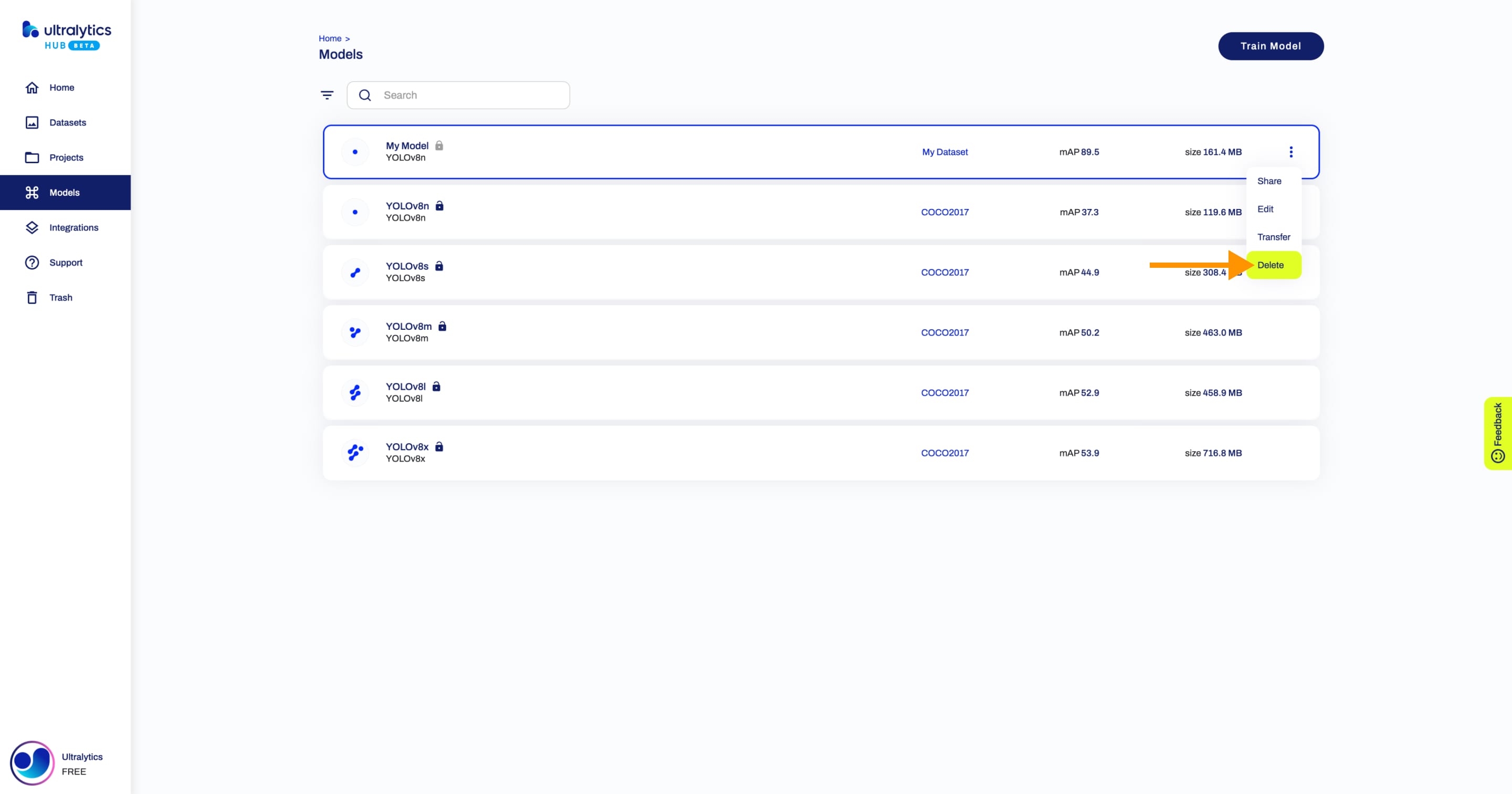
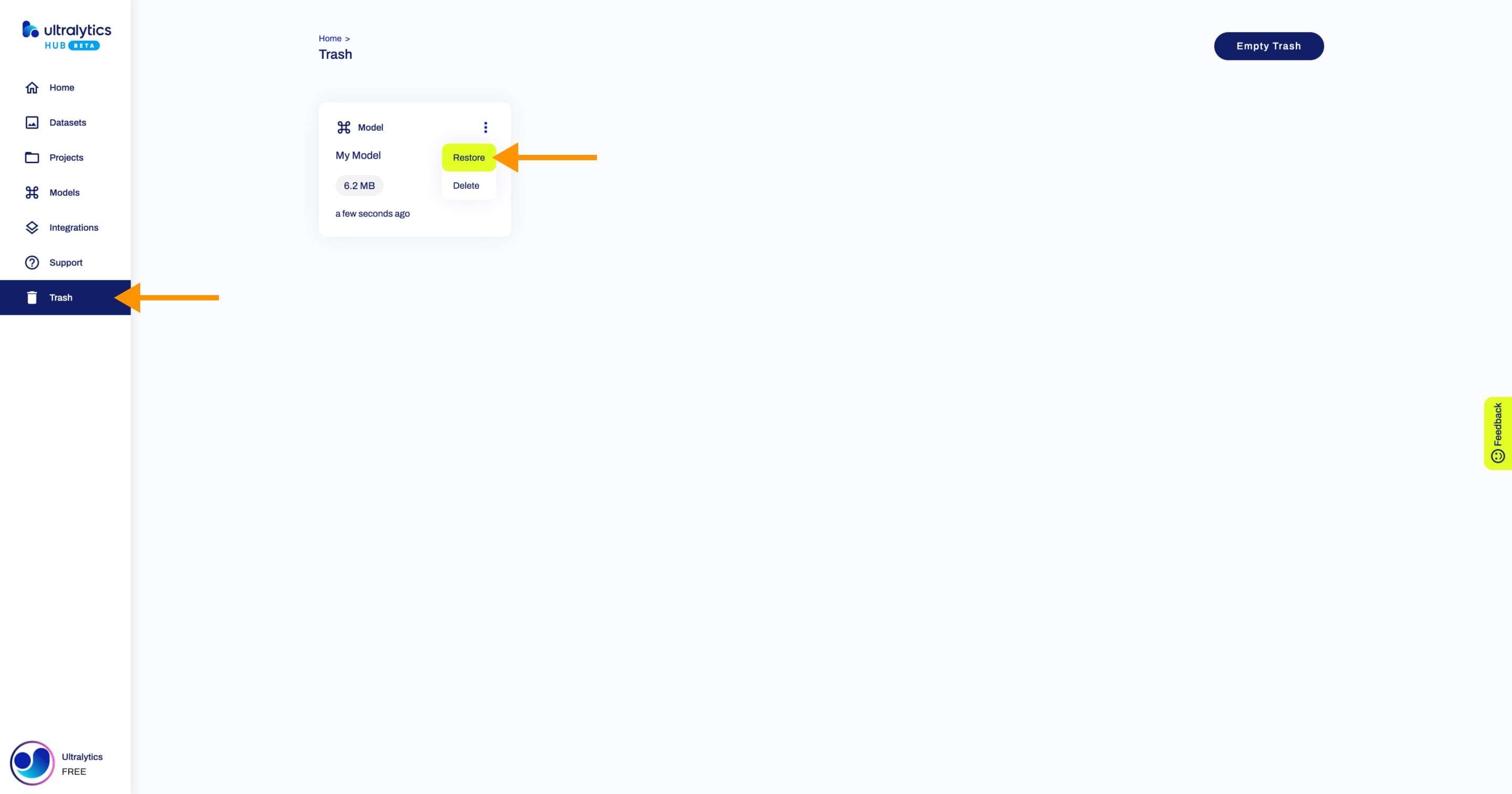
+## Delete Model
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to delete, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Delete** option. This action will delete the model.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also delete a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 
+
+??? note "Note"
-## Deploy to Real World
+ If you change your mind, you can restore the model from the [Trash](https://hub.ultralytics.com/trash) page.
-Export your model to 13 different formats, including TensorFlow, ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, Paddle and many others. Run
-models directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or
-[Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by downloading
-the [Ultralytics App](https://ultralytics.com/app_install)!
\ No newline at end of file
+ 
diff --git a/docs/hub/projects.md b/docs/hub/projects.md
index 6a006b365..d8e0f8649 100644
--- a/docs/hub/projects.md
+++ b/docs/hub/projects.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Click on the **Create Project** button on the top right of the page. This action
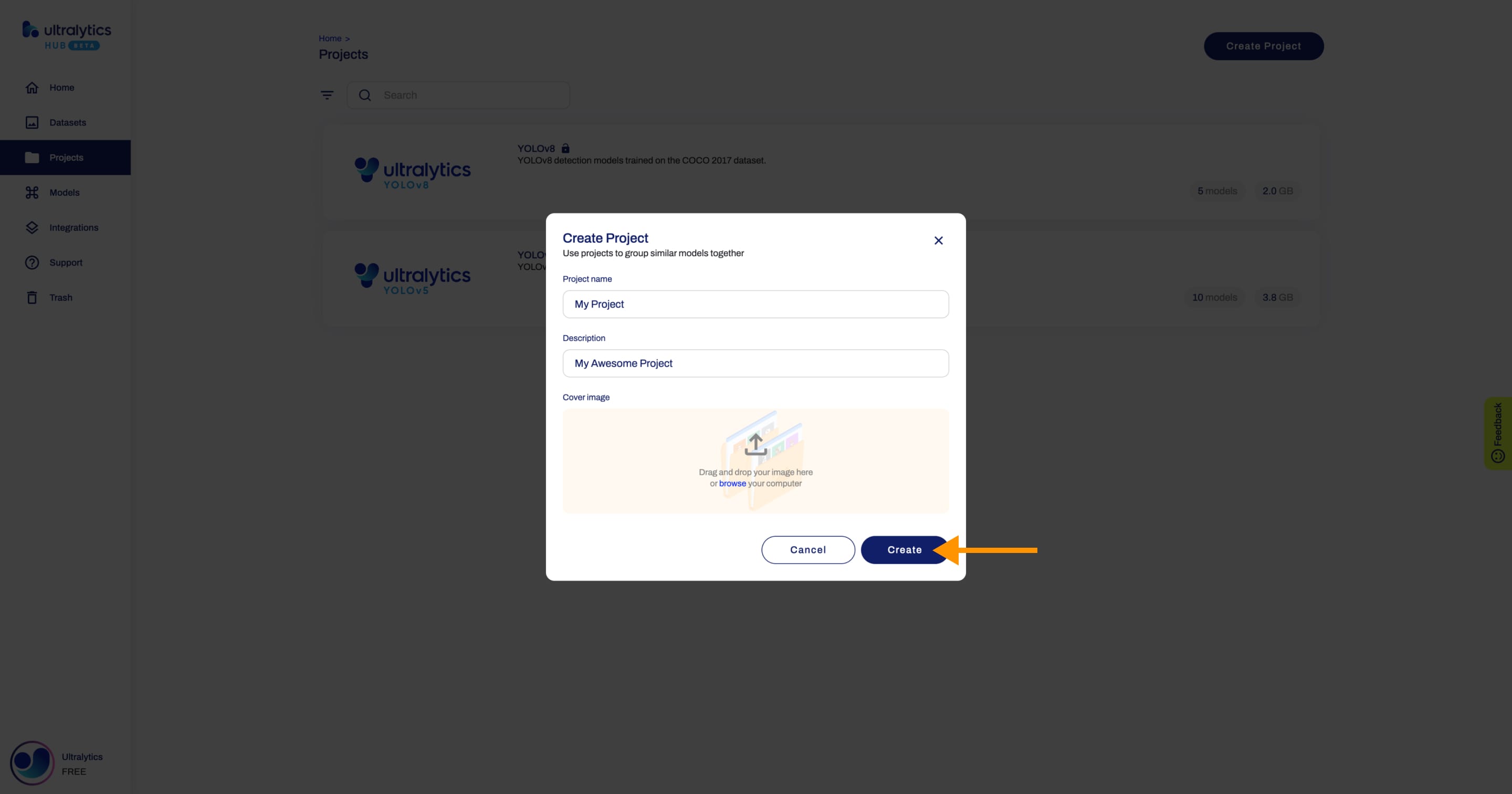
-Type the name of your project in the *Project name* field or keep the default name and finalize the project creation with a single click.
+Type the name of your project in the _Project name_ field or keep the default name and finalize the project creation with a single click.
You have the additional option to enrich your project with a description and a unique image, enhancing its recognizability on the Projects page.
@@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ After your project is created, you will be able to access it from the Projects p
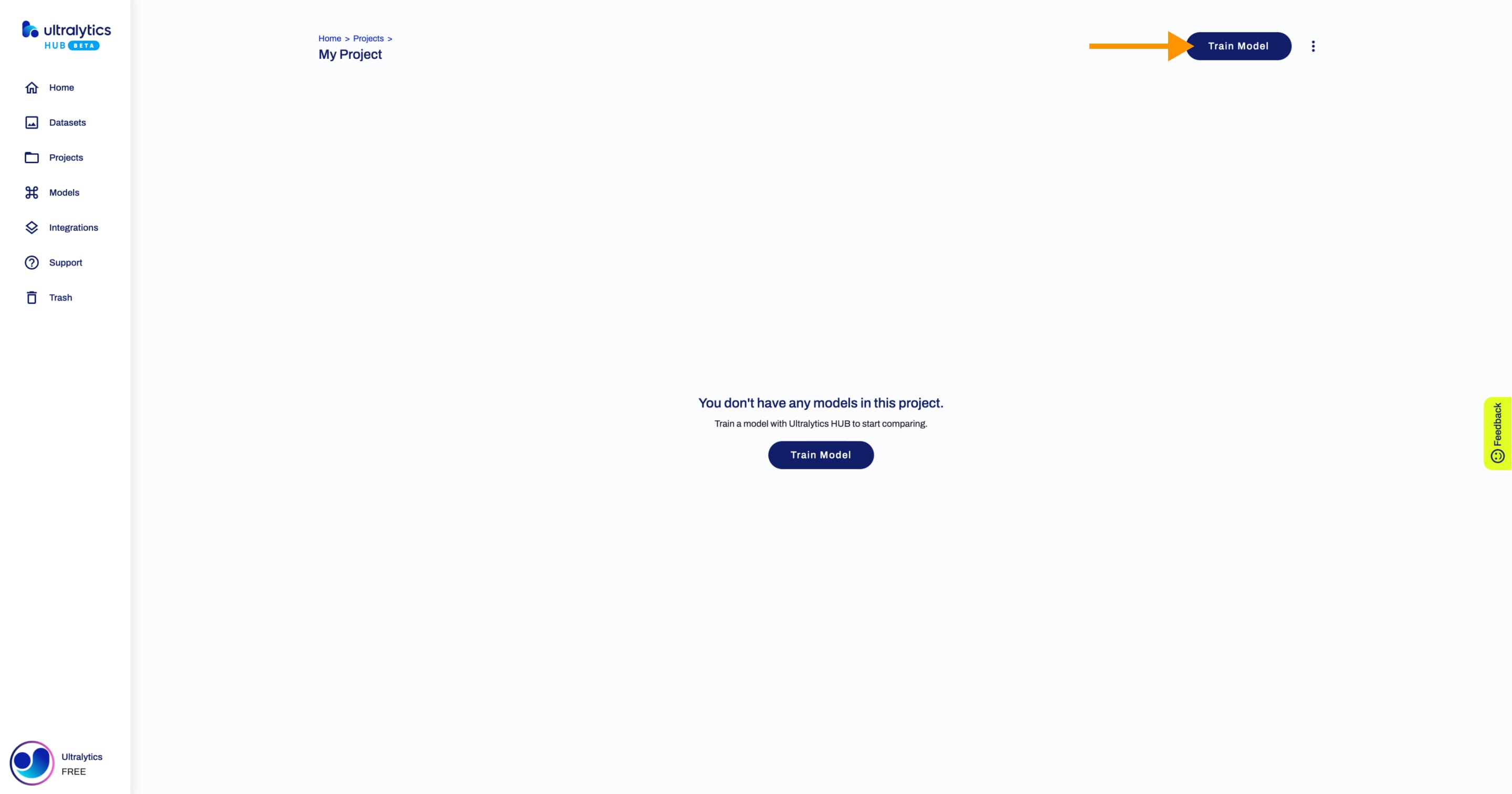
-Next, [create a model](./models.md) inside your project.
+Next, [train a model](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/models/#train-model) inside your project.
-
+
## Share Project
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ Navigate to the Project page of the project you want to delete, open the project
## Compare Models
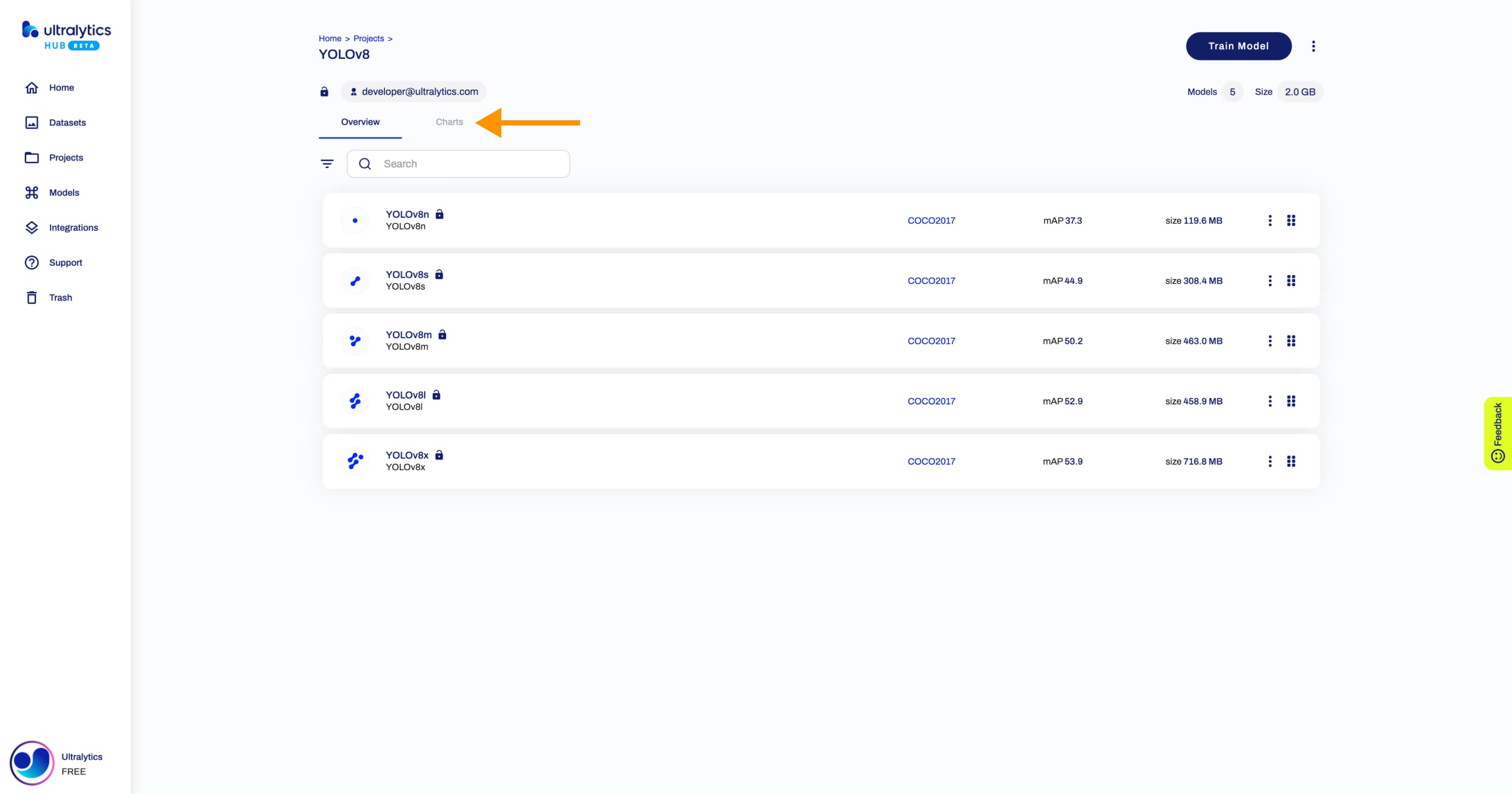
-Navigate to the Project page of the project where the models you want to compare are located. To use the model comparison feature, click on the **Charts** tab.
+Navigate to the Project page of the project where the models you want to compare are located. To use the model comparison feature, click on the **Charts** tab.
@@ -166,4 +166,4 @@ Navigate to the Project page of the project where the model you want to mode is
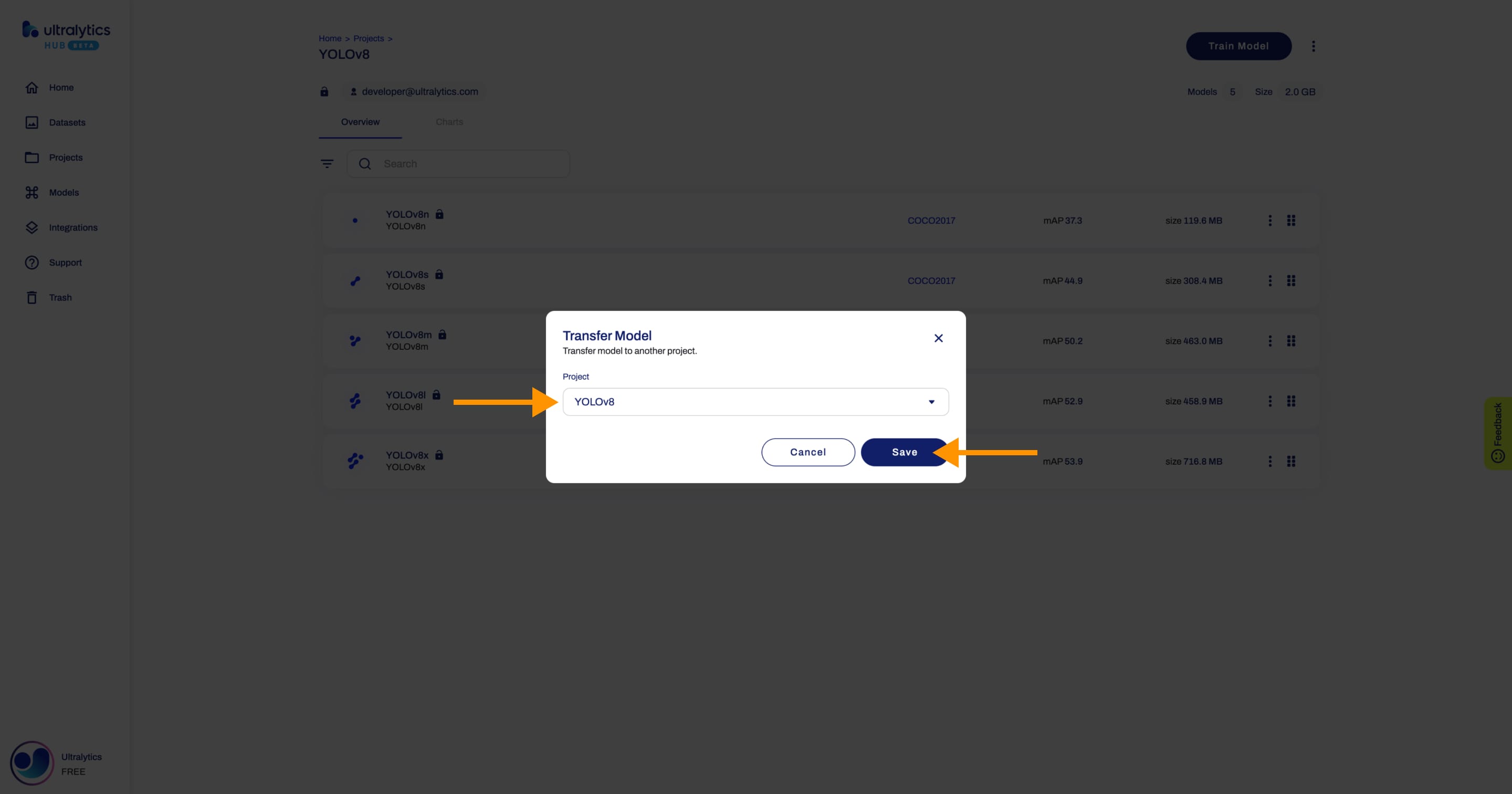
Select the project you want to transfer the model to and click **Save**.
-
\ No newline at end of file
+
diff --git a/docs/models/fast-sam.md b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..eefb58093
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
@@ -0,0 +1,169 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore the Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM), a real-time solution for the segment anything task that leverages a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for segmenting any object within an image, guided by user interaction prompts.
+keywords: FastSAM, Segment Anything Model, SAM, Convolutional Neural Network, CNN, image segmentation, real-time image processing
+---
+
+# Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)
+
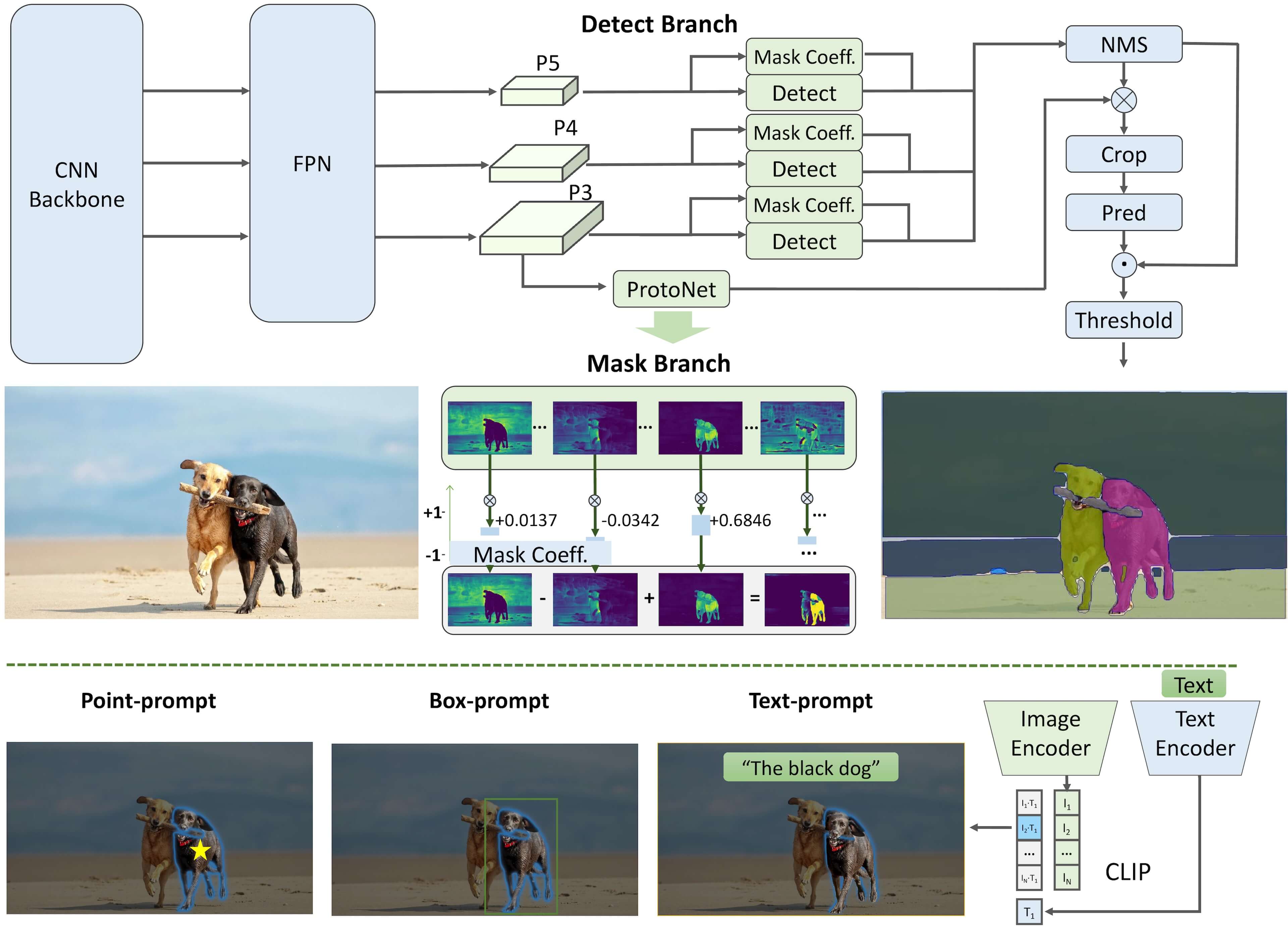
+The Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM) is a novel, real-time CNN-based solution for the Segment Anything task. This task is designed to segment any object within an image based on various possible user interaction prompts. FastSAM significantly reduces computational demands while maintaining competitive performance, making it a practical choice for a variety of vision tasks.
+
+
+
+## Overview
+
+FastSAM is designed to address the limitations of the [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](sam.md), a heavy Transformer model with substantial computational resource requirements. The FastSAM decouples the segment anything task into two sequential stages: all-instance segmentation and prompt-guided selection. The first stage uses [YOLOv8-seg](../tasks/segment.md) to produce the segmentation masks of all instances in the image. In the second stage, it outputs the region-of-interest corresponding to the prompt.
+
+## Key Features
+
+1. **Real-time Solution:** By leveraging the computational efficiency of CNNs, FastSAM provides a real-time solution for the segment anything task, making it valuable for industrial applications that require quick results.
+
+2. **Efficiency and Performance:** FastSAM offers a significant reduction in computational and resource demands without compromising on performance quality. It achieves comparable performance to SAM but with drastically reduced computational resources, enabling real-time application.
+
+3. **Prompt-guided Segmentation:** FastSAM can segment any object within an image guided by various possible user interaction prompts, providing flexibility and adaptability in different scenarios.
+
+4. **Based on YOLOv8-seg:** FastSAM is based on [YOLOv8-seg](../tasks/segment.md), an object detector equipped with an instance segmentation branch. This allows it to effectively produce the segmentation masks of all instances in an image.
+
+5. **Competitive Results on Benchmarks:** On the object proposal task on MS COCO, FastSAM achieves high scores at a significantly faster speed than [SAM](sam.md) on a single NVIDIA RTX 3090, demonstrating its efficiency and capability.
+
+6. **Practical Applications:** The proposed approach provides a new, practical solution for a large number of vision tasks at a really high speed, tens or hundreds of times faster than current methods.
+
+7. **Model Compression Feasibility:** FastSAM demonstrates the feasibility of a path that can significantly reduce the computational effort by introducing an artificial prior to the structure, thus opening new possibilities for large model architecture for general vision tasks.
+
+## Usage
+
+### Python API
+
+The FastSAM models are easy to integrate into your Python applications. Ultralytics provides a user-friendly Python API to streamline the process.
+
+#### Predict Usage
+
+To perform object detection on an image, use the `predict` method as shown below:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import FastSAM
+from ultralytics.yolo.fastsam import FastSAMPrompt
+
+# Define image path and inference device
+IMAGE_PATH = 'ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg'
+DEVICE = 'cpu'
+
+# Create a FastSAM model
+model = FastSAM('FastSAM-s.pt') # or FastSAM-x.pt
+
+# Run inference on an image
+everything_results = model(IMAGE_PATH,
+ device=DEVICE,
+ retina_masks=True,
+ imgsz=1024,
+ conf=0.4,
+ iou=0.9)
+
+prompt_process = FastSAMPrompt(IMAGE_PATH, everything_results, device=DEVICE)
+
+# Everything prompt
+ann = prompt_process.everything_prompt()
+
+# Bbox default shape [0,0,0,0] -> [x1,y1,x2,y2]
+ann = prompt_process.box_prompt(bbox=[200, 200, 300, 300])
+
+# Text prompt
+ann = prompt_process.text_prompt(text='a photo of a dog')
+
+# Point prompt
+# points default [[0,0]] [[x1,y1],[x2,y2]]
+# point_label default [0] [1,0] 0:background, 1:foreground
+ann = prompt_process.point_prompt(points=[[200, 200]], pointlabel=[1])
+prompt_process.plot(annotations=ann, output='./')
+```
+
+This snippet demonstrates the simplicity of loading a pre-trained model and running a prediction on an image.
+
+#### Val Usage
+
+Validation of the model on a dataset can be done as follows:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import FastSAM
+
+# Create a FastSAM model
+model = FastSAM('FastSAM-s.pt') # or FastSAM-x.pt
+
+# Validate the model
+results = model.val(data='coco8-seg.yaml')
+```
+
+Please note that FastSAM only supports detection and segmentation of a single class of object. This means it will recognize and segment all objects as the same class. Therefore, when preparing the dataset, you need to convert all object category IDs to 0.
+
+### FastSAM official Usage
+
+FastSAM is also available directly from the [https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM](https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM) repository. Here is a brief overview of the typical steps you might take to use FastSAM:
+
+#### Installation
+
+1. Clone the FastSAM repository:
+ ```shell
+ git clone https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM.git
+ ```
+
+2. Create and activate a Conda environment with Python 3.9:
+ ```shell
+ conda create -n FastSAM python=3.9
+ conda activate FastSAM
+ ```
+
+3. Navigate to the cloned repository and install the required packages:
+ ```shell
+ cd FastSAM
+ pip install -r requirements.txt
+ ```
+
+4. Install the CLIP model:
+ ```shell
+ pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git
+ ```
+
+#### Example Usage
+
+1. Download a [model checkpoint](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1m1sjY4ihXBU1fZXdQ-Xdj-mDltW-2Rqv/view?usp=sharing).
+
+2. Use FastSAM for inference. Example commands:
+
+ - Segment everything in an image:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg
+ ```
+
+ - Segment specific objects using text prompt:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --text_prompt "the yellow dog"
+ ```
+
+ - Segment objects within a bounding box (provide box coordinates in xywh format):
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --box_prompt "[570,200,230,400]"
+ ```
+
+ - Segment objects near specific points:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --point_prompt "[[520,360],[620,300]]" --point_label "[1,0]"
+ ```
+
+Additionally, you can try FastSAM through a [Colab demo](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1oX14f6IneGGw612WgVlAiy91UHwFAvr9?usp=sharing) or on the [HuggingFace web demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/An-619/FastSAM) for a visual experience.
+
+## Citations and Acknowledgements
+
+We would like to acknowledge the FastSAM authors for their significant contributions in the field of real-time instance segmentation:
+
+```bibtex
+@misc{zhao2023fast,
+ title={Fast Segment Anything},
+ author={Xu Zhao and Wenchao Ding and Yongqi An and Yinglong Du and Tao Yu and Min Li and Ming Tang and Jinqiao Wang},
+ year={2023},
+ eprint={2306.12156},
+ archivePrefix={arXiv},
+ primaryClass={cs.CV}
+}
+```
+
+The original FastSAM paper can be found on [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.12156). The authors have made their work publicly available, and the codebase can be accessed on [GitHub](https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM). We appreciate their efforts in advancing the field and making their work accessible to the broader community.
diff --git a/docs/models/index.md b/docs/models/index.md
index cce8af13f..611cad7fb 100644
--- a/docs/models/index.md
+++ b/docs/models/index.md
@@ -17,24 +17,29 @@ In this documentation, we provide information on four major models:
5. [YOLOv7](./yolov7.md): Updated YOLO models released in 2022 by the authors of YOLOv4.
6. [YOLOv8](./yolov8.md): The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
7. [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](./sam.md): Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
-8. [YOLO-NAS](./yolo-nas.md): YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
-9. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
+8. [Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)](./fast-sam.md): FastSAM by Image & Video Analysis Group, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
+9. [YOLO-NAS](./yolo-nas.md): YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
+10. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
-You can use these models directly in the Command Line Interface (CLI) or in a Python environment. Below are examples of how to use the models with CLI and Python:
+You can use many of these models directly in the Command Line Interface (CLI) or in a Python environment. Below are examples of how to use the models with CLI and Python:
## CLI Example
+Use the `model` argument to pass a model YAML such as `model=yolov8n.yaml` or a pretrained *.pt file such as `model=yolov8n.pt`
+
```bash
-yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8n.yaml data=coco128.yaml epochs=100
+yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8n.pt data=coco128.yaml epochs=100
```
## Python Example
+PyTorch pretrained models as well as model YAML files can also be passed to the `YOLO()`, `SAM()`, `NAS()` and `RTDETR()` classes to create a model instance in python:
+
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-model = YOLO("model.yaml") # build a YOLOv8n model from scratch
-# YOLO("model.pt") use pre-trained model if available
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
model.info() # display model information
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=100) # train the model
```
diff --git a/docs/models/sam.md b/docs/models/sam.md
index 8dd1e35c2..79bbd01aa 100644
--- a/docs/models/sam.md
+++ b/docs/models/sam.md
@@ -30,13 +30,30 @@ For an in-depth look at the Segment Anything Model and the SA-1B dataset, please
The Segment Anything Model can be employed for a multitude of downstream tasks that go beyond its training data. This includes edge detection, object proposal generation, instance segmentation, and preliminary text-to-mask prediction. With prompt engineering, SAM can swiftly adapt to new tasks and data distributions in a zero-shot manner, establishing it as a versatile and potent tool for all your image segmentation needs.
-```python
-from ultralytics import SAM
-
-model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
-model.info() # display model information
-model.predict('path/to/image.jpg') # predict
-```
+!!! example "SAM prediction example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise inference will run on CPU.
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import SAM
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
+
+ # Display model information (optional)
+ model.info()
+
+ # Run inference with the model
+ model('path/to/image.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Run inference with a SAM model
+ yolo predict model=sam_b.pt source=path/to/image.jpg
+ ```
## Available Models and Supported Tasks
@@ -53,6 +70,33 @@ model.predict('path/to/image.jpg') # predict
| Validation | :x: |
| Training | :x: |
+## SAM comparison vs YOLOv8
+
+Here we compare Meta's smallest SAM model, SAM-b, with Ultralytics smallest segmentation model, [YOLOv8n-seg](../tasks/segment.md):
+
+| Model | Size | Parameters | Speed (CPU) |
+|------------------------------------------------|----------------------------|------------------------|-------------------------|
+| Meta's SAM-b | 358 MB | 94.7 M | 51096 ms |
+| Ultralytics [YOLOv8n-seg](../tasks/segment.md) | **6.7 MB** (53.4x smaller) | **3.4 M** (27.9x less) | **59 ms** (866x faster) |
+
+This comparison shows the order-of-magnitude differences in the model sizes and speeds. Whereas SAM presents unique capabilities for automatic segmenting, it is not a direct competitor to YOLOv8 segment models, which are smaller, faster and more efficient since they are dedicated to more targeted use cases.
+
+To reproduce this test:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import SAM, YOLO
+
+# Profile SAM-b
+model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
+model.info()
+model('ultralytics/assets')
+
+# Profile YOLOv8n-seg
+model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
+model.info()
+model('ultralytics/assets')
+```
+
## Auto-Annotation: A Quick Path to Segmentation Datasets
Auto-annotation is a key feature of SAM, allowing users to generate a [segmentation dataset](https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/segment) using a pre-trained detection model. This feature enables rapid and accurate annotation of a large number of images, bypassing the need for time-consuming manual labeling.
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov5.md b/docs/models/yolov5.md
index 959c06af1..884fea6bc 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov5.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov5.md
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ If you use YOLOv5 or YOLOv5u in your research, please cite the Ultralytics YOLOv
```bibtex
@software{yolov5,
- title = {YOLOv5 by Ultralytics},
+ title = {Ultralytics YOLOv5},
author = {Glenn Jocher},
year = {2020},
version = {7.0},
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov8.md b/docs/models/yolov8.md
index 8c78d87e7..8907248cd 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov8.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov8.md
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ If you use the YOLOv8 model or any other software from this repository in your w
```bibtex
@software{yolov8_ultralytics,
author = {Glenn Jocher and Ayush Chaurasia and Jing Qiu},
- title = {YOLO by Ultralytics},
+ title = {Ultralytics YOLOv8},
version = {8.0.0},
year = {2023},
url = {https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics},
diff --git a/docs/modes/benchmark.md b/docs/modes/benchmark.md
index c1c159e6b..0c5b35fae 100644
--- a/docs/modes/benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/modes/benchmark.md
@@ -70,5 +70,6 @@ Benchmarks will attempt to run automatically on all possible export formats belo
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ |
| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ |
See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/export.md b/docs/modes/export.md
index 42e45272a..bff65d334 100644
--- a/docs/modes/export.md
+++ b/docs/modes/export.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
comments: true
description: 'Export mode: Create a deployment-ready YOLOv8 model by converting it to various formats. Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup.'
-keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, PaddlePaddle, TorchScript, ONNX format, OpenVINO format, TensorRT format, CoreML format, TF SavedModel format, PaddlePaddle format
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, PaddlePaddle, TorchScript, ONNX format, OpenVINO format, TensorRT format, CoreML format, TF SavedModel format, PaddlePaddle format, Tencent ncnn format
---
+
+
+When the training starts, you can click **Done** and monitor the training progress on the Model page.
+
+
+
+
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ In case the training stops and a checkpoint was saved, you can resume training your model from the Model page.
+
+ 
+
+## Preview Model
+
+Ultralytics HUB offers a variety of ways to preview your trained model.
+
+You can preview your model if you click on the **Preview** tab and upload an image in the **Test** card.
+
+
+
+You can also use our Ultralytics Cloud API to effortlessly [run inference](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/inference_api) with your custom model.
+
+
+
+Furthermore, you can preview your model in real-time directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or [Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by [downloading](https://ultralytics.com/app_install) our [Ultralytics HUB Mobile Application](./app/index.md).
+
+
+
+## Deploy Model
+
+You can export your model to 13 different formats, including ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, TensorFlow, Paddle and many others.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can customize the export options of each format if you open the export actions dropdown and click on the **Advanced** option.
+
+ 
+
+## Share Model
+
+!!! info "Info"
+
+ Ultralytics HUB's sharing functionality provides a convenient way to share models with others. This feature is designed to accommodate both existing Ultralytics HUB users and those who have yet to create an account.
+
+??? note "Note"
+
+ You have control over the general access of your models.
+
+ You can choose to set the general access to "Private", in which case, only you will have access to it. Alternatively, you can set the general access to "Unlisted" which grants viewing access to anyone who has the direct link to the model, regardless of whether they have an Ultralytics HUB account or not.
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to share, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Share** option. This action will trigger the **Share Model** dialog.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also share a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 
+
+Set the general access to "Unlisted" and click **Save**.
+
+
+
+Now, anyone who has the direct link to your model can view it.
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can easily click on the models's link shown in the **Share Model** dialog to copy it.
+
+ 
+
+## Edit Model
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to edit, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Edit** option. This action will trigger the **Update Model** dialog.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also edit a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 
+
+Apply the desired modifications to your model and then confirm the changes by clicking **Save**.
+
+
+
+## Delete Model
+
+Navigate to the Model page of the model you want to delete, open the model actions dropdown and click on the **Delete** option. This action will delete the model.
+
+
+
+??? tip "Tip"
+
+ You can also delete a model directly from the [Models](https://hub.ultralytics.com/models) page or from the Project page of the project where your model is located.
+
+ 
+
+??? note "Note"
-## Deploy to Real World
+ If you change your mind, you can restore the model from the [Trash](https://hub.ultralytics.com/trash) page.
-Export your model to 13 different formats, including TensorFlow, ONNX, OpenVINO, CoreML, Paddle and many others. Run
-models directly on your [iOS](https://apps.apple.com/xk/app/ultralytics/id1583935240) or
-[Android](https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ultralytics.ultralytics_app) mobile device by downloading
-the [Ultralytics App](https://ultralytics.com/app_install)!
\ No newline at end of file
+ 
diff --git a/docs/hub/projects.md b/docs/hub/projects.md
index 6a006b365..d8e0f8649 100644
--- a/docs/hub/projects.md
+++ b/docs/hub/projects.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Click on the **Create Project** button on the top right of the page. This action

-Type the name of your project in the *Project name* field or keep the default name and finalize the project creation with a single click.
+Type the name of your project in the _Project name_ field or keep the default name and finalize the project creation with a single click.
You have the additional option to enrich your project with a description and a unique image, enhancing its recognizability on the Projects page.
@@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ After your project is created, you will be able to access it from the Projects p

-Next, [create a model](./models.md) inside your project.
+Next, [train a model](https://docs.ultralytics.com/hub/models/#train-model) inside your project.
-
+
## Share Project
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ Navigate to the Project page of the project you want to delete, open the project
## Compare Models
-Navigate to the Project page of the project where the models you want to compare are located. To use the model comparison feature, click on the **Charts** tab.
+Navigate to the Project page of the project where the models you want to compare are located. To use the model comparison feature, click on the **Charts** tab.

@@ -166,4 +166,4 @@ Navigate to the Project page of the project where the model you want to mode is
Select the project you want to transfer the model to and click **Save**.
-
\ No newline at end of file
+
diff --git a/docs/models/fast-sam.md b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..eefb58093
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/models/fast-sam.md
@@ -0,0 +1,169 @@
+---
+comments: true
+description: Explore the Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM), a real-time solution for the segment anything task that leverages a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for segmenting any object within an image, guided by user interaction prompts.
+keywords: FastSAM, Segment Anything Model, SAM, Convolutional Neural Network, CNN, image segmentation, real-time image processing
+---
+
+# Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)
+
+The Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM) is a novel, real-time CNN-based solution for the Segment Anything task. This task is designed to segment any object within an image based on various possible user interaction prompts. FastSAM significantly reduces computational demands while maintaining competitive performance, making it a practical choice for a variety of vision tasks.
+
+
+
+## Overview
+
+FastSAM is designed to address the limitations of the [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](sam.md), a heavy Transformer model with substantial computational resource requirements. The FastSAM decouples the segment anything task into two sequential stages: all-instance segmentation and prompt-guided selection. The first stage uses [YOLOv8-seg](../tasks/segment.md) to produce the segmentation masks of all instances in the image. In the second stage, it outputs the region-of-interest corresponding to the prompt.
+
+## Key Features
+
+1. **Real-time Solution:** By leveraging the computational efficiency of CNNs, FastSAM provides a real-time solution for the segment anything task, making it valuable for industrial applications that require quick results.
+
+2. **Efficiency and Performance:** FastSAM offers a significant reduction in computational and resource demands without compromising on performance quality. It achieves comparable performance to SAM but with drastically reduced computational resources, enabling real-time application.
+
+3. **Prompt-guided Segmentation:** FastSAM can segment any object within an image guided by various possible user interaction prompts, providing flexibility and adaptability in different scenarios.
+
+4. **Based on YOLOv8-seg:** FastSAM is based on [YOLOv8-seg](../tasks/segment.md), an object detector equipped with an instance segmentation branch. This allows it to effectively produce the segmentation masks of all instances in an image.
+
+5. **Competitive Results on Benchmarks:** On the object proposal task on MS COCO, FastSAM achieves high scores at a significantly faster speed than [SAM](sam.md) on a single NVIDIA RTX 3090, demonstrating its efficiency and capability.
+
+6. **Practical Applications:** The proposed approach provides a new, practical solution for a large number of vision tasks at a really high speed, tens or hundreds of times faster than current methods.
+
+7. **Model Compression Feasibility:** FastSAM demonstrates the feasibility of a path that can significantly reduce the computational effort by introducing an artificial prior to the structure, thus opening new possibilities for large model architecture for general vision tasks.
+
+## Usage
+
+### Python API
+
+The FastSAM models are easy to integrate into your Python applications. Ultralytics provides a user-friendly Python API to streamline the process.
+
+#### Predict Usage
+
+To perform object detection on an image, use the `predict` method as shown below:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import FastSAM
+from ultralytics.yolo.fastsam import FastSAMPrompt
+
+# Define image path and inference device
+IMAGE_PATH = 'ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg'
+DEVICE = 'cpu'
+
+# Create a FastSAM model
+model = FastSAM('FastSAM-s.pt') # or FastSAM-x.pt
+
+# Run inference on an image
+everything_results = model(IMAGE_PATH,
+ device=DEVICE,
+ retina_masks=True,
+ imgsz=1024,
+ conf=0.4,
+ iou=0.9)
+
+prompt_process = FastSAMPrompt(IMAGE_PATH, everything_results, device=DEVICE)
+
+# Everything prompt
+ann = prompt_process.everything_prompt()
+
+# Bbox default shape [0,0,0,0] -> [x1,y1,x2,y2]
+ann = prompt_process.box_prompt(bbox=[200, 200, 300, 300])
+
+# Text prompt
+ann = prompt_process.text_prompt(text='a photo of a dog')
+
+# Point prompt
+# points default [[0,0]] [[x1,y1],[x2,y2]]
+# point_label default [0] [1,0] 0:background, 1:foreground
+ann = prompt_process.point_prompt(points=[[200, 200]], pointlabel=[1])
+prompt_process.plot(annotations=ann, output='./')
+```
+
+This snippet demonstrates the simplicity of loading a pre-trained model and running a prediction on an image.
+
+#### Val Usage
+
+Validation of the model on a dataset can be done as follows:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import FastSAM
+
+# Create a FastSAM model
+model = FastSAM('FastSAM-s.pt') # or FastSAM-x.pt
+
+# Validate the model
+results = model.val(data='coco8-seg.yaml')
+```
+
+Please note that FastSAM only supports detection and segmentation of a single class of object. This means it will recognize and segment all objects as the same class. Therefore, when preparing the dataset, you need to convert all object category IDs to 0.
+
+### FastSAM official Usage
+
+FastSAM is also available directly from the [https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM](https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM) repository. Here is a brief overview of the typical steps you might take to use FastSAM:
+
+#### Installation
+
+1. Clone the FastSAM repository:
+ ```shell
+ git clone https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM.git
+ ```
+
+2. Create and activate a Conda environment with Python 3.9:
+ ```shell
+ conda create -n FastSAM python=3.9
+ conda activate FastSAM
+ ```
+
+3. Navigate to the cloned repository and install the required packages:
+ ```shell
+ cd FastSAM
+ pip install -r requirements.txt
+ ```
+
+4. Install the CLIP model:
+ ```shell
+ pip install git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git
+ ```
+
+#### Example Usage
+
+1. Download a [model checkpoint](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1m1sjY4ihXBU1fZXdQ-Xdj-mDltW-2Rqv/view?usp=sharing).
+
+2. Use FastSAM for inference. Example commands:
+
+ - Segment everything in an image:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg
+ ```
+
+ - Segment specific objects using text prompt:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --text_prompt "the yellow dog"
+ ```
+
+ - Segment objects within a bounding box (provide box coordinates in xywh format):
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --box_prompt "[570,200,230,400]"
+ ```
+
+ - Segment objects near specific points:
+ ```shell
+ python Inference.py --model_path ./weights/FastSAM.pt --img_path ./images/dogs.jpg --point_prompt "[[520,360],[620,300]]" --point_label "[1,0]"
+ ```
+
+Additionally, you can try FastSAM through a [Colab demo](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1oX14f6IneGGw612WgVlAiy91UHwFAvr9?usp=sharing) or on the [HuggingFace web demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/An-619/FastSAM) for a visual experience.
+
+## Citations and Acknowledgements
+
+We would like to acknowledge the FastSAM authors for their significant contributions in the field of real-time instance segmentation:
+
+```bibtex
+@misc{zhao2023fast,
+ title={Fast Segment Anything},
+ author={Xu Zhao and Wenchao Ding and Yongqi An and Yinglong Du and Tao Yu and Min Li and Ming Tang and Jinqiao Wang},
+ year={2023},
+ eprint={2306.12156},
+ archivePrefix={arXiv},
+ primaryClass={cs.CV}
+}
+```
+
+The original FastSAM paper can be found on [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.12156). The authors have made their work publicly available, and the codebase can be accessed on [GitHub](https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FastSAM). We appreciate their efforts in advancing the field and making their work accessible to the broader community.
diff --git a/docs/models/index.md b/docs/models/index.md
index cce8af13f..611cad7fb 100644
--- a/docs/models/index.md
+++ b/docs/models/index.md
@@ -17,24 +17,29 @@ In this documentation, we provide information on four major models:
5. [YOLOv7](./yolov7.md): Updated YOLO models released in 2022 by the authors of YOLOv4.
6. [YOLOv8](./yolov8.md): The latest version of the YOLO family, featuring enhanced capabilities such as instance segmentation, pose/keypoints estimation, and classification.
7. [Segment Anything Model (SAM)](./sam.md): Meta's Segment Anything Model (SAM).
-8. [YOLO-NAS](./yolo-nas.md): YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
-9. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
+8. [Fast Segment Anything Model (FastSAM)](./fast-sam.md): FastSAM by Image & Video Analysis Group, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
+9. [YOLO-NAS](./yolo-nas.md): YOLO Neural Architecture Search (NAS) Models.
+10. [Realtime Detection Transformers (RT-DETR)](./rtdetr.md): Baidu's PaddlePaddle Realtime Detection Transformer (RT-DETR) models.
-You can use these models directly in the Command Line Interface (CLI) or in a Python environment. Below are examples of how to use the models with CLI and Python:
+You can use many of these models directly in the Command Line Interface (CLI) or in a Python environment. Below are examples of how to use the models with CLI and Python:
## CLI Example
+Use the `model` argument to pass a model YAML such as `model=yolov8n.yaml` or a pretrained *.pt file such as `model=yolov8n.pt`
+
```bash
-yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8n.yaml data=coco128.yaml epochs=100
+yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8n.pt data=coco128.yaml epochs=100
```
## Python Example
+PyTorch pretrained models as well as model YAML files can also be passed to the `YOLO()`, `SAM()`, `NAS()` and `RTDETR()` classes to create a model instance in python:
+
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
-model = YOLO("model.yaml") # build a YOLOv8n model from scratch
-# YOLO("model.pt") use pre-trained model if available
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
model.info() # display model information
model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=100) # train the model
```
diff --git a/docs/models/sam.md b/docs/models/sam.md
index 8dd1e35c2..79bbd01aa 100644
--- a/docs/models/sam.md
+++ b/docs/models/sam.md
@@ -30,13 +30,30 @@ For an in-depth look at the Segment Anything Model and the SA-1B dataset, please
The Segment Anything Model can be employed for a multitude of downstream tasks that go beyond its training data. This includes edge detection, object proposal generation, instance segmentation, and preliminary text-to-mask prediction. With prompt engineering, SAM can swiftly adapt to new tasks and data distributions in a zero-shot manner, establishing it as a versatile and potent tool for all your image segmentation needs.
-```python
-from ultralytics import SAM
-
-model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
-model.info() # display model information
-model.predict('path/to/image.jpg') # predict
-```
+!!! example "SAM prediction example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise inference will run on CPU.
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import SAM
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
+
+ # Display model information (optional)
+ model.info()
+
+ # Run inference with the model
+ model('path/to/image.jpg')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Run inference with a SAM model
+ yolo predict model=sam_b.pt source=path/to/image.jpg
+ ```
## Available Models and Supported Tasks
@@ -53,6 +70,33 @@ model.predict('path/to/image.jpg') # predict
| Validation | :x: |
| Training | :x: |
+## SAM comparison vs YOLOv8
+
+Here we compare Meta's smallest SAM model, SAM-b, with Ultralytics smallest segmentation model, [YOLOv8n-seg](../tasks/segment.md):
+
+| Model | Size | Parameters | Speed (CPU) |
+|------------------------------------------------|----------------------------|------------------------|-------------------------|
+| Meta's SAM-b | 358 MB | 94.7 M | 51096 ms |
+| Ultralytics [YOLOv8n-seg](../tasks/segment.md) | **6.7 MB** (53.4x smaller) | **3.4 M** (27.9x less) | **59 ms** (866x faster) |
+
+This comparison shows the order-of-magnitude differences in the model sizes and speeds. Whereas SAM presents unique capabilities for automatic segmenting, it is not a direct competitor to YOLOv8 segment models, which are smaller, faster and more efficient since they are dedicated to more targeted use cases.
+
+To reproduce this test:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import SAM, YOLO
+
+# Profile SAM-b
+model = SAM('sam_b.pt')
+model.info()
+model('ultralytics/assets')
+
+# Profile YOLOv8n-seg
+model = YOLO('yolov8n-seg.pt')
+model.info()
+model('ultralytics/assets')
+```
+
## Auto-Annotation: A Quick Path to Segmentation Datasets
Auto-annotation is a key feature of SAM, allowing users to generate a [segmentation dataset](https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/segment) using a pre-trained detection model. This feature enables rapid and accurate annotation of a large number of images, bypassing the need for time-consuming manual labeling.
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov5.md b/docs/models/yolov5.md
index 959c06af1..884fea6bc 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov5.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov5.md
@@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ If you use YOLOv5 or YOLOv5u in your research, please cite the Ultralytics YOLOv
```bibtex
@software{yolov5,
- title = {YOLOv5 by Ultralytics},
+ title = {Ultralytics YOLOv5},
author = {Glenn Jocher},
year = {2020},
version = {7.0},
diff --git a/docs/models/yolov8.md b/docs/models/yolov8.md
index 8c78d87e7..8907248cd 100644
--- a/docs/models/yolov8.md
+++ b/docs/models/yolov8.md
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ If you use the YOLOv8 model or any other software from this repository in your w
```bibtex
@software{yolov8_ultralytics,
author = {Glenn Jocher and Ayush Chaurasia and Jing Qiu},
- title = {YOLO by Ultralytics},
+ title = {Ultralytics YOLOv8},
version = {8.0.0},
year = {2023},
url = {https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics},
diff --git a/docs/modes/benchmark.md b/docs/modes/benchmark.md
index c1c159e6b..0c5b35fae 100644
--- a/docs/modes/benchmark.md
+++ b/docs/modes/benchmark.md
@@ -70,5 +70,6 @@ Benchmarks will attempt to run automatically on all possible export formats belo
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ |
| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ |
See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/export.md b/docs/modes/export.md
index 42e45272a..bff65d334 100644
--- a/docs/modes/export.md
+++ b/docs/modes/export.md
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
---
comments: true
description: 'Export mode: Create a deployment-ready YOLOv8 model by converting it to various formats. Export to ONNX or OpenVINO for up to 3x CPU speedup.'
-keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, PaddlePaddle, TorchScript, ONNX format, OpenVINO format, TensorRT format, CoreML format, TF SavedModel format, PaddlePaddle format
+keywords: ultralytics docs, YOLOv8, export YOLOv8, YOLOv8 model deployment, exporting YOLOv8, ONNX, OpenVINO, TensorRT, CoreML, TF SavedModel, PaddlePaddle, TorchScript, ONNX format, OpenVINO format, TensorRT format, CoreML format, TF SavedModel format, PaddlePaddle format, Tencent ncnn format
---
 @@ -84,4 +84,5 @@ i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/predict.md b/docs/modes/predict.md
index 581d4221d..8708933e6 100644
--- a/docs/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/modes/predict.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
comments: true
-description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
+description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
keywords: YOLOv8, predict mode, generator, streaming mode, input sources, video formats, arguments customization
---
@@ -12,60 +12,279 @@ passing `stream=True` in the predictor's call method.
!!! example "Predict"
- === "Return a list with `Stream=False`"
+ === "Return a list with `stream=False`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs) # list of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg']) # return a list of Results objects
+ # Process results list
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
- === "Return a generator with `Stream=True`"
+ === "Return a generator with `stream=True`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg'], stream=True) # return a generator of Results objects
+ # Process results generator
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
-!!! tip "Tip"
-
- Streaming mode with `stream=True` should be used for long videos or large predict sources, otherwise results will accumuate in memory and will eventually cause out-of-memory errors.
+## Inference Sources
-## Sources
+YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in the table below. The sources include static images, video streams, and various data formats. The table also indicates whether each source can be used in streaming mode with the argument `stream=True` ✅. Streaming mode is beneficial for processing videos or live streams as it creates a generator of results instead of loading all frames into memory.
-YOLOv8 can accept various input sources, as shown in the table below. This includes images, URLs, PIL images, OpenCV,
-numpy arrays, torch tensors, CSV files, videos, directories, globs, YouTube videos, and streams. The table indicates
-whether each source can be used in streaming mode with `stream=True` ✅ and an example argument for each source.
+!!! tip "Tip"
-| source | model(arg) | type | notes |
-|-------------|--------------------------------------------|----------------|------------------|
-| image | `'im.jpg'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | |
-| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | |
-| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC, RGB |
-| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC, BGR |
-| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC |
-| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW, RGB |
-| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str`, `Path` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
-| video ✅ | `'vid.mp4'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Use `*` operator |
-| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | |
-| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
+ Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
+
+| Source | Argument | Type | Notes |
+|-------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. |
+| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. |
+| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. |
+| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. |
+| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` of `float32 (0.0-1.0)` | BCHW format with RGB channels. |
+| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. |
+| video ✅ | `'video.mp4'` | `str` or `Path` | Video file in formats like MP4, AVI, etc. |
+| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str` or `Path` | Path to a directory containing images or videos. |
+| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Glob pattern to match multiple files. Use the `*` character as a wildcard. |
+| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | URL to a YouTube video. |
+| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | URL for streaming protocols such as RTSP, RTMP, or an IP address. |
+
+Below are code examples for using each source type:
+
+!!! example "Prediction sources"
+
+ === "image"
+ Run inference on an image file.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to the image file
+ source = 'path/to/image.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "screenshot"
+ Run inference on the current screen content as a screenshot.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define current screenshot as source
+ source = 'screen'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "URL"
+ Run inference on an image or video hosted remotely via URL.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define remote image or video URL
+ source = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "PIL"
+ Run inference on an image opened with Python Imaging Library (PIL).
+ ```python
+ from PIL import Image
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Open an image using PIL
+ source = Image.open('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "OpenCV"
+ Run inference on an image read with OpenCV.
+ ```python
+ import cv2
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Read an image using OpenCV
+ source = cv2.imread('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "numpy"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a numpy array.
+ ```python
+ import numpy as np
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random numpy array of HWC shape (640, 640, 3) with values in range [0, 255] and type uint8
+ source = np.random.randint(low=0, high=255, size=(640, 640, 3), dtype='uint8')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "torch"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a PyTorch tensor.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
+ source = torch.rand(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "CSV"
+ Run inference on a collection of images, URLs, videos and directories listed in a CSV file.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a path to a CSV file with images, URLs, videos and directories
+ source = 'path/to/file.csv'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "video"
+ Run inference on a video file. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to video file
+ source = 'path/to/video.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "directory"
+ Run inference on all images and videos in a directory. To also capture images and videos in subdirectories use a glob pattern, i.e. `path/to/dir/**/*`.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to directory containing images and videos for inference
+ source = 'path/to/dir'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "glob"
+ Run inference on all images and videos that match a glob expression with `*` characters.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a glob search for all JPG files in a directory
+ source = 'path/to/dir/*.jpg'
+
+ # OR define a recursive glob search for all JPG files including subdirectories
+ source = 'path/to/dir/**/*.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "YouTube"
+ Run inference on a YouTube video. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage for long videos.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as YouTube video URL
+ source = 'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "Stream"
+ Run inference on remote streaming sources using RTSP, RTMP, and IP address protocols.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as RTSP, RTMP or IP streaming address
+ source = 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
-## Arguments
+## Inference Arguments
`model.predict` accepts multiple arguments that control the prediction operation. These arguments can be passed directly to `model.predict`:
!!! example
- ```
+ ```python
model.predict(source, save=True, imgsz=320, conf=0.5)
```
@@ -97,12 +316,12 @@ All supported arguments:
## Image and Video Formats
-YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified
-in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the
-tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
+YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Image Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
+
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .bmp | `yolo predict source=image.bmp` | [Microsoft BMP File Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format) |
@@ -118,6 +337,8 @@ tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Video Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics video formats.
+
| Video Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .asf | `yolo predict source=video.asf` | [Advanced Systems Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Systems_Format) |
diff --git a/docs/modes/train.md b/docs/modes/train.md
index 882c0d1f1..16c32ef84 100644
--- a/docs/modes/train.md
+++ b/docs/modes/train.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, train mode, train a custom YOLOv8 model, hyperparameters, trai
@@ -84,4 +84,5 @@ i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/predict.md b/docs/modes/predict.md
index 581d4221d..8708933e6 100644
--- a/docs/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/modes/predict.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
comments: true
-description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
+description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
keywords: YOLOv8, predict mode, generator, streaming mode, input sources, video formats, arguments customization
---
@@ -12,60 +12,279 @@ passing `stream=True` in the predictor's call method.
!!! example "Predict"
- === "Return a list with `Stream=False`"
+ === "Return a list with `stream=False`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs) # list of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg']) # return a list of Results objects
+ # Process results list
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
- === "Return a generator with `Stream=True`"
+ === "Return a generator with `stream=True`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg'], stream=True) # return a generator of Results objects
+ # Process results generator
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
-!!! tip "Tip"
-
- Streaming mode with `stream=True` should be used for long videos or large predict sources, otherwise results will accumuate in memory and will eventually cause out-of-memory errors.
+## Inference Sources
-## Sources
+YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in the table below. The sources include static images, video streams, and various data formats. The table also indicates whether each source can be used in streaming mode with the argument `stream=True` ✅. Streaming mode is beneficial for processing videos or live streams as it creates a generator of results instead of loading all frames into memory.
-YOLOv8 can accept various input sources, as shown in the table below. This includes images, URLs, PIL images, OpenCV,
-numpy arrays, torch tensors, CSV files, videos, directories, globs, YouTube videos, and streams. The table indicates
-whether each source can be used in streaming mode with `stream=True` ✅ and an example argument for each source.
+!!! tip "Tip"
-| source | model(arg) | type | notes |
-|-------------|--------------------------------------------|----------------|------------------|
-| image | `'im.jpg'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | |
-| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | |
-| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC, RGB |
-| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC, BGR |
-| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC |
-| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW, RGB |
-| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str`, `Path` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
-| video ✅ | `'vid.mp4'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Use `*` operator |
-| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | |
-| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
+ Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
+
+| Source | Argument | Type | Notes |
+|-------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. |
+| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. |
+| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. |
+| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. |
+| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` of `float32 (0.0-1.0)` | BCHW format with RGB channels. |
+| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. |
+| video ✅ | `'video.mp4'` | `str` or `Path` | Video file in formats like MP4, AVI, etc. |
+| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str` or `Path` | Path to a directory containing images or videos. |
+| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Glob pattern to match multiple files. Use the `*` character as a wildcard. |
+| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | URL to a YouTube video. |
+| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | URL for streaming protocols such as RTSP, RTMP, or an IP address. |
+
+Below are code examples for using each source type:
+
+!!! example "Prediction sources"
+
+ === "image"
+ Run inference on an image file.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to the image file
+ source = 'path/to/image.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "screenshot"
+ Run inference on the current screen content as a screenshot.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define current screenshot as source
+ source = 'screen'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "URL"
+ Run inference on an image or video hosted remotely via URL.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define remote image or video URL
+ source = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "PIL"
+ Run inference on an image opened with Python Imaging Library (PIL).
+ ```python
+ from PIL import Image
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Open an image using PIL
+ source = Image.open('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "OpenCV"
+ Run inference on an image read with OpenCV.
+ ```python
+ import cv2
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Read an image using OpenCV
+ source = cv2.imread('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "numpy"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a numpy array.
+ ```python
+ import numpy as np
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random numpy array of HWC shape (640, 640, 3) with values in range [0, 255] and type uint8
+ source = np.random.randint(low=0, high=255, size=(640, 640, 3), dtype='uint8')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "torch"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a PyTorch tensor.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
+ source = torch.rand(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "CSV"
+ Run inference on a collection of images, URLs, videos and directories listed in a CSV file.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a path to a CSV file with images, URLs, videos and directories
+ source = 'path/to/file.csv'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "video"
+ Run inference on a video file. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to video file
+ source = 'path/to/video.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "directory"
+ Run inference on all images and videos in a directory. To also capture images and videos in subdirectories use a glob pattern, i.e. `path/to/dir/**/*`.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to directory containing images and videos for inference
+ source = 'path/to/dir'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "glob"
+ Run inference on all images and videos that match a glob expression with `*` characters.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a glob search for all JPG files in a directory
+ source = 'path/to/dir/*.jpg'
+
+ # OR define a recursive glob search for all JPG files including subdirectories
+ source = 'path/to/dir/**/*.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "YouTube"
+ Run inference on a YouTube video. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage for long videos.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as YouTube video URL
+ source = 'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "Stream"
+ Run inference on remote streaming sources using RTSP, RTMP, and IP address protocols.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as RTSP, RTMP or IP streaming address
+ source = 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
-## Arguments
+## Inference Arguments
`model.predict` accepts multiple arguments that control the prediction operation. These arguments can be passed directly to `model.predict`:
!!! example
- ```
+ ```python
model.predict(source, save=True, imgsz=320, conf=0.5)
```
@@ -97,12 +316,12 @@ All supported arguments:
## Image and Video Formats
-YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified
-in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the
-tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
+YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Image Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
+
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .bmp | `yolo predict source=image.bmp` | [Microsoft BMP File Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format) |
@@ -118,6 +337,8 @@ tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Video Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics video formats.
+
| Video Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .asf | `yolo predict source=video.asf` | [Advanced Systems Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Systems_Format) |
diff --git a/docs/modes/train.md b/docs/modes/train.md
index 882c0d1f1..16c32ef84 100644
--- a/docs/modes/train.md
+++ b/docs/modes/train.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, train mode, train a custom YOLOv8 model, hyperparameters, trai
 -**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the
-specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can
-accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
+**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,10 +14,11 @@ accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
## Usage Examples
-Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of
-training arguments.
+Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of training arguments.
-!!! example ""
+!!! example "Single-GPU and CPU Training Example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise training will start on CPU.
=== "Python"
@@ -47,14 +46,95 @@ training arguments.
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml pretrained=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
```
+### Multi-GPU Training
+
+The training device can be specified using the `device` argument. If no argument is passed GPU `device=0` will be used if available, otherwise `device=cpu` will be used.
+
+!!! example "Multi-GPU Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device=[0, 1])
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=0,1
+ ```
+
+### Apple M1 and M2 MPS Training
+
+With the support for Apple M1 and M2 chips integrated in the Ultralytics YOLO models, it's now possible to train your models on devices utilizing the powerful Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) framework. The MPS offers a high-performance way of executing computation and image processing tasks on Apple's custom silicon.
+
+To enable training on Apple M1 and M2 chips, you should specify 'mps' as your device when initiating the training process. Below is an example of how you could do this in Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "MPS Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device='mps')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=mps
+ ```
+
+While leveraging the computational power of the M1/M2 chips, this enables more efficient processing of the training tasks. For more detailed guidance and advanced configuration options, please refer to the [PyTorch MPS documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html).
+
+### Resuming Interrupted Trainings
+
+Resuming training from a previously saved state is a crucial feature when working with deep learning models. This can come in handy in various scenarios, like when the training process has been unexpectedly interrupted, or when you wish to continue training a model with new data or for more epochs.
+
+When training is resumed, Ultralytics YOLO loads the weights from the last saved model and also restores the optimizer state, learning rate scheduler, and the epoch number. This allows you to continue the training process seamlessly from where it was left off.
+
+You can easily resume training in Ultralytics YOLO by setting the `resume` argument to `True` when calling the `train` method, and specifying the path to the `.pt` file containing the partially trained model weights.
+
+Below is an example of how to resume an interrupted training using Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "Resume Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('path/to/last.pt') # load a partially trained model
+
+ # Resume training
+ model.train(resume=True)
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Resume an interrupted training
+ yolo train resume model=path/to/last.pt
+ ```
+
+By setting `resume=True`, the `train` function will continue training from where it left off, using the state stored in the 'path/to/last.pt' file. If the `resume` argument is omitted or set to `False`, the `train` function will start a new training session.
+
+Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at fixed interval using the `save_period` argument, so you must complete at least 1 epoch to resume a training run.
+
## Arguments
-Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a
-dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings
-include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process
-include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given
-task.
+Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given task.
| Key | Value | Description |
|-------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/modes/val.md b/docs/modes/val.md
index 79fdf6f8e..4ffff738d 100644
--- a/docs/modes/val.md
+++ b/docs/modes/val.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, YOLOv8, Val, Validation, Hyperparameters, Performan
-**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the
-specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can
-accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
+**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,10 +14,11 @@ accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
## Usage Examples
-Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of
-training arguments.
+Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of training arguments.
-!!! example ""
+!!! example "Single-GPU and CPU Training Example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise training will start on CPU.
=== "Python"
@@ -47,14 +46,95 @@ training arguments.
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml pretrained=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
```
+### Multi-GPU Training
+
+The training device can be specified using the `device` argument. If no argument is passed GPU `device=0` will be used if available, otherwise `device=cpu` will be used.
+
+!!! example "Multi-GPU Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device=[0, 1])
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=0,1
+ ```
+
+### Apple M1 and M2 MPS Training
+
+With the support for Apple M1 and M2 chips integrated in the Ultralytics YOLO models, it's now possible to train your models on devices utilizing the powerful Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) framework. The MPS offers a high-performance way of executing computation and image processing tasks on Apple's custom silicon.
+
+To enable training on Apple M1 and M2 chips, you should specify 'mps' as your device when initiating the training process. Below is an example of how you could do this in Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "MPS Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device='mps')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=mps
+ ```
+
+While leveraging the computational power of the M1/M2 chips, this enables more efficient processing of the training tasks. For more detailed guidance and advanced configuration options, please refer to the [PyTorch MPS documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html).
+
+### Resuming Interrupted Trainings
+
+Resuming training from a previously saved state is a crucial feature when working with deep learning models. This can come in handy in various scenarios, like when the training process has been unexpectedly interrupted, or when you wish to continue training a model with new data or for more epochs.
+
+When training is resumed, Ultralytics YOLO loads the weights from the last saved model and also restores the optimizer state, learning rate scheduler, and the epoch number. This allows you to continue the training process seamlessly from where it was left off.
+
+You can easily resume training in Ultralytics YOLO by setting the `resume` argument to `True` when calling the `train` method, and specifying the path to the `.pt` file containing the partially trained model weights.
+
+Below is an example of how to resume an interrupted training using Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "Resume Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('path/to/last.pt') # load a partially trained model
+
+ # Resume training
+ model.train(resume=True)
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Resume an interrupted training
+ yolo train resume model=path/to/last.pt
+ ```
+
+By setting `resume=True`, the `train` function will continue training from where it left off, using the state stored in the 'path/to/last.pt' file. If the `resume` argument is omitted or set to `False`, the `train` function will start a new training session.
+
+Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at fixed interval using the `save_period` argument, so you must complete at least 1 epoch to resume a training run.
+
## Arguments
-Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a
-dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings
-include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process
-include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given
-task.
+Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given task.
| Key | Value | Description |
|-------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/modes/val.md b/docs/modes/val.md
index 79fdf6f8e..4ffff738d 100644
--- a/docs/modes/val.md
+++ b/docs/modes/val.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, YOLOv8, Val, Validation, Hyperparameters, Performan
 -**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a
-validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters
-of the model to improve its performance.
+**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters of the model to improve its performance.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,8 +14,7 @@ of the model to improve its performance.
## Usage Examples
-Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's
-training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
+Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
!!! example ""
@@ -46,13 +43,7 @@ training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below f
## Arguments
-Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to
-evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and
-accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed
-during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation
-process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the
-validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
+Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| Key | Value | Description |
|---------------|---------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|
@@ -70,23 +61,4 @@ validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| `plots` | `False` | show plots during training |
| `rect` | `False` | rectangular val with each batch collated for minimum padding |
| `split` | `val` | dataset split to use for validation, i.e. 'val', 'test' or 'train' |
-
-## Export Formats
-
-Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument,
-i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
-
-| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
-| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
-| [OpenVINO](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
-| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
-| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
-| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
-| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+|
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/quickstart.md b/docs/quickstart.md
index b762e5ab4..cd8d63054 100644
--- a/docs/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/quickstart.md
@@ -4,27 +4,74 @@ description: Install and use YOLOv8 via CLI or Python. Run single-line commands
keywords: YOLOv8, object detection, segmentation, classification, pip, git, CLI, Python
---
-## Install
+## Install Ultralytics
-Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning
-the [https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) repository for the most
-up-to-date version.
+Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Docker. Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning the [Ultralytics GitHub repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) for the most up-to-date version. Docker can be used to execute the package in an isolated container, avoiding local installation.
!!! example "Install"
- === "pip install (recommended)"
+ === "Pip install (recommended)"
+ Install the `ultralytics` package using pip, or update an existing installation by running `pip install -U ultralytics`. Visit the Python Package Index (PyPI) for more details on the `ultralytics` package: [https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/).
+
+ [](https://badge.fury.io/py/ultralytics) [](https://pepy.tech/project/ultralytics)
+
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using pip
pip install ultralytics
```
+
+ === "Conda install"
+ Conda is an alternative package manager to pip which may also be used for installation. Visit Anaconda for more details at [https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics). Ultralytics feedstock repository for updating the conda package is at [https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/](https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/).
+
+
+ [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics)
- === "git clone (for development)"
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using conda
+ conda install ultralytics
+ ```
+
+ === "Git clone"
+ Clone the `ultralytics` repository if you are interested in contributing to the development or wish to experiment with the latest source code. After cloning, navigate into the directory and install the package in editable mode `-e` using pip.
+ ```bash
+ # Clone the ultralytics repository
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
+
+ # Navigate to the cloned directory
cd ultralytics
+
+ # Install the package in editable mode for development
pip install -e .
```
-See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that `pip` automatically installs all required dependencies.
+ === "Docker"
+ Utilize Docker to execute the `ultralytics` package in an isolated container. By employing the official `ultralytics` image from [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics), you can avoid local installation. Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
+
+
-**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a
-validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters
-of the model to improve its performance.
+**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters of the model to improve its performance.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,8 +14,7 @@ of the model to improve its performance.
## Usage Examples
-Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's
-training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
+Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
!!! example ""
@@ -46,13 +43,7 @@ training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below f
## Arguments
-Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to
-evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and
-accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed
-during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation
-process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the
-validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
+Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| Key | Value | Description |
|---------------|---------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|
@@ -70,23 +61,4 @@ validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| `plots` | `False` | show plots during training |
| `rect` | `False` | rectangular val with each batch collated for minimum padding |
| `split` | `val` | dataset split to use for validation, i.e. 'val', 'test' or 'train' |
-
-## Export Formats
-
-Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument,
-i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
-
-| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
-| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
-| [OpenVINO](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
-| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
-| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
-| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
-| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+|
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/quickstart.md b/docs/quickstart.md
index b762e5ab4..cd8d63054 100644
--- a/docs/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/quickstart.md
@@ -4,27 +4,74 @@ description: Install and use YOLOv8 via CLI or Python. Run single-line commands
keywords: YOLOv8, object detection, segmentation, classification, pip, git, CLI, Python
---
-## Install
+## Install Ultralytics
-Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning
-the [https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) repository for the most
-up-to-date version.
+Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Docker. Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning the [Ultralytics GitHub repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) for the most up-to-date version. Docker can be used to execute the package in an isolated container, avoiding local installation.
!!! example "Install"
- === "pip install (recommended)"
+ === "Pip install (recommended)"
+ Install the `ultralytics` package using pip, or update an existing installation by running `pip install -U ultralytics`. Visit the Python Package Index (PyPI) for more details on the `ultralytics` package: [https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/).
+
+ [](https://badge.fury.io/py/ultralytics) [](https://pepy.tech/project/ultralytics)
+
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using pip
pip install ultralytics
```
+
+ === "Conda install"
+ Conda is an alternative package manager to pip which may also be used for installation. Visit Anaconda for more details at [https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics). Ultralytics feedstock repository for updating the conda package is at [https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/](https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/).
+
+
+ [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics)
- === "git clone (for development)"
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using conda
+ conda install ultralytics
+ ```
+
+ === "Git clone"
+ Clone the `ultralytics` repository if you are interested in contributing to the development or wish to experiment with the latest source code. After cloning, navigate into the directory and install the package in editable mode `-e` using pip.
+ ```bash
+ # Clone the ultralytics repository
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
+
+ # Navigate to the cloned directory
cd ultralytics
+
+ # Install the package in editable mode for development
pip install -e .
```
-See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that `pip` automatically installs all required dependencies.
+ === "Docker"
+ Utilize Docker to execute the `ultralytics` package in an isolated container. By employing the official `ultralytics` image from [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics), you can avoid local installation. Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
+
+  +
+ ```bash
+ # Set image name as a variable
+ t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
+
+ # Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
+ sudo docker pull $t
+
+ # Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t
+ ```
+
+ The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
+
+ Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
+ ```
+
+ Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
+
+See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -34,9 +81,9 @@ See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralyt
+
+ ```bash
+ # Set image name as a variable
+ t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
+
+ # Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
+ sudo docker pull $t
+
+ # Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t
+ ```
+
+ The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
+
+ Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
+ ```
+
+ Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
+
+See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -34,9 +81,9 @@ See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralyt
 -## Use with CLI
+## Use Ultralytics with CLI
-The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
+The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! example
@@ -103,7 +150,7 @@ CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button .md-button--primary}
-## Use with Python
+## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
index c979186ea..f4446087c 100644
--- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
+++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
@@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETR, Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, speed, accuracy, implemen
## RTDETR
---
### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.model.RTDETR
-
-## Use with CLI
+## Use Ultralytics with CLI
-The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
+The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! example
@@ -103,7 +150,7 @@ CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button .md-button--primary}
-## Use with Python
+## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
index c979186ea..f4446087c 100644
--- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
+++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
@@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETR, Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, speed, accuracy, implemen
## RTDETR
---
### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.model.RTDETR
-
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md index c5b5420a4..032c2da59 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRPredictor, object detection, vision transformer, Ultralytics YOL ## RTDETRPredictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.predict.RTDETRPredictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md index b7bb384eb..03f33f7c8 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRTrainer, Ultralytics YOLO Docs, object detection, VIT-based RTDE ## train --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.train.train -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md index 43c1898b3..32359b32f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRDataset, RTDETRValidator, data validation, documentation ## RTDETRValidator --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.val.RTDETRValidator -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md index 82c66e8b1..a5b5e4f82 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md @@ -86,4 +86,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, SAM, MaskData, mask_to_rle_pytorch, area_from_rle, genera ## batched_mask_to_box --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.amg.batched_mask_to_box -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md index cbb0ca7c0..ca84d37f6 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: ResizeLongestSide, Ultralytics YOLO, automatic image resizing, image r ## ResizeLongestSide --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.autosize.ResizeLongestSide -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md index faa26eead..6c3962112 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md @@ -26,4 +26,4 @@ keywords: SAM, VIT, computer vision models, build SAM models, build VIT models, ## build_sam --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.build.build_sam -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md index 7d924d4a9..4149847fc 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, VIT, SAM, object detection, computer vision, deep learnin ## SAM --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.model.SAM -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md index e89ca9d68..940d720c6 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md @@ -1,3 +1,8 @@ +--- +description: Learn about Ultralytics YOLO's MaskDecoder, Transformer architecture, MLP, mask prediction, and quality prediction. +keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, MaskDecoder, Transformer architecture, mask prediction, image embeddings, prompt embeddings, multi-mask output, MLP, mask quality prediction +--- + ## MaskDecoder --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.decoders.MaskDecoder diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md index 8c338bc6d..bd5760a97 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md @@ -51,4 +51,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, ViT Encoder, Position Embeddings, Attention, Window ## add_decomposed_rel_pos --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.encoders.add_decomposed_rel_pos -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md index e2e1251c1..beec1d3f0 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: SamAutomaticMaskGenerator, Ultralytics YOLO, automatic mask generator, ## SamAutomaticMaskGenerator --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.mask_generator.SamAutomaticMaskGenerator -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md index f7e3b3713..00de169ef 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: PromptPredictor, Ultralytics, YOLO, VIT SAM, image captioning, deep le ## PromptPredictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.prompt_predictor.PromptPredictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md index acd467b19..7ead8cb7f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics VIT, Sam module, PyTorch vision library, image classificat ## Sam --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.sam.Sam -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md index 994b98455..e0d8eeb86 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md @@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, Attention module, TwoWayTransformer module, Object D ## Attention --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.transformer.Attention -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md index 836d91e3c..35479518b 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, VIT SAM Predictor, object detection, YOLO ## Predictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.predict.Predictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md b/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md index 3eb366ed3..cd45d5f5f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: DETRLoss, RTDETRDetectionLoss, Ultralytics, object detection, image cl ## RTDETRDetectionLoss --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.utils.loss.RTDETRDetectionLoss -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md b/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md index f4b7c8176..e4660f094 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md @@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, HungarianMatcher, inverse_sigmoid ## inverse_sigmoid --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.utils.ops.inverse_sigmoid -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md index dd07646c1..3e06f8f34 100644 --- a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md +++ b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md @@ -23,6 +23,11 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, downloads, trained models, datasets, weights, deep l ### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.safe_download
+## get_github_assets +--- +### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.get_github_assets +
+ ## attempt_download_asset --- ### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.attempt_download_asset diff --git a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..bf9300089 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +--- +description: Optimize YOLO models' hyperparameters with Ultralytics YOLO's `run_ray_tune` function using Ray Tune and ASHA scheduler. +keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, Hyperparameter Tuning, Ray Tune, ASHAScheduler, Optimization, Object Detection +--- + +## run_ray_tune +--- +### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.tuner.run_ray_tune +
diff --git a/docs/tasks/classify.md b/docs/tasks/classify.md index fe0b939b3..8d71093d8 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/classify.md +++ b/docs/tasks/classify.md @@ -176,5 +176,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-cls.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your mo | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-cls_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-cls_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-cls_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-cls_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/detect.md b/docs/tasks/detect.md index 35a3d444c..6573b75b9 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/detect.md +++ b/docs/tasks/detect.md @@ -167,5 +167,6 @@ Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can predict or valid | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/pose.md b/docs/tasks/pose.md index 094f95b87..ef8495dc7 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/pose.md +++ b/docs/tasks/pose.md @@ -181,5 +181,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-pose.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your m | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-pose_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-pose_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-pose_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-pose_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/segment.md b/docs/tasks/segment.md index 4f9192ffc..659ac8267 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/segment.md +++ b/docs/tasks/segment.md @@ -181,5 +181,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your mo | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-seg_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-seg_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-seg_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-seg_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md b/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md index 06a384144..1b25ade16 100644 --- a/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md +++ b/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md @@ -1,29 +1,26 @@ --- comments: true -description: Discover how to integrate hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune and Ultralytics YOLOv8. Speed up the tuning process and optimize your model's performance. +description: Learn to integrate hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune with Ultralytics YOLOv8, and optimize your model's performance efficiently. keywords: yolov8, ray tune, hyperparameter tuning, hyperparameter optimization, machine learning, computer vision, deep learning, image recognition --- -# Hyperparameter Tuning with Ray Tune and YOLOv8 +# Efficient Hyperparameter Tuning with Ray Tune and YOLOv8 -Hyperparameter tuning (or hyperparameter optimization) is the process of determining the right combination of hyperparameters that maximizes model performance. It works by running multiple trials in a single training process, evaluating the performance of each trial, and selecting the best hyperparameter values based on the evaluation results. +Hyperparameter tuning is vital in achieving peak model performance by discovering the optimal set of hyperparameters. This involves running trials with different hyperparameters and evaluating each trial’s performance. -## Ultralytics YOLOv8 and Ray Tune Integration +## Accelerate Tuning with Ultralytics YOLOv8 and Ray Tune -[Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) YOLOv8 integrates hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune, allowing you to easily optimize your YOLOv8 model's hyperparameters. By using Ray Tune, you can leverage advanced search algorithms, parallelism, and early stopping to speed up the tuning process and achieve better model performance. +[Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) incorporates Ray Tune for hyperparameter tuning, streamlining the optimization of YOLOv8 model hyperparameters. With Ray Tune, you can utilize advanced search strategies, parallelism, and early stopping to expedite the tuning process. ### Ray Tune -
 -
+
-
+
 \ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/README.md b/examples/README.md
index d2c27c13d..120c04be5 100644
--- a/examples/README.md
+++ b/examples/README.md
@@ -8,9 +8,12 @@ This repository features a collection of real-world applications and walkthrough
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------- |
| [YOLO ONNX Detection Inference with C++](./YOLOv8-CPP-Inference) | C++/ONNX | [Justas Bartnykas](https://github.com/JustasBart) |
| [YOLO OpenCV ONNX Detection Python](./YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python) | OpenCV/Python/ONNX | [Farid Inawan](https://github.com/frdteknikelektro) |
+| [YOLOv8 .NET ONNX ImageSharp](https://github.com/dme-compunet/YOLOv8) | C#/ONNX/ImageSharp | [Compunet](https://github.com/dme-compunet) |
| [YOLO .Net ONNX Detection C#](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Yolov8.Net) | C# .Net | [Samuel Stainback](https://github.com/sstainba) |
| [YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson(TensorRT and DeepStream)](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/YOLOv8-DeepStream-TRT-Jetson/) | Python | [Lakshantha](https://github.com/lakshanthad) |
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
+| [YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP) | C++/ONNXRuntime | [DennisJcy](https://github.com/DennisJcy) |
+| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime C#](https://github.com/Kayzwer/yolo-cs/blob/master/RTDETR.cs) | C#/ONNX | [Kayzwer](https://github.com/Kayzwer) |
### How to Contribute
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c49866497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+# YOLOv8 OnnxRuntime C++
+
+This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 in C++ with ONNX Runtime and OpenCV's API.
+
+We recommend using Visual Studio to build the project.
+
+## Benefits
+
+- Friendly for deployment in the industrial sector.
+- Faster than OpenCV's DNN inference on both CPU and GPU.
+- Supports CUDA acceleration.
+- Easy to add FP16 inference (using template functions).
+
+## Exporting YOLOv8 Models
+
+To export YOLOv8 models, use the following Python script:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+# Load a YOLOv8 model
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
+
+# Export the model
+model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
+```
+
+## Dependencies
+
+| Dependency | Version |
+| ----------------------- | -------- |
+| Onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu | >=1.14.1 |
+| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
+| C++ | >=17 |
+
+Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
+
+## Usage
+
+```c++
+// CPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, false};
+// GPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, true};
+
+// Load your image
+cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
+
+char* ret = p1->CreateSession(params);
+
+ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
+```
+
+This repository should also work for YOLOv5, which needs a permute operator for the output of the YOLOv5 model, but this has not been implemented yet.
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5af395dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+#include "inference.h"
+#include
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/README.md b/examples/README.md
index d2c27c13d..120c04be5 100644
--- a/examples/README.md
+++ b/examples/README.md
@@ -8,9 +8,12 @@ This repository features a collection of real-world applications and walkthrough
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------- |
| [YOLO ONNX Detection Inference with C++](./YOLOv8-CPP-Inference) | C++/ONNX | [Justas Bartnykas](https://github.com/JustasBart) |
| [YOLO OpenCV ONNX Detection Python](./YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python) | OpenCV/Python/ONNX | [Farid Inawan](https://github.com/frdteknikelektro) |
+| [YOLOv8 .NET ONNX ImageSharp](https://github.com/dme-compunet/YOLOv8) | C#/ONNX/ImageSharp | [Compunet](https://github.com/dme-compunet) |
| [YOLO .Net ONNX Detection C#](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Yolov8.Net) | C# .Net | [Samuel Stainback](https://github.com/sstainba) |
| [YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson(TensorRT and DeepStream)](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/YOLOv8-DeepStream-TRT-Jetson/) | Python | [Lakshantha](https://github.com/lakshanthad) |
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
+| [YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP) | C++/ONNXRuntime | [DennisJcy](https://github.com/DennisJcy) |
+| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime C#](https://github.com/Kayzwer/yolo-cs/blob/master/RTDETR.cs) | C#/ONNX | [Kayzwer](https://github.com/Kayzwer) |
### How to Contribute
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c49866497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+# YOLOv8 OnnxRuntime C++
+
+This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 in C++ with ONNX Runtime and OpenCV's API.
+
+We recommend using Visual Studio to build the project.
+
+## Benefits
+
+- Friendly for deployment in the industrial sector.
+- Faster than OpenCV's DNN inference on both CPU and GPU.
+- Supports CUDA acceleration.
+- Easy to add FP16 inference (using template functions).
+
+## Exporting YOLOv8 Models
+
+To export YOLOv8 models, use the following Python script:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+# Load a YOLOv8 model
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
+
+# Export the model
+model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
+```
+
+## Dependencies
+
+| Dependency | Version |
+| ----------------------- | -------- |
+| Onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu | >=1.14.1 |
+| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
+| C++ | >=17 |
+
+Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
+
+## Usage
+
+```c++
+// CPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, false};
+// GPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, true};
+
+// Load your image
+cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
+
+char* ret = p1->CreateSession(params);
+
+ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
+```
+
+This repository should also work for YOLOv5, which needs a permute operator for the output of the YOLOv5 model, but this has not been implemented yet.
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5af395dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+#include "inference.h"
+#include
+
+#define benchmark
+#define ELOG
+
+DCSP_CORE::DCSP_CORE()
+{
+
+}
+
+
+DCSP_CORE::~DCSP_CORE()
+{
+ delete session;
+}
+
+
+template
+char* BlobFromImage(cv::Mat& iImg, T& iBlob)
+{
+ int channels = iImg.channels();
+ int imgHeight = iImg.rows;
+ int imgWidth = iImg.cols;
+
+ for (int c = 0; c < channels; c++)
+ {
+ for (int h = 0; h < imgHeight; h++)
+ {
+ for (int w = 0; w < imgWidth; w++)
+ {
+ iBlob[c * imgWidth * imgHeight + h * imgWidth + w] = (std::remove_pointer::type)((iImg.at(h, w)[c]) / 255.0f);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return RET_OK;
+}
+
+
+char* PostProcess(cv::Mat& iImg, std::vector iImgSize, cv::Mat& oImg)
+{
+ cv::Mat img = iImg.clone();
+ cv::resize(iImg, oImg, cv::Size(iImgSize.at(0), iImgSize.at(1)));
+ if (img.channels() == 1)
+ {
+ cv::cvtColor(oImg, oImg, cv::COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
+ }
+ cv::cvtColor(oImg, oImg, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
+ return RET_OK;
+}
+
+
+char* DCSP_CORE::CreateSession(DCSP_INIT_PARAM &iParams)
+{
+ char* Ret = RET_OK;
+ std::regex pattern("[\u4e00-\u9fa5]");
+ bool result = std::regex_search(iParams.ModelPath, pattern);
+ if (result)
+ {
+ Ret = "[DCSP_ONNX]:model path error.change your model path without chinese characters.";
+ std::cout << Ret << std::endl;
+ return Ret;
+ }
+ try
+ {
+ rectConfidenceThreshold = iParams.RectConfidenceThreshold;
+ iouThreshold = iParams.iouThreshold;
+ imgSize = iParams.imgSize;
+ modelType = iParams.ModelType;
+ env = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "Yolo");
+ Ort::SessionOptions sessionOption;
+ if (iParams.CudaEnable)
+ {
+ cudaEnable = iParams.CudaEnable;
+ OrtCUDAProviderOptions cudaOption;
+ cudaOption.device_id = 0;
+ sessionOption.AppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(cudaOption);
+ //OrtOpenVINOProviderOptions ovOption;
+ //sessionOption.AppendExecutionProvider_OpenVINO(ovOption);
+ }
+ sessionOption.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_ALL);
+ sessionOption.SetIntraOpNumThreads(iParams.IntraOpNumThreads);
+ sessionOption.SetLogSeverityLevel(iParams.LogSeverityLevel);
+ int ModelPathSize = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, iParams.ModelPath.c_str(), static_cast(iParams.ModelPath.length()), nullptr, 0);
+ wchar_t* wide_cstr = new wchar_t[ModelPathSize + 1];
+ MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, iParams.ModelPath.c_str(), static_cast(iParams.ModelPath.length()), wide_cstr, ModelPathSize);
+ wide_cstr[ModelPathSize] = L'\0';
+ const wchar_t* modelPath = wide_cstr;
+ session = new Ort::Session(env, modelPath, sessionOption);
+ Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
+ size_t inputNodesNum = session->GetInputCount();
+ for (size_t i = 0; i < inputNodesNum; i++)
+ {
+ Ort::AllocatedStringPtr input_node_name = session->GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
+ char* temp_buf = new char[50];
+ strcpy(temp_buf, input_node_name.get());
+ inputNodeNames.push_back(temp_buf);
+ }
+
+ size_t OutputNodesNum = session->GetOutputCount();
+ for (size_t i = 0; i < OutputNodesNum; i++)
+ {
+ Ort::AllocatedStringPtr output_node_name = session->GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator);
+ char* temp_buf = new char[10];
+ strcpy(temp_buf, output_node_name.get());
+ outputNodeNames.push_back(temp_buf);
+ }
+ options = Ort::RunOptions{ nullptr };
+ WarmUpSession();
+ //std::cout << OrtGetApiBase()->GetVersionString() << std::endl;;
+ Ret = RET_OK;
+ return Ret;
+ }
+ catch (const std::exception& e)
+ {
+ const char* str1 = "[DCSP_ONNX]:";
+ const char* str2 = e.what();
+ std::string result = std::string(str1) + std::string(str2);
+ char* merged = new char[result.length() + 1];
+ std::strcpy(merged, result.c_str());
+ std::cout << merged << std::endl;
+ delete[] merged;
+ //return merged;
+ return "[DCSP_ONNX]:Create session failed.";
+ }
+
+}
+
+
+char* DCSP_CORE::RunSession(cv::Mat &iImg, std::vector& oResult)
+{
+#ifdef benchmark
+ clock_t starttime_1 = clock();
+#endif // benchmark
+
+ char* Ret = RET_OK;
+ cv::Mat processedImg;
+ PostProcess(iImg, imgSize, processedImg);
+ if (modelType < 4)
+ {
+ float* blob = new float[processedImg.total() * 3];
+ BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
+ std::vector inputNodeDims = { 1,3,imgSize.at(0),imgSize.at(1) };
+ TensorProcess(starttime_1, iImg, blob, inputNodeDims, oResult);
+ }
+
+ return Ret;
+}
+
+
+template
+char* DCSP_CORE::TensorProcess(clock_t& starttime_1, cv::Mat& iImg, N& blob, std::vector& inputNodeDims, std::vector& oResult)
+{
+ Ort::Value inputTensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor::type>(Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), blob, 3 * imgSize.at(0) * imgSize.at(1), inputNodeDims.data(), inputNodeDims.size());
+#ifdef benchmark
+ clock_t starttime_2 = clock();
+#endif // benchmark
+ auto outputTensor = session->Run(options, inputNodeNames.data(), &inputTensor, 1, outputNodeNames.data(), outputNodeNames.size());
+#ifdef benchmark
+ clock_t starttime_3 = clock();
+#endif // benchmark
+ Ort::TypeInfo typeInfo = outputTensor.front().GetTypeInfo();
+ auto tensor_info = typeInfo.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
+ std::vectoroutputNodeDims = tensor_info.GetShape();
+ std::remove_pointer::type* output = outputTensor.front().GetTensorMutableData::type>();
+ delete blob;
+ switch (modelType)
+ {
+ case 1:
+ {
+ int strideNum = outputNodeDims[2];
+ int signalResultNum = outputNodeDims[1];
+ std::vector class_ids;
+ std::vector confidences;
+ std::vector boxes;
+ cv::Mat rowData(signalResultNum, strideNum, CV_32F, output);
+ rowData = rowData.t();
+
+ float* data = (float*)rowData.data;
+
+ float x_factor = iImg.cols / 640.;
+ float y_factor = iImg.rows / 640.;
+ for (int i = 0; i < strideNum; ++i)
+ {
+ float* classesScores = data + 4;
+ cv::Mat scores(1, classesNum, CV_32FC1, classesScores);
+ cv::Point class_id;
+ double maxClassScore;
+ cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &maxClassScore, 0, &class_id);
+ if (maxClassScore > rectConfidenceThreshold)
+ {
+ confidences.push_back(maxClassScore);
+ class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
+
+ float x = data[0];
+ float y = data[1];
+ float w = data[2];
+ float h = data[3];
+
+ int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor);
+ int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor);
+
+ int width = int(w * x_factor);
+ int height = int(h * y_factor);
+
+ boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, width, height));
+ }
+ data += signalResultNum;
+ }
+
+ std::vector nmsResult;
+ cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, rectConfidenceThreshold, iouThreshold, nmsResult);
+ for (int i = 0; i < nmsResult.size(); ++i)
+ {
+ int idx = nmsResult[i];
+ DCSP_RESULT result;
+ result.classId = class_ids[idx];
+ result.confidence = confidences[idx];
+ result.box = boxes[idx];
+ oResult.push_back(result);
+ }
+
+
+#ifdef benchmark
+ clock_t starttime_4 = clock();
+ double pre_process_time = (double)(starttime_2 - starttime_1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
+ double process_time = (double)(starttime_3 - starttime_2) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
+ double post_process_time = (double)(starttime_4 - starttime_3) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
+ if (cudaEnable)
+ {
+ std::cout << "[DCSP_ONNX(CUDA)]: " << pre_process_time << "ms pre-process, " << process_time << "ms inference, " << post_process_time << "ms post-process." << std::endl;
+ }
+ else
+ {
+ std::cout << "[DCSP_ONNX(CPU)]: " << pre_process_time << "ms pre-process, " << process_time << "ms inference, " << post_process_time << "ms post-process." << std::endl;
+ }
+#endif // benchmark
+
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ char* Ret = RET_OK;
+ return Ret;
+}
+
+
+char* DCSP_CORE::WarmUpSession()
+{
+ clock_t starttime_1 = clock();
+ char* Ret = RET_OK;
+ cv::Mat iImg = cv::Mat(cv::Size(imgSize.at(0), imgSize.at(1)), CV_8UC3);
+ cv::Mat processedImg;
+ PostProcess(iImg, imgSize, processedImg);
+ if (modelType < 4)
+ {
+ float* blob = new float[iImg.total() * 3];
+ BlobFromImage(processedImg, blob);
+ std::vector YOLO_input_node_dims = { 1,3,imgSize.at(0),imgSize.at(1) };
+ Ort::Value input_tensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor(Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), blob, 3 * imgSize.at(0) * imgSize.at(1), YOLO_input_node_dims.data(), YOLO_input_node_dims.size());
+ auto output_tensors = session->Run(options, inputNodeNames.data(), &input_tensor, 1, outputNodeNames.data(), outputNodeNames.size());
+ delete[] blob;
+ clock_t starttime_4 = clock();
+ double post_process_time = (double)(starttime_4 - starttime_1) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC * 1000;
+ if (cudaEnable)
+ {
+ std::cout << "[DCSP_ONNX(CUDA)]: " << "Cuda warm-up cost " << post_process_time << " ms. " << std::endl;
+ }
+ }
+
+ return Ret;
+}
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.h b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.h
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d00fecd12
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.h
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+#pragma once
+
+#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
+#define RET_OK nullptr
+
+#include
+#include
+#include
+#include "io.h"
+#include "direct.h"
+#include "opencv.hpp"
+#include
+#include "onnxruntime_cxx_api.h"
+
+
+enum MODEL_TYPE
+{
+ //FLOAT32 MODEL
+ YOLO_ORIGIN_V5 = 0,
+ YOLO_ORIGIN_V8 = 1,//only support v8 detector currently
+ YOLO_POSE_V8 = 2,
+ YOLO_CLS_V8 = 3
+};
+
+
+typedef struct _DCSP_INIT_PARAM
+{
+ std::string ModelPath;
+ MODEL_TYPE ModelType = YOLO_ORIGIN_V8;
+ std::vector imgSize={640, 640};
+
+ int classesNum=80;
+ float RectConfidenceThreshold = 0.6;
+ float iouThreshold = 0.5;
+ bool CudaEnable = false;
+ int LogSeverityLevel = 3;
+ int IntraOpNumThreads = 1;
+}DCSP_INIT_PARAM;
+
+
+typedef struct _DCSP_RESULT
+{
+ int classId;
+ float confidence;
+ cv::Rect box;
+}DCSP_RESULT;
+
+
+class DCSP_CORE
+{
+public:
+ DCSP_CORE();
+ ~DCSP_CORE();
+
+public:
+ char* CreateSession(DCSP_INIT_PARAM &iParams);
+
+
+ char* RunSession(cv::Mat &iImg, std::vector& oResult);
+
+
+ char* WarmUpSession();
+
+
+ template
+ char* TensorProcess(clock_t& starttime_1, cv::Mat& iImg, N& blob, std::vector& inputNodeDims, std::vector& oResult);
+
+
+private:
+ Ort::Env env;
+ Ort::Session* session;
+ bool cudaEnable;
+ Ort::RunOptions options;
+ std::vector inputNodeNames;
+ std::vector outputNodeNames;
+
+
+ int classesNum;
+ MODEL_TYPE modelType;
+ std::vector imgSize;
+ float rectConfidenceThreshold;
+ float iouThreshold;
+};
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/main.cpp b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/main.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f13d78250
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/main.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+#include
+#include
+#include "inference.h"
+#include
+
+
+
+void file_iterator(DCSP_CORE*& p)
+{
+ std::filesystem::path img_path = R"(E:\project\Project_C++\DCPS_ONNX\TEST_ORIGIN)";
+ int k = 0;
+ for (auto& i : std::filesystem::directory_iterator(img_path))
+ {
+ if (i.path().extension() == ".jpg")
+ {
+ std::string img_path = i.path().string();
+ //std::cout << img_path << std::endl;
+ cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
+ std::vector res;
+ char* ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
+ for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++)
+ {
+ cv::rectangle(img, res.at(i).box, cv::Scalar(125, 123, 0), 3);
+ }
+
+ k++;
+ cv::imshow("TEST_ORIGIN", img);
+ cv::waitKey(0);
+ cv::destroyAllWindows();
+ //cv::imwrite("E:\\output\\" + std::to_string(k) + ".png", img);
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+
+
+int main()
+{
+ DCSP_CORE* p1 = new DCSP_CORE;
+ std::string model_path = "yolov8n.onnx";
+ DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {640, 640}, 80, 0.1, 0.5, false };
+ char* ret = p1->CreateSession(params);
+ file_iterator(p1);
+}
diff --git a/examples/hub.ipynb b/examples/hub.ipynb
index bcfd94e99..252891424 100644
--- a/examples/hub.ipynb
+++ b/examples/hub.ipynb
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@
"\n",
"Welcome to the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com/) HUB notebook! \n",
"\n",
- "This notebook allows you to train [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) and [YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) 🚀 models using [HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/). Please browse the YOLOv8 Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!\n",
+ "This notebook allows you to train [YOLOv5](https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5) and [YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) 🚀 models using [HUB](https://hub.ultralytics.com/). Please browse the YOLOv8 Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!\n",
""
]
},
diff --git a/examples/tutorial.ipynb b/examples/tutorial.ipynb
index 6a433e746..818bf7f58 100644
--- a/examples/tutorial.ipynb
+++ b/examples/tutorial.ipynb
@@ -36,7 +36,7 @@
"\n",
"YOLOv8 models are fast, accurate, and easy to use, making them ideal for various object detection and image segmentation tasks. They can be trained on large datasets and run on diverse hardware platforms, from CPUs to GPUs.\n",
"\n",
- "We hope that the resources in this notebook will help you get the most out of YOLOv8. Please browse the YOLOv8 Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!\n",
+ "We hope that the resources in this notebook will help you get the most out of YOLOv8. Please browse the YOLOv8 Docs for details, raise an issue on GitHub for support, and join our Discord community for questions and discussions!\n",
"\n",
""
]
diff --git a/mkdocs.yml b/mkdocs.yml
index 146da1233..3295fb922 100644
--- a/mkdocs.yml
+++ b/mkdocs.yml
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ theme:
- content.tabs.link # all code tabs change simultaneously
# Customization
-copyright: Ultralytics 2023. All rights reserved.
+copyright: © 2023 Ultralytics Inc. All rights reserved.
extra:
# version:
# provider: mike # version drop-down menu
@@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ extra:
- icon: fontawesome/brands/python
link: https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/
- icon: fontawesome/brands/discord
- link: https://discord.gg/7aegy5d8
+ link: https://discord.gg/2wNGbc6g9X
extra_css:
- stylesheets/style.css
@@ -168,6 +168,7 @@ nav:
- YOLOv7: models/yolov7.md
- YOLOv8: models/yolov8.md
- SAM (Segment Anything Model): models/sam.md
+ - FastSAM (Fast Segment Anything Model): models/fast-sam.md
- YOLO-NAS (Neural Architecture Search): models/yolo-nas.md
- RT-DETR (Realtime Detection Transformer): models/rtdetr.md
- Datasets:
@@ -350,6 +351,7 @@ nav:
- plotting: reference/yolo/utils/plotting.md
- tal: reference/yolo/utils/tal.md
- torch_utils: reference/yolo/utils/torch_utils.md
+ - tuner: reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md
- v8:
- classify:
- predict: reference/yolo/v8/classify/predict.md
@@ -376,6 +378,7 @@ nav:
- Contributor License Agreement (CLA): help/CLA.md
- Minimum Reproducible Example (MRE) Guide: help/minimum_reproducible_example.md
- Code of Conduct: help/code_of_conduct.md
+ - Environmental, Health and Safety (EHS) Policy: help/environmental-health-safety.md
- Security Policy: SECURITY.md
# Plugins including 301 redirects navigation ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
diff --git a/requirements.txt b/requirements.txt
index c062769d0..be1fce9b4 100644
--- a/requirements.txt
+++ b/requirements.txt
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ tqdm>=4.64.0
# Logging -------------------------------------
# tensorboard>=2.13.0
-# dvclive>=2.11.0
+# dvclive>=2.12.0
# clearml
# comet
diff --git a/setup.py b/setup.py
index 59510c3ed..76f6b7d99 100644
--- a/setup.py
+++ b/setup.py
@@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ setup(
'mkdocs-material',
'mkdocstrings[python]',
'mkdocs-redirects', # for 301 redirects
- 'mkdocs-ultralytics-plugin', # for meta descriptions and images, dates and authors
+ 'mkdocs-ultralytics-plugin>=0.0.21', # for meta descriptions and images, dates and authors
],
'export': ['coremltools>=6.0', 'openvino-dev>=2022.3', 'tensorflowjs'], # automatically installs tensorflow
},
diff --git a/tests/test_python.py b/tests/test_python.py
index f633bd6fc..10f24fd3d 100644
--- a/tests/test_python.py
+++ b/tests/test_python.py
@@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ import cv2
import numpy as np
import torch
from PIL import Image
+from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
from ultralytics import RTDETR, YOLO
from ultralytics.yolo.data.build import load_inference_source
@@ -70,7 +71,7 @@ def test_predict_img():
# Test tensor inference
im = cv2.imread(str(SOURCE)) # OpenCV
t = cv2.resize(im, (32, 32))
- t = torch.from_numpy(t.transpose((2, 0, 1)))
+ t = ToTensor()(t)
t = torch.stack([t, t, t, t])
results = model(t, visualize=True)
assert len(results) == t.shape[0]
diff --git a/ultralytics/__init__.py b/ultralytics/__init__.py
index 4cbd5cb0f..d33711595 100644
--- a/ultralytics/__init__.py
+++ b/ultralytics/__init__.py
@@ -1,12 +1,14 @@
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
-__version__ = '8.0.118'
+__version__ = '8.0.132'
from ultralytics.hub import start
from ultralytics.vit.rtdetr import RTDETR
from ultralytics.vit.sam import SAM
from ultralytics.yolo.engine.model import YOLO
+from ultralytics.yolo.fastsam import FastSAM
from ultralytics.yolo.nas import NAS
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_yolo as checks
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads import download
-__all__ = '__version__', 'YOLO', 'NAS', 'SAM', 'RTDETR', 'checks', 'start' # allow simpler import
+__all__ = '__version__', 'YOLO', 'NAS', 'SAM', 'FastSAM', 'RTDETR', 'checks', 'download', 'start' # allow simpler import
diff --git a/ultralytics/hub/utils.py b/ultralytics/hub/utils.py
index 26f560d72..ecd64a95e 100644
--- a/ultralytics/hub/utils.py
+++ b/ultralytics/hub/utils.py
@@ -78,10 +78,13 @@ def requests_with_progress(method, url, **kwargs):
return requests.request(method, url, **kwargs)
response = requests.request(method, url, stream=True, **kwargs)
total = int(response.headers.get('content-length', 0)) # total size
- pbar = tqdm(total=total, unit='B', unit_scale=True, unit_divisor=1024, bar_format=TQDM_BAR_FORMAT)
- for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
- pbar.update(len(data))
- pbar.close()
+ try:
+ pbar = tqdm(total=total, unit='B', unit_scale=True, unit_divisor=1024, bar_format=TQDM_BAR_FORMAT)
+ for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
+ pbar.update(len(data))
+ pbar.close()
+ except requests.exceptions.ChunkedEncodingError: # avoid 'Connection broken: IncompleteRead' warnings
+ response.close()
return response
diff --git a/ultralytics/nn/autobackend.py b/ultralytics/nn/autobackend.py
index 7fb9e6d13..01e335ba7 100644
--- a/ultralytics/nn/autobackend.py
+++ b/ultralytics/nn/autobackend.py
@@ -3,6 +3,7 @@
import ast
import contextlib
import json
+import os
import platform
import zipfile
from collections import OrderedDict, namedtuple
@@ -15,7 +16,7 @@ import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import Image
-from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LINUX, LOGGER, ROOT, yaml_load
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import ARM64, LINUX, LOGGER, ROOT, yaml_load
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_requirements, check_suffix, check_version, check_yaml
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads import attempt_download_asset, is_url
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.ops import xywh2xyxy
@@ -75,11 +76,13 @@ class AutoBackend(nn.Module):
| TensorFlow Lite | *.tflite |
| TensorFlow Edge TPU | *_edgetpu.tflite |
| PaddlePaddle | *_paddle_model |
+ | ncnn | *_ncnn_model |
"""
super().__init__()
w = str(weights[0] if isinstance(weights, list) else weights)
nn_module = isinstance(weights, torch.nn.Module)
- pt, jit, onnx, xml, engine, coreml, saved_model, pb, tflite, edgetpu, tfjs, paddle, triton = self._model_type(w)
+ pt, jit, onnx, xml, engine, coreml, saved_model, pb, tflite, edgetpu, tfjs, paddle, ncnn, triton = \
+ self._model_type(w)
fp16 &= pt or jit or onnx or engine or nn_module or triton # FP16
nhwc = coreml or saved_model or pb or tflite or edgetpu # BHWC formats (vs torch BCWH)
stride = 32 # default stride
@@ -237,7 +240,7 @@ class AutoBackend(nn.Module):
meta_file = model.namelist()[0]
metadata = ast.literal_eval(model.read(meta_file).decode('utf-8'))
elif tfjs: # TF.js
- raise NotImplementedError('YOLOv8 TF.js inference is not supported')
+ raise NotImplementedError('YOLOv8 TF.js inference is not currently supported.')
elif paddle: # PaddlePaddle
LOGGER.info(f'Loading {w} for PaddlePaddle inference...')
check_requirements('paddlepaddle-gpu' if cuda else 'paddlepaddle')
@@ -252,6 +255,19 @@ class AutoBackend(nn.Module):
input_handle = predictor.get_input_handle(predictor.get_input_names()[0])
output_names = predictor.get_output_names()
metadata = w.parents[1] / 'metadata.yaml'
+ elif ncnn: # ncnn
+ LOGGER.info(f'Loading {w} for ncnn inference...')
+ check_requirements('git+https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn.git' if ARM64 else 'ncnn') # requires NCNN
+ import ncnn as pyncnn
+ net = pyncnn.Net()
+ net.opt.num_threads = os.cpu_count()
+ net.opt.use_vulkan_compute = cuda
+ w = Path(w)
+ if not w.is_file(): # if not *.param
+ w = next(w.glob('*.param')) # get *.param file from *_ncnn_model dir
+ net.load_param(str(w))
+ net.load_model(str(w.with_suffix('.bin')))
+ metadata = w.parent / 'metadata.yaml'
elif triton: # NVIDIA Triton Inference Server
LOGGER.info('Triton Inference Server not supported...')
'''
@@ -340,7 +356,7 @@ class AutoBackend(nn.Module):
elif self.coreml: # CoreML
im = im[0].cpu().numpy()
im_pil = Image.fromarray((im * 255).astype('uint8'))
- # im = im.resize((192, 320), Image.ANTIALIAS)
+ # im = im.resize((192, 320), Image.BILINEAR)
y = self.model.predict({'image': im_pil}) # coordinates are xywh normalized
if 'confidence' in y:
box = xywh2xyxy(y['coordinates'] * [[w, h, w, h]]) # xyxy pixels
@@ -355,6 +371,16 @@ class AutoBackend(nn.Module):
self.input_handle.copy_from_cpu(im)
self.predictor.run()
y = [self.predictor.get_output_handle(x).copy_to_cpu() for x in self.output_names]
+ elif self.ncnn: # ncnn
+ mat_in = self.pyncnn.Mat(im[0].cpu().numpy())
+ ex = self.net.create_extractor()
+ input_names, output_names = self.net.input_names(), self.net.output_names()
+ ex.input(input_names[0], mat_in)
+ y = []
+ for output_name in output_names:
+ mat_out = self.pyncnn.Mat()
+ ex.extract(output_name, mat_out)
+ y.append(np.array(mat_out)[None])
elif self.triton: # NVIDIA Triton Inference Server
y = self.model(im)
else: # TensorFlow (SavedModel, GraphDef, Lite, Edge TPU)
diff --git a/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py b/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py
index 8b55fd0e5..3b70d7025 100644
--- a/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py
+++ b/ultralytics/nn/modules/head.py
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ class Detect(nn.Module):
self.reg_max = 16 # DFL channels (ch[0] // 16 to scale 4/8/12/16/20 for n/s/m/l/x)
self.no = nc + self.reg_max * 4 # number of outputs per anchor
self.stride = torch.zeros(self.nl) # strides computed during build
- c2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], self.nc) # channels
+ c2, c3 = max((16, ch[0] // 4, self.reg_max * 4)), max(ch[0], min(self.nc, 100)) # channels
self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList(
nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c2, 3), Conv(c2, c2, 3), nn.Conv2d(c2, 4 * self.reg_max, 1)) for x in ch)
self.cv3 = nn.ModuleList(nn.Sequential(Conv(x, c3, 3), Conv(c3, c3, 3), nn.Conv2d(c3, self.nc, 1)) for x in ch)
@@ -158,6 +158,7 @@ class Classify(nn.Module):
class RTDETRDecoder(nn.Module):
+ export = False # export mode
def __init__(
self,
@@ -246,9 +247,12 @@ class RTDETRDecoder(nn.Module):
self.dec_score_head,
self.query_pos_head,
attn_mask=attn_mask)
- if not self.training:
- dec_scores = dec_scores.sigmoid_()
- return dec_bboxes, dec_scores, enc_bboxes, enc_scores, dn_meta
+ x = dec_bboxes, dec_scores, enc_bboxes, enc_scores, dn_meta
+ if self.training:
+ return x
+ # (bs, 300, 4+nc)
+ y = torch.cat((dec_bboxes.squeeze(0), dec_scores.squeeze(0).sigmoid()), -1)
+ return y if self.export else (y, x)
def _generate_anchors(self, shapes, grid_size=0.05, dtype=torch.float32, device='cpu', eps=1e-2):
anchors = []
@@ -266,7 +270,7 @@ class RTDETRDecoder(nn.Module):
anchors = torch.cat(anchors, 1) # (1, h*w*nl, 4)
valid_mask = ((anchors > eps) * (anchors < 1 - eps)).all(-1, keepdim=True) # 1, h*w*nl, 1
anchors = torch.log(anchors / (1 - anchors))
- anchors = torch.where(valid_mask, anchors, torch.inf)
+ anchors = anchors.masked_fill(~valid_mask, float('inf'))
return anchors, valid_mask
def _get_encoder_input(self, x):
@@ -290,7 +294,7 @@ class RTDETRDecoder(nn.Module):
bs = len(feats)
# prepare input for decoder
anchors, valid_mask = self._generate_anchors(shapes, dtype=feats.dtype, device=feats.device)
- features = self.enc_output(torch.where(valid_mask, feats, 0)) # bs, h*w, 256
+ features = self.enc_output(valid_mask * feats) # bs, h*w, 256
enc_outputs_scores = self.enc_score_head(features) # (bs, h*w, nc)
# dynamic anchors + static content
diff --git a/ultralytics/nn/modules/transformer.py b/ultralytics/nn/modules/transformer.py
index 89a7d9142..b3304cc8d 100644
--- a/ultralytics/nn/modules/transformer.py
+++ b/ultralytics/nn/modules/transformer.py
@@ -77,7 +77,7 @@ class AIFI(TransformerEncoderLayer):
pos_embed = self.build_2d_sincos_position_embedding(w, h, c)
# flatten [B, C, H, W] to [B, HxW, C]
x = super().forward(x.flatten(2).permute(0, 2, 1), pos=pos_embed.to(device=x.device, dtype=x.dtype))
- return x.permute((0, 2, 1)).view([-1, c, h, w])
+ return x.permute(0, 2, 1).view([-1, c, h, w]).contiguous()
@staticmethod
def build_2d_sincos_position_embedding(w, h, embed_dim=256, temperature=10000.):
diff --git a/ultralytics/nn/tasks.py b/ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
index 38fd3fcda..e05c53f79 100644
--- a/ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
+++ b/ultralytics/nn/tasks.py
@@ -243,6 +243,8 @@ class DetectionModel(BaseModel):
m.stride = torch.tensor([s / x.shape[-2] for x in forward(torch.zeros(1, ch, s, s))]) # forward
self.stride = m.stride
m.bias_init() # only run once
+ else:
+ self.stride = torch.Tensor([32]) # default stride for i.e. RTDETR
# Init weights, biases
initialize_weights(self)
@@ -430,7 +432,7 @@ class RTDETRDetectionModel(DetectionModel):
'gt_groups': gt_groups}
preds = self.predict(img, batch=targets) if preds is None else preds
- dec_bboxes, dec_scores, enc_bboxes, enc_scores, dn_meta = preds
+ dec_bboxes, dec_scores, enc_bboxes, enc_scores, dn_meta = preds if self.training else preds[1]
if dn_meta is None:
dn_bboxes, dn_scores = None, None
else:
@@ -682,7 +684,7 @@ def yaml_model_load(path):
if path.stem in (f'yolov{d}{x}6' for x in 'nsmlx' for d in (5, 8)):
new_stem = re.sub(r'(\d+)([nslmx])6(.+)?$', r'\1\2-p6\3', path.stem)
LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ Ultralytics YOLO P6 models now use -p6 suffix. Renaming {path.stem} to {new_stem}.')
- path = path.with_stem(new_stem)
+ path = path.with_name(new_stem + path.suffix)
unified_path = re.sub(r'(\d+)([nslmx])(.+)?$', r'\1\3', str(path)) # i.e. yolov8x.yaml -> yolov8.yaml
yaml_file = check_yaml(unified_path, hard=False) or check_yaml(path)
diff --git a/ultralytics/tracker/utils/matching.py b/ultralytics/tracker/utils/matching.py
index f2d458eb7..0b22b3de8 100644
--- a/ultralytics/tracker/utils/matching.py
+++ b/ultralytics/tracker/utils/matching.py
@@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ try:
except (ImportError, AssertionError, AttributeError):
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_requirements
- check_requirements('lap>=0.4') # install
+ check_requirements('lapx>=0.5.2') # update to lap package from https://github.com/rathaROG/lapx
import lap
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/model.py b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/model.py
index 5142056cb..259c7c976 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/model.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/model.py
@@ -5,6 +5,8 @@ RT-DETR model interface
from pathlib import Path
+import torch.nn as nn
+
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import RTDETRDetectionModel, attempt_load_one_weight, yaml_model_load
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
from ultralytics.yolo.engine.exporter import Exporter
@@ -37,7 +39,7 @@ class RTDETR:
self.task = 'detect'
self.model = RTDETRDetectionModel(cfg_dict, verbose=verbose) # build model
- # Below added to allow export from yamls
+ # Below added to allow export from YAMLs
self.model.args = DEFAULT_CFG_DICT # attach args to model
self.model.task = self.task
@@ -125,6 +127,23 @@ class RTDETR:
"""Get model info"""
return model_info(self.model, verbose=verbose)
+ def _check_is_pytorch_model(self):
+ """
+ Raises TypeError is model is not a PyTorch model
+ """
+ pt_str = isinstance(self.model, (str, Path)) and Path(self.model).suffix == '.pt'
+ pt_module = isinstance(self.model, nn.Module)
+ if not (pt_module or pt_str):
+ raise TypeError(f"model='{self.model}' must be a *.pt PyTorch model, but is a different type. "
+ f'PyTorch models can be used to train, val, predict and export, i.e. '
+ f"'yolo export model=yolov8n.pt', but exported formats like ONNX, TensorRT etc. only "
+ f"support 'predict' and 'val' modes, i.e. 'yolo predict model=yolov8n.onnx'.")
+
+ def fuse(self):
+ """Fuse PyTorch Conv2d and BatchNorm2d layers."""
+ self._check_is_pytorch_model()
+ self.model.fuse()
+
@smart_inference_mode()
def export(self, **kwargs):
"""
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/predict.py b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/predict.py
index 78219b2ea..77c02c24d 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/predict.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/predict.py
@@ -12,8 +12,8 @@ class RTDETRPredictor(BasePredictor):
def postprocess(self, preds, img, orig_imgs):
"""Postprocess predictions and returns a list of Results objects."""
- bboxes, scores = preds[:2] # (1, bs, 300, 4), (1, bs, 300, nc)
- bboxes, scores = bboxes.squeeze_(0), scores.squeeze_(0)
+ nd = preds[0].shape[-1]
+ bboxes, scores = preds[0].split((4, nd - 4), dim=-1)
results = []
for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes): # (300, 4)
bbox = ops.xywh2xyxy(bbox)
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/val.py b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/val.py
index 57376a6ce..cfee29253 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/val.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/rtdetr/val.py
@@ -89,9 +89,9 @@ class RTDETRValidator(DetectionValidator):
def postprocess(self, preds):
"""Apply Non-maximum suppression to prediction outputs."""
- bboxes, scores = preds[:2] # (1, bs, 300, 4), (1, bs, 300, nc)
- bboxes, scores = bboxes.squeeze_(0), scores.squeeze_(0) # (bs, 300, 4)
- bs = len(bboxes)
+ bs, _, nd = preds[0].shape
+ bboxes, scores = preds[0].split((4, nd - 4), dim=-1)
+ bboxes *= self.args.imgsz
outputs = [torch.zeros((0, 6), device=bboxes.device)] * bs
for i, bbox in enumerate(bboxes): # (300, 4)
bbox = ops.xywh2xyxy(bbox)
@@ -127,8 +127,8 @@ class RTDETRValidator(DetectionValidator):
if self.args.single_cls:
pred[:, 5] = 0
predn = pred.clone()
- predn[..., [0, 2]] *= shape[1] # native-space pred
- predn[..., [1, 3]] *= shape[0] # native-space pred
+ predn[..., [0, 2]] *= shape[1] / self.args.imgsz # native-space pred
+ predn[..., [1, 3]] *= shape[0] / self.args.imgsz # native-space pred
# Evaluate
if nl:
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/sam/build.py b/ultralytics/vit/sam/build.py
index b2e098649..73b1a03a3 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/sam/build.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/sam/build.py
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ def _build_sam(
)
sam.eval()
if checkpoint is not None:
- attempt_download_asset(checkpoint)
+ checkpoint = attempt_download_asset(checkpoint)
with open(checkpoint, 'rb') as f:
state_dict = torch.load(f)
sam.load_state_dict(state_dict)
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/sam/model.py b/ultralytics/vit/sam/model.py
index 420d6a613..83861f4b9 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/sam/model.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/sam/model.py
@@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ class SAM:
# Should raise AssertionError instead?
raise NotImplementedError('Segment anything prediction requires pre-trained checkpoint')
self.model = build_sam(model)
+ self.task = 'segment' # required
self.predictor = None # reuse predictor
def predict(self, source, stream=False, **kwargs):
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/utils/loss.py b/ultralytics/vit/utils/loss.py
index 6ba24c2de..cb2de206f 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/utils/loss.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/utils/loss.py
@@ -284,11 +284,11 @@ class RTDETRDetectionLoss(DETRLoss):
idx_groups = torch.as_tensor([0, *gt_groups[:-1]]).cumsum_(0)
for i, num_gt in enumerate(gt_groups):
if num_gt > 0:
- gt_idx = torch.arange(end=num_gt, dtype=torch.int32) + idx_groups[i]
+ gt_idx = torch.arange(end=num_gt, dtype=torch.long) + idx_groups[i]
gt_idx = gt_idx.repeat(dn_num_group)
assert len(dn_pos_idx[i]) == len(gt_idx), 'Expected the same length, '
f'but got {len(dn_pos_idx[i])} and {len(gt_idx)} respectively.'
dn_match_indices.append((dn_pos_idx[i], gt_idx))
else:
- dn_match_indices.append((torch.zeros([0], dtype=torch.int32), torch.zeros([0], dtype=torch.int32)))
+ dn_match_indices.append((torch.zeros([0], dtype=torch.long), torch.zeros([0], dtype=torch.long)))
return dn_match_indices
diff --git a/ultralytics/vit/utils/ops.py b/ultralytics/vit/utils/ops.py
index 658598721..4b3793192 100644
--- a/ultralytics/vit/utils/ops.py
+++ b/ultralytics/vit/utils/ops.py
@@ -31,9 +31,6 @@ class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
_cost_mask(bs, num_gts, masks=None, gt_mask=None): Computes the mask cost and dice cost if masks are predicted.
"""
- class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
- ...
-
def __init__(self, cost_gain=None, use_fl=True, with_mask=False, num_sample_points=12544, alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0):
super().__init__()
if cost_gain is None:
@@ -74,7 +71,7 @@ class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
bs, nq, nc = pred_scores.shape
if sum(gt_groups) == 0:
- return [(torch.tensor([], dtype=torch.int32), torch.tensor([], dtype=torch.int32)) for _ in range(bs)]
+ return [(torch.tensor([], dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor([], dtype=torch.long)) for _ in range(bs)]
# We flatten to compute the cost matrices in a batch
# [batch_size * num_queries, num_classes]
@@ -110,7 +107,7 @@ class HungarianMatcher(nn.Module):
indices = [linear_sum_assignment(c[i]) for i, c in enumerate(C.split(gt_groups, -1))]
gt_groups = torch.as_tensor([0, *gt_groups[:-1]]).cumsum_(0)
# (idx for queries, idx for gt)
- return [(torch.tensor(i, dtype=torch.int32), torch.tensor(j, dtype=torch.int32) + gt_groups[k])
+ return [(torch.tensor(i, dtype=torch.long), torch.tensor(j, dtype=torch.long) + gt_groups[k])
for k, (i, j) in enumerate(indices)]
def _cost_mask(self, bs, num_gts, masks=None, gt_mask=None):
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/__init__.py b/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/__init__.py
index ea112e4c5..0876919b0 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/__init__.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/__init__.py
@@ -16,16 +16,18 @@ from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (DEFAULT_CFG, DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, DEFAULT_CFG_P
# Define valid tasks and modes
MODES = 'train', 'val', 'predict', 'export', 'track', 'benchmark'
TASKS = 'detect', 'segment', 'classify', 'pose'
-TASK2DATA = {
- 'detect': 'coco128.yaml',
- 'segment': 'coco128-seg.yaml',
- 'classify': 'imagenet100',
- 'pose': 'coco8-pose.yaml'}
+TASK2DATA = {'detect': 'coco8.yaml', 'segment': 'coco8-seg.yaml', 'classify': 'imagenet100', 'pose': 'coco8-pose.yaml'}
TASK2MODEL = {
'detect': 'yolov8n.pt',
'segment': 'yolov8n-seg.pt',
'classify': 'yolov8n-cls.pt',
'pose': 'yolov8n-pose.pt'}
+TASK2METRIC = {
+ 'detect': 'metrics/mAP50-95(B)',
+ 'segment': 'metrics/mAP50-95(M)',
+ 'classify': 'metrics/accuracy_top1',
+ 'pose': 'metrics/mAP50-95(P)'}
+
CLI_HELP_MSG = \
f"""
@@ -366,10 +368,17 @@ def entrypoint(debug=''):
if model is None:
model = 'yolov8n.pt'
LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ 'model' is missing. Using default 'model={model}'.")
- from ultralytics.yolo.engine.model import YOLO
overrides['model'] = model
kwargs = {k: overrides[k] for k in ('nc', 'activation') if k in overrides} # model kwargs (optional)
- model = YOLO(model, task=task, **kwargs)
+ if 'rtdetr' in model.lower(): # guess architecture
+ from ultralytics import RTDETR
+ model = RTDETR(model) # no task argument
+ elif 'sam' in model.lower():
+ from ultralytics import SAM
+ model = SAM(model)
+ else:
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+ model = YOLO(model, task=task, **kwargs)
if isinstance(overrides.get('pretrained'), str):
model.load(overrides['pretrained'])
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml b/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml
index 4f16ed452..feadf0154 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/cfg/default.yaml
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ data: # (str, optional) path to data file, i.e. coco128.yaml
epochs: 100 # (int) number of epochs to train for
patience: 50 # (int) epochs to wait for no observable improvement for early stopping of training
batch: 16 # (int) number of images per batch (-1 for AutoBatch)
-imgsz: 640 # (int) size of input images as integer or w,h
+imgsz: 640 # (int | list) input images size as int for train and val modes, or list[w,h] for predict and export modes
save: True # (bool) save train checkpoints and predict results
save_period: -1 # (int) Save checkpoint every x epochs (disabled if < 1)
cache: False # (bool) True/ram, disk or False. Use cache for data loading
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ workers: 8 # (int) number of worker threads for data loading (per RANK if DDP)
project: # (str, optional) project name
name: # (str, optional) experiment name, results saved to 'project/name' directory
exist_ok: False # (bool) whether to overwrite existing experiment
-pretrained: True # (bool) whether to use a pretrained model
+pretrained: True # (bool | str) whether to use a pretrained model (bool) or a model to load weights from (str)
optimizer: auto # (str) optimizer to use, choices=[SGD, Adam, Adamax, AdamW, NAdam, RAdam, RMSProp, auto]
verbose: True # (bool) whether to print verbose output
seed: 0 # (int) random seed for reproducibility
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ deterministic: True # (bool) whether to enable deterministic mode
single_cls: False # (bool) train multi-class data as single-class
rect: False # (bool) rectangular training if mode='train' or rectangular validation if mode='val'
cos_lr: False # (bool) use cosine learning rate scheduler
-close_mosaic: 0 # (int) disable mosaic augmentation for final epochs
+close_mosaic: 10 # (int) disable mosaic augmentation for final epochs
resume: False # (bool) resume training from last checkpoint
amp: True # (bool) Automatic Mixed Precision (AMP) training, choices=[True, False], True runs AMP check
fraction: 1.0 # (float) dataset fraction to train on (default is 1.0, all images in train set)
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/data/augment.py b/ultralytics/yolo/data/augment.py
index 42688c97c..f3c44834c 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/data/augment.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/data/augment.py
@@ -427,7 +427,7 @@ class RandomPerspective:
"""
if self.pre_transform and 'mosaic_border' not in labels:
labels = self.pre_transform(labels)
- labels.pop('ratio_pad') # do not need ratio pad
+ labels.pop('ratio_pad', None) # do not need ratio pad
img = labels['img']
cls = labels['cls']
@@ -772,10 +772,10 @@ def v8_transforms(dataset, imgsz, hyp, stretch=False):
perspective=hyp.perspective,
pre_transform=None if stretch else LetterBox(new_shape=(imgsz, imgsz)),
)])
- flip_idx = dataset.data.get('flip_idx', None) # for keypoints augmentation
+ flip_idx = dataset.data.get('flip_idx', []) # for keypoints augmentation
if dataset.use_keypoints:
kpt_shape = dataset.data.get('kpt_shape', None)
- if flip_idx is None and hyp.fliplr > 0.0:
+ if len(flip_idx) == 0 and hyp.fliplr > 0.0:
hyp.fliplr = 0.0
LOGGER.warning("WARNING ⚠️ No 'flip_idx' array defined in data.yaml, setting augmentation 'fliplr=0.0'")
elif flip_idx and (len(flip_idx) != kpt_shape[0]):
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/data/converter.py b/ultralytics/yolo/data/converter.py
index aa391b6c5..c1278dd95 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/data/converter.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/data/converter.py
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ def convert_coco(labels_dir='../coco/annotations/', use_segments=False, use_keyp
data = json.load(f)
# Create image dict
- images = {'%g' % x['id']: x for x in data['images']}
+ images = {f'{x["id"]:d}': x for x in data['images']}
# Create image-annotations dict
imgToAnns = defaultdict(list)
for ann in data['annotations']:
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ def convert_coco(labels_dir='../coco/annotations/', use_segments=False, use_keyp
# Write labels file
for img_id, anns in tqdm(imgToAnns.items(), desc=f'Annotations {json_file}'):
- img = images['%g' % img_id]
+ img = images[f'{img_id:d}']
h, w, f = img['height'], img['width'], img['file_name']
bboxes = []
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/data/dataloaders/stream_loaders.py b/ultralytics/yolo/data/dataloaders/stream_loaders.py
index 400cee69f..f497cb1c1 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/data/dataloaders/stream_loaders.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/data/dataloaders/stream_loaders.py
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ class LoadStreams:
sources = Path(sources).read_text().rsplit() if os.path.isfile(sources) else [sources]
n = len(sources)
self.sources = [ops.clean_str(x) for x in sources] # clean source names for later
- self.imgs, self.fps, self.frames, self.threads = [None] * n, [0] * n, [0] * n, [None] * n
+ self.imgs, self.fps, self.frames, self.threads, self.shape = [[]] * n, [0] * n, [0] * n, [None] * n, [None] * n
for i, s in enumerate(sources): # index, source
# Start thread to read frames from video stream
st = f'{i + 1}/{n}: {s}... '
@@ -59,9 +59,11 @@ class LoadStreams:
self.frames[i] = max(int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT)), 0) or float('inf') # infinite stream fallback
self.fps[i] = max((fps if math.isfinite(fps) else 0) % 100, 0) or 30 # 30 FPS fallback
- success, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame
- if not success or self.imgs[i] is None:
+ success, im = cap.read() # guarantee first frame
+ if not success or im is None:
raise ConnectionError(f'{st}Failed to read images from {s}')
+ self.imgs[i].append(im)
+ self.shape[i] = im.shape
self.threads[i] = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap, s]), daemon=True)
LOGGER.info(f'{st}Success ✅ ({self.frames[i]} frames of shape {w}x{h} at {self.fps[i]:.2f} FPS)')
self.threads[i].start()
@@ -74,17 +76,20 @@ class LoadStreams:
"""Read stream `i` frames in daemon thread."""
n, f = 0, self.frames[i] # frame number, frame array
while cap.isOpened() and n < f:
- n += 1
- cap.grab() # .read() = .grab() followed by .retrieve()
- if n % self.vid_stride == 0:
- success, im = cap.retrieve()
- if success:
- self.imgs[i] = im
- else:
- LOGGER.warning('WARNING ⚠️ Video stream unresponsive, please check your IP camera connection.')
- self.imgs[i] = np.zeros_like(self.imgs[i])
- cap.open(stream) # re-open stream if signal was lost
- time.sleep(0.0) # wait time
+ # Only read a new frame if the buffer is empty
+ if not self.imgs[i]:
+ n += 1
+ cap.grab() # .read() = .grab() followed by .retrieve()
+ if n % self.vid_stride == 0:
+ success, im = cap.retrieve()
+ if success:
+ self.imgs[i].append(im) # add image to buffer
+ else:
+ LOGGER.warning('WARNING ⚠️ Video stream unresponsive, please check your IP camera connection.')
+ self.imgs[i].append(np.zeros(self.shape[i]))
+ cap.open(stream) # re-open stream if signal was lost
+ else:
+ time.sleep(0.01) # wait until the buffer is empty
def __iter__(self):
"""Iterates through YOLO image feed and re-opens unresponsive streams."""
@@ -92,14 +97,18 @@ class LoadStreams:
return self
def __next__(self):
- """Returns source paths, transformed and original images for processing YOLOv5."""
+ """Returns source paths, transformed and original images for processing."""
self.count += 1
- if not all(x.is_alive() for x in self.threads) or cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- raise StopIteration
- im0 = self.imgs.copy()
- return self.sources, im0, None, ''
+ # Wait until a frame is available in each buffer
+ while not all(self.imgs):
+ if not all(x.is_alive() for x in self.threads) or cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit
+ cv2.destroyAllWindows()
+ raise StopIteration
+ time.sleep(1 / min(self.fps))
+
+ # Get and remove the next frame from imgs buffer
+ return self.sources, [x.pop(0) for x in self.imgs], None, ''
def __len__(self):
"""Return the length of the sources object."""
@@ -294,10 +303,31 @@ class LoadPilAndNumpy:
class LoadTensor:
- def __init__(self, imgs) -> None:
- self.im0 = imgs
- self.bs = imgs.shape[0]
+ def __init__(self, im0) -> None:
+ self.im0 = self._single_check(im0)
+ self.bs = self.im0.shape[0]
self.mode = 'image'
+ self.paths = [getattr(im, 'filename', f'image{i}.jpg') for i, im in enumerate(im0)]
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _single_check(im, stride=32):
+ """Validate and format an image to torch.Tensor."""
+ s = f'WARNING ⚠️ torch.Tensor inputs should be BCHW i.e. shape(1, 3, 640, 640) ' \
+ f'divisible by stride {stride}. Input shape{tuple(im.shape)} is incompatible.'
+ if len(im.shape) != 4:
+ if len(im.shape) == 3:
+ LOGGER.warning(s)
+ im = im.unsqueeze(0)
+ else:
+ raise ValueError(s)
+ if im.shape[2] % stride or im.shape[3] % stride:
+ raise ValueError(s)
+ if im.max() > 1.0:
+ LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ torch.Tensor inputs should be normalized 0.0-1.0 but max value is {im.max()}. '
+ f'Dividing input by 255.')
+ im = im.float() / 255.0
+
+ return im
def __iter__(self):
"""Returns an iterator object."""
@@ -309,7 +339,7 @@ class LoadTensor:
if self.count == 1:
raise StopIteration
self.count += 1
- return None, self.im0, None, '' # self.paths, im, self.im0, None, ''
+ return self.paths, self.im0, None, ''
def __len__(self):
"""Returns the batch size."""
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py b/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py
index a3338fec7..a4ce973be 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py
@@ -226,7 +226,7 @@ def check_det_dataset(dataset, autodownload=True):
if not path.is_absolute():
path = (DATASETS_DIR / path).resolve()
- data['path'] = path # download scripts
+ data['path'] = path # download scripts
for k in 'train', 'val', 'test':
if data.get(k): # prepend path
if isinstance(data[k], str):
@@ -268,28 +268,33 @@ def check_det_dataset(dataset, autodownload=True):
def check_cls_dataset(dataset: str, split=''):
"""
- Check a classification dataset such as Imagenet.
+ Checks a classification dataset such as Imagenet.
- This function takes a `dataset` name as input and returns a dictionary containing information about the dataset.
- If the dataset is not found, it attempts to download the dataset from the internet and save it locally.
+ This function accepts a `dataset` name and attempts to retrieve the corresponding dataset information.
+ If the dataset is not found locally, it attempts to download the dataset from the internet and save it locally.
Args:
- dataset (str): Name of the dataset.
- split (str, optional): Dataset split, either 'val', 'test', or ''. Defaults to ''.
+ dataset (str): The name of the dataset.
+ split (str, optional): The split of the dataset. Either 'val', 'test', or ''. Defaults to ''.
Returns:
- data (dict): A dictionary containing the following keys and values:
- 'train': Path object for the directory containing the training set of the dataset
- 'val': Path object for the directory containing the validation set of the dataset
- 'test': Path object for the directory containing the test set of the dataset
- 'nc': Number of classes in the dataset
- 'names': List of class names in the dataset
+ dict: A dictionary containing the following keys:
+ - 'train' (Path): The directory path containing the training set of the dataset.
+ - 'val' (Path): The directory path containing the validation set of the dataset.
+ - 'test' (Path): The directory path containing the test set of the dataset.
+ - 'nc' (int): The number of classes in the dataset.
+ - 'names' (dict): A dictionary of class names in the dataset.
+
+ Raises:
+ FileNotFoundError: If the specified dataset is not found and cannot be downloaded.
"""
- data_dir = (DATASETS_DIR / dataset).resolve()
+
+ dataset = Path(dataset)
+ data_dir = (dataset if dataset.is_dir() else (DATASETS_DIR / dataset)).resolve()
if not data_dir.is_dir():
LOGGER.info(f'\nDataset not found ⚠️, missing path {data_dir}, attempting download...')
t = time.time()
- if dataset == 'imagenet':
+ if str(dataset) == 'imagenet':
subprocess.run(f"bash {ROOT / 'yolo/data/scripts/get_imagenet.sh'}", shell=True, check=True)
else:
url = f'https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v1.0/{dataset}.zip'
@@ -312,12 +317,12 @@ def check_cls_dataset(dataset: str, split=''):
class HUBDatasetStats():
"""
- Class for generating HUB dataset JSON and `-hub` dataset directory
+ A class for generating HUB dataset JSON and `-hub` dataset directory.
- Arguments
- path: Path to data.yaml or data.zip (with data.yaml inside data.zip)
- task: Dataset task. Options are 'detect', 'segment', 'pose', 'classify'.
- autodownload: Attempt to download dataset if not found locally
+ Args:
+ path (str): Path to data.yaml or data.zip (with data.yaml inside data.zip). Default is 'coco128.yaml'.
+ task (str): Dataset task. Options are 'detect', 'segment', 'pose', 'classify'. Default is 'detect'.
+ autodownload (bool): Attempt to download dataset if not found locally. Default is False.
Usage
from ultralytics.yolo.data.utils import HUBDatasetStats
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/exporter.py b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/exporter.py
index 8017a2f70..8401bbf5c 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/exporter.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/exporter.py
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@ TensorFlow Lite | `tflite` | yolov8n.tflite
TensorFlow Edge TPU | `edgetpu` | yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite
TensorFlow.js | `tfjs` | yolov8n_web_model/
PaddlePaddle | `paddle` | yolov8n_paddle_model/
+NCNN | `ncnn` | yolov8n_ncnn_model/
Requirements:
$ pip install ultralytics[export]
@@ -49,7 +50,7 @@ TensorFlow.js:
"""
import json
import os
-import platform
+import shutil
import subprocess
import time
import warnings
@@ -59,18 +60,17 @@ from pathlib import Path
import torch
from ultralytics.nn.autobackend import check_class_names
-from ultralytics.nn.modules import C2f, Detect, Segment
+from ultralytics.nn.modules import C2f, Detect, RTDETRDecoder
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import DetectionModel, SegmentationModel
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
-from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (DEFAULT_CFG, LINUX, LOGGER, MACOS, __version__, callbacks, colorstr,
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (ARM64, DEFAULT_CFG, LINUX, LOGGER, MACOS, ROOT, __version__, callbacks, colorstr,
get_default_args, yaml_save)
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_imgsz, check_requirements, check_version
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads import attempt_download_asset, get_github_assets
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.files import file_size
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.ops import Profile
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils import get_latest_opset, select_device, smart_inference_mode
-ARM64 = platform.machine() in ('arm64', 'aarch64')
-
def export_formats():
"""YOLOv8 export formats."""
@@ -87,7 +87,8 @@ def export_formats():
['TensorFlow Lite', 'tflite', '.tflite', True, False],
['TensorFlow Edge TPU', 'edgetpu', '_edgetpu.tflite', True, False],
['TensorFlow.js', 'tfjs', '_web_model', True, False],
- ['PaddlePaddle', 'paddle', '_paddle_model', True, True], ]
+ ['PaddlePaddle', 'paddle', '_paddle_model', True, True],
+ ['NCNN', 'ncnn', '_ncnn_model', True, True], ]
return pandas.DataFrame(x, columns=['Format', 'Argument', 'Suffix', 'CPU', 'GPU'])
@@ -153,20 +154,21 @@ class Exporter:
flags = [x == format for x in fmts]
if sum(flags) != 1:
raise ValueError(f"Invalid export format='{format}'. Valid formats are {fmts}")
- jit, onnx, xml, engine, coreml, saved_model, pb, tflite, edgetpu, tfjs, paddle = flags # export booleans
+ jit, onnx, xml, engine, coreml, saved_model, pb, tflite, edgetpu, tfjs, paddle, ncnn = flags # export booleans
# Load PyTorch model
self.device = select_device('cpu' if self.args.device is None else self.args.device)
+
+ # Checks
+ model.names = check_class_names(model.names)
if self.args.half and onnx and self.device.type == 'cpu':
LOGGER.warning('WARNING ⚠️ half=True only compatible with GPU export, i.e. use device=0')
self.args.half = False
assert not self.args.dynamic, 'half=True not compatible with dynamic=True, i.e. use only one.'
-
- # Checks
- model.names = check_class_names(model.names)
self.imgsz = check_imgsz(self.args.imgsz, stride=model.stride, min_dim=2) # check image size
if self.args.optimize:
- assert self.device.type == 'cpu', '--optimize not compatible with cuda devices, i.e. use --device cpu'
+ assert not ncnn, "optimize=True not compatible with format='ncnn', i.e. use optimize=False"
+ assert self.device.type == 'cpu', "optimize=True not compatible with cuda devices, i.e. use device='cpu'"
if edgetpu and not LINUX:
raise SystemError('Edge TPU export only supported on Linux. See https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/compiler/')
@@ -185,7 +187,7 @@ class Exporter:
model.float()
model = model.fuse()
for k, m in model.named_modules():
- if isinstance(m, (Detect, Segment)):
+ if isinstance(m, (Detect, RTDETRDecoder)): # Segment and Pose use Detect base class
m.dynamic = self.args.dynamic
m.export = True
m.format = self.args.format
@@ -199,7 +201,7 @@ class Exporter:
if self.args.half and (engine or onnx) and self.device.type != 'cpu':
im, model = im.half(), model.half() # to FP16
- # Warnings
+ # Filter warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=torch.jit.TracerWarning) # suppress TracerWarning
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=UserWarning) # suppress shape prim::Constant missing ONNX warning
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=DeprecationWarning) # suppress CoreML np.bool deprecation warning
@@ -224,14 +226,14 @@ class Exporter:
'imgsz': self.imgsz,
'names': model.names} # model metadata
if model.task == 'pose':
- self.metadata['kpt_shape'] = model.kpt_shape
+ self.metadata['kpt_shape'] = model.model[-1].kpt_shape
LOGGER.info(f"\n{colorstr('PyTorch:')} starting from {file} with input shape {tuple(im.shape)} BCHW and "
f'output shape(s) {self.output_shape} ({file_size(file):.1f} MB)')
# Exports
f = [''] * len(fmts) # exported filenames
- if jit: # TorchScript
+ if jit or ncnn: # TorchScript
f[0], _ = self.export_torchscript()
if engine: # TensorRT required before ONNX
f[1], _ = self.export_engine()
@@ -254,6 +256,8 @@ class Exporter:
f[9], _ = self.export_tfjs()
if paddle: # PaddlePaddle
f[10], _ = self.export_paddle()
+ if ncnn: # NCNN
+ f[11], _ = self.export_ncnn()
# Finish
f = [str(x) for x in f if x] # filter out '' and None
@@ -394,6 +398,59 @@ class Exporter:
yaml_save(Path(f) / 'metadata.yaml', self.metadata) # add metadata.yaml
return f, None
+ @try_export
+ def export_ncnn(self, prefix=colorstr('NCNN:')):
+ """
+ YOLOv8 NCNN export using PNNX https://github.com/pnnx/pnnx.
+ """
+ check_requirements('git+https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn.git' if ARM64 else 'ncnn') # requires NCNN
+ import ncnn # noqa
+
+ LOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with NCNN {ncnn.__version__}...')
+ f = Path(str(self.file).replace(self.file.suffix, f'_ncnn_model{os.sep}'))
+ f_ts = str(self.file.with_suffix('.torchscript'))
+
+ if Path('./pnnx').is_file():
+ pnnx = './pnnx'
+ elif (ROOT / 'pnnx').is_file():
+ pnnx = ROOT / 'pnnx'
+ else:
+ LOGGER.warning(
+ f'{prefix} WARNING ⚠️ PNNX not found. Attempting to download binary file from '
+ 'https://github.com/pnnx/pnnx/.\nNote PNNX Binary file must be placed in current working directory '
+ f'or in {ROOT}. See PNNX repo for full installation instructions.')
+ _, assets = get_github_assets(repo='pnnx/pnnx')
+ asset = [x for x in assets if ('macos' if MACOS else 'ubuntu' if LINUX else 'windows') in x][0]
+ attempt_download_asset(asset, repo='pnnx/pnnx', release='latest')
+ unzip_dir = Path(asset).with_suffix('')
+ pnnx = ROOT / 'pnnx' # new location
+ (unzip_dir / 'pnnx').rename(pnnx) # move binary to ROOT
+ shutil.rmtree(unzip_dir) # delete unzip dir
+ Path(asset).unlink() # delete zip
+ pnnx.chmod(0o777) # set read, write, and execute permissions for everyone
+
+ cmd = [
+ str(pnnx),
+ f_ts,
+ f'pnnxparam={f / "model.pnnx.param"}',
+ f'pnnxbin={f / "model.pnnx.bin"}',
+ f'pnnxpy={f / "model_pnnx.py"}',
+ f'pnnxonnx={f / "model.pnnx.onnx"}',
+ f'ncnnparam={f / "model.ncnn.param"}',
+ f'ncnnbin={f / "model.ncnn.bin"}',
+ f'ncnnpy={f / "model_ncnn.py"}',
+ f'fp16={int(self.args.half)}',
+ f'device={self.device.type}',
+ f'inputshape="{[self.args.batch, 3, *self.imgsz]}"', ]
+ f.mkdir(exist_ok=True) # make ncnn_model directory
+ LOGGER.info(f"{prefix} running '{' '.join(cmd)}'")
+ subprocess.run(cmd, check=True)
+ for f_debug in 'debug.bin', 'debug.param', 'debug2.bin', 'debug2.param': # remove debug files
+ Path(f_debug).unlink(missing_ok=True)
+
+ yaml_save(f / 'metadata.yaml', self.metadata) # add metadata.yaml
+ return str(f), None
+
@try_export
def export_coreml(self, prefix=colorstr('CoreML:')):
"""YOLOv8 CoreML export."""
@@ -447,7 +504,7 @@ class Exporter:
check_requirements('nvidia-tensorrt', cmds='-U --index-url https://pypi.ngc.nvidia.com')
import tensorrt as trt # noqa
- check_version(trt.__version__, '7.0.0', hard=True) # require tensorrt>=8.0.0
+ check_version(trt.__version__, '7.0.0', hard=True) # require tensorrt>=7.0.0
self.args.simplify = True
f_onnx, _ = self.export_onnx()
@@ -534,7 +591,7 @@ class Exporter:
# Remove/rename TFLite models
if self.args.int8:
for file in f.rglob('*_dynamic_range_quant.tflite'):
- file.rename(file.with_stem(file.stem.replace('_dynamic_range_quant', '_int8')))
+ file.rename(file.with_name(file.stem.replace('_dynamic_range_quant', '_int8') + file.suffix))
for file in f.rglob('*_integer_quant_with_int16_act.tflite'):
file.unlink() # delete extra fp16 activation TFLite files
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/model.py b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/model.py
index ece622f5d..387dae75c 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/model.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/model.py
@@ -9,8 +9,8 @@ from ultralytics.nn.tasks import (ClassificationModel, DetectionModel, PoseModel
attempt_load_one_weight, guess_model_task, nn, yaml_model_load)
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
from ultralytics.yolo.engine.exporter import Exporter
-from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (DEFAULT_CFG, DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS, LOGGER, NUM_THREADS, RANK, ROOT,
- callbacks, is_git_dir, yaml_load)
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (DEFAULT_CFG, DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, DEFAULT_CFG_KEYS, LOGGER, RANK, ROOT, callbacks,
+ is_git_dir, yaml_load)
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_file, check_imgsz, check_pip_update_available, check_yaml
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads import GITHUB_ASSET_STEMS
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils import smart_inference_mode
@@ -390,23 +390,9 @@ class YOLO:
self._check_is_pytorch_model()
self.model.to(device)
- def tune(self,
- data: str,
- space: dict = None,
- grace_period: int = 10,
- gpu_per_trial: int = None,
- max_samples: int = 10,
- train_args: dict = None):
+ def tune(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
- Runs hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune.
-
- Args:
- data (str): The dataset to run the tuner on.
- space (dict, optional): The hyperparameter search space. Defaults to None.
- grace_period (int, optional): The grace period in epochs of the ASHA scheduler. Defaults to 10.
- gpu_per_trial (int, optional): The number of GPUs to allocate per trial. Defaults to None.
- max_samples (int, optional): The maximum number of trials to run. Defaults to 10.
- train_args (dict, optional): Additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method. Defaults to {}.
+ Runs hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune. See ultralytics.yolo.utils.tuner.run_ray_tune for Args.
Returns:
(dict): A dictionary containing the results of the hyperparameter search.
@@ -414,66 +400,9 @@ class YOLO:
Raises:
ModuleNotFoundError: If Ray Tune is not installed.
"""
- if train_args is None:
- train_args = {}
-
- try:
- from ultralytics.yolo.utils.tuner import (ASHAScheduler, RunConfig, WandbLoggerCallback, default_space,
- task_metric_map, tune)
- except ImportError:
- raise ModuleNotFoundError("Install Ray Tune: `pip install 'ray[tune]'`")
-
- try:
- import wandb
- from wandb import __version__ # noqa
- except ImportError:
- wandb = False
-
- def _tune(config):
- """
- Trains the YOLO model with the specified hyperparameters and additional arguments.
-
- Args:
- config (dict): A dictionary of hyperparameters to use for training.
-
- Returns:
- None.
- """
- self._reset_callbacks()
- config.update(train_args)
- self.train(**config)
-
- if not space:
- LOGGER.warning('WARNING: search space not provided. Using default search space')
- space = default_space
-
- space['data'] = data
-
- # Define the trainable function with allocated resources
- trainable_with_resources = tune.with_resources(_tune, {'cpu': NUM_THREADS, 'gpu': gpu_per_trial or 0})
-
- # Define the ASHA scheduler for hyperparameter search
- asha_scheduler = ASHAScheduler(time_attr='epoch',
- metric=task_metric_map[self.task],
- mode='max',
- max_t=train_args.get('epochs') or 100,
- grace_period=grace_period,
- reduction_factor=3)
-
- # Define the callbacks for the hyperparameter search
- tuner_callbacks = [WandbLoggerCallback(project='YOLOv8-tune')] if wandb else []
-
- # Create the Ray Tune hyperparameter search tuner
- tuner = tune.Tuner(trainable_with_resources,
- param_space=space,
- tune_config=tune.TuneConfig(scheduler=asha_scheduler, num_samples=max_samples),
- run_config=RunConfig(callbacks=tuner_callbacks, local_dir='./runs'))
-
- # Run the hyperparameter search
- tuner.fit()
-
- # Return the results of the hyperparameter search
- return tuner.get_results()
+ self._check_is_pytorch_model()
+ from ultralytics.yolo.utils.tuner import run_ray_tune
+ return run_ray_tune(self, *args, **kwargs)
@property
def names(self):
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/predictor.py b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/predictor.py
index b71785cb7..0f6eb0d38 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/predictor.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/predictor.py
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ from ultralytics.nn.autobackend import AutoBackend
from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
from ultralytics.yolo.data import load_inference_source
from ultralytics.yolo.data.augment import LetterBox, classify_transforms
-from ultralytics.yolo.utils import DEFAULT_CFG, LOGGER, SETTINGS, callbacks, colorstr, ops
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import DEFAULT_CFG, LOGGER, MACOS, SETTINGS, WINDOWS, callbacks, colorstr, ops
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_imgsz, check_imshow
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.files import increment_path
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils import select_device, smart_inference_mode
@@ -116,21 +116,23 @@ class BasePredictor:
"""Prepares input image before inference.
Args:
- im (torch.Tensor | List(np.ndarray)): (N, 3, h, w) for tensor, [(h, w, 3) x N] for list.
+ im (torch.Tensor | List(np.ndarray)): BCHW for tensor, [(HWC) x B] for list.
"""
- if not isinstance(im, torch.Tensor):
+ not_tensor = not isinstance(im, torch.Tensor)
+ if not_tensor:
im = np.stack(self.pre_transform(im))
im = im[..., ::-1].transpose((0, 3, 1, 2)) # BGR to RGB, BHWC to BCHW, (n, 3, h, w)
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im) # contiguous
im = torch.from_numpy(im)
- # NOTE: assuming im with (b, 3, h, w) if it's a tensor
+
img = im.to(self.device)
img = img.half() if self.model.fp16 else img.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
- img /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
+ if not_tensor:
+ img /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
return img
def pre_transform(self, im):
- """Pre-tranform input image before inference.
+ """Pre-transform input image before inference.
Args:
im (List(np.ndarray)): (N, 3, h, w) for tensor, [(h, w, 3) x N] for list.
@@ -147,8 +149,7 @@ class BasePredictor:
log_string = ''
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
- self.seen += 1
- if self.source_type.webcam or self.source_type.from_img: # batch_size >= 1
+ if self.source_type.webcam or self.source_type.from_img or self.source_type.tensor: # batch_size >= 1
log_string += f'{idx}: '
frame = self.dataset.count
else:
@@ -160,10 +161,11 @@ class BasePredictor:
log_string += result.verbose()
if self.args.save or self.args.show: # Add bbox to image
- plot_args = dict(line_width=self.args.line_width,
- boxes=self.args.boxes,
- conf=self.args.show_conf,
- labels=self.args.show_labels)
+ plot_args = {
+ 'line_width': self.args.line_width,
+ 'boxes': self.args.boxes,
+ 'conf': self.args.show_conf,
+ 'labels': self.args.show_labels}
if not self.args.retina_masks:
plot_args['im_gpu'] = im[idx]
self.plotted_img = result.plot(**plot_args)
@@ -215,12 +217,14 @@ class BasePredictor:
# Setup model
if not self.model:
self.setup_model(model)
+
# Setup source every time predict is called
self.setup_source(source if source is not None else self.args.source)
# Check if save_dir/ label file exists
if self.args.save or self.args.save_txt:
(self.save_dir / 'labels' if self.args.save_txt else self.save_dir).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
+
# Warmup model
if not self.done_warmup:
self.model.warmup(imgsz=(1 if self.model.pt or self.model.triton else self.dataset.bs, 3, *self.imgsz))
@@ -251,13 +255,12 @@ class BasePredictor:
# Visualize, save, write results
n = len(im0s)
for i in range(n):
+ self.seen += 1
self.results[i].speed = {
'preprocess': profilers[0].dt * 1E3 / n,
'inference': profilers[1].dt * 1E3 / n,
'postprocess': profilers[2].dt * 1E3 / n}
- if self.source_type.tensor: # skip write, show and plot operations if input is raw tensor
- continue
- p, im0 = path[i], im0s[i].copy()
+ p, im0 = path[i], None if self.source_type.tensor else im0s[i].copy()
p = Path(p)
if self.args.verbose or self.args.save or self.args.save_txt or self.args.show:
@@ -284,7 +287,7 @@ class BasePredictor:
if self.args.verbose and self.seen:
t = tuple(x.t / self.seen * 1E3 for x in profilers) # speeds per image
LOGGER.info(f'Speed: %.1fms preprocess, %.1fms inference, %.1fms postprocess per image at shape '
- f'{(1, 3, *self.imgsz)}' % t)
+ f'{(1, 3, *im.shape[2:])}' % t)
if self.args.save or self.args.save_txt or self.args.save_crop:
nl = len(list(self.save_dir.glob('labels/*.txt'))) # number of labels
s = f"\n{nl} label{'s' * (nl > 1)} saved to {self.save_dir / 'labels'}" if self.args.save_txt else ''
@@ -334,8 +337,10 @@ class BasePredictor:
h = int(vid_cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
else: # stream
fps, w, h = 30, im0.shape[1], im0.shape[0]
- save_path = str(Path(save_path).with_suffix('.mp4')) # force *.mp4 suffix on results videos
- self.vid_writer[idx] = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), fps, (w, h))
+ suffix = '.mp4' if MACOS else '.avi' if WINDOWS else '.avi'
+ fourcc = 'avc1' if MACOS else 'WMV2' if WINDOWS else 'MJPG'
+ save_path = str(Path(save_path).with_suffix(suffix))
+ self.vid_writer[idx] = cv2.VideoWriter(save_path, cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*fourcc), fps, (w, h))
self.vid_writer[idx].write(im0)
def run_callbacks(self, event: str):
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/results.py b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/results.py
index 68e0de2d7..4e9f6f317 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/results.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/results.py
@@ -198,6 +198,9 @@ class Results(SimpleClass):
Returns:
(numpy.ndarray): A numpy array of the annotated image.
"""
+ if img is None and isinstance(self.orig_img, torch.Tensor):
+ img = np.ascontiguousarray(self.orig_img[0].permute(1, 2, 0).cpu().detach().numpy()) * 255
+
# Deprecation warn TODO: remove in 8.2
if 'show_conf' in kwargs:
deprecation_warn('show_conf', 'conf')
@@ -287,8 +290,8 @@ class Results(SimpleClass):
seg = masks[j].xyn[0].copy().reshape(-1) # reversed mask.xyn, (n,2) to (n*2)
line = (c, *seg)
if kpts is not None:
- kpt = kpts[j].xyn.reshape(-1).tolist()
- line += (*kpt, )
+ kpt = torch.cat((kpts[j].xyn, kpts[j].conf[..., None]), 2) if kpts[j].has_visible else kpts[j].xyn
+ line += (*kpt.reshape(-1).tolist(), )
line += (conf, ) * save_conf + (() if id is None else (id, ))
texts.append(('%g ' * len(line)).rstrip() % line)
@@ -305,7 +308,7 @@ class Results(SimpleClass):
file_name (str | pathlib.Path): File name.
"""
if self.probs is not None:
- LOGGER.warning('Warning: Classify task do not support `save_crop`.')
+ LOGGER.warning('WARNING ⚠️ Classify task do not support `save_crop`.')
return
if isinstance(save_dir, str):
save_dir = Path(save_dir)
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/trainer.py b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/trainer.py
index e4925b345..144be9c8d 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/engine/trainer.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/engine/trainer.py
@@ -197,10 +197,11 @@ class BaseTrainer:
self.device = torch.device('cuda', RANK)
LOGGER.info(f'DDP info: RANK {RANK}, WORLD_SIZE {world_size}, DEVICE {self.device}')
os.environ['NCCL_BLOCKING_WAIT'] = '1' # set to enforce timeout
- dist.init_process_group('nccl' if dist.is_nccl_available() else 'gloo',
- timeout=timedelta(seconds=3600),
- rank=RANK,
- world_size=world_size)
+ dist.init_process_group(
+ 'nccl' if dist.is_nccl_available() else 'gloo',
+ timeout=timedelta(seconds=10800), # 3 hours
+ rank=RANK,
+ world_size=world_size)
def _setup_train(self, world_size):
"""
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/__init__.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8f47772fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+
+from .model import FastSAM
+from .predict import FastSAMPredictor
+from .prompt import FastSAMPrompt
+from .val import FastSAMValidator
+
+__all__ = 'FastSAMPredictor', 'FastSAM', 'FastSAMPrompt', 'FastSAMValidator'
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/model.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/model.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..36c7d4270
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/model.py
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+"""
+FastSAM model interface.
+
+Usage - Predict:
+ from ultralytics import FastSAM
+
+ model = FastSAM('last.pt')
+ results = model.predict('ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg')
+"""
+
+from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import get_cfg
+from ultralytics.yolo.engine.exporter import Exporter
+from ultralytics.yolo.engine.model import YOLO
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import DEFAULT_CFG, LOGGER, ROOT, is_git_dir
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_imgsz
+
+from ...yolo.utils.torch_utils import model_info, smart_inference_mode
+from .predict import FastSAMPredictor
+
+
+class FastSAM(YOLO):
+
+ def __init__(self, model='FastSAM-x.pt'):
+ """Call the __init__ method of the parent class (YOLO) with the updated default model"""
+ if model == 'FastSAM.pt':
+ model = 'FastSAM-x.pt'
+ super().__init__(model=model)
+ # any additional initialization code for FastSAM
+
+ @smart_inference_mode()
+ def predict(self, source=None, stream=False, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Perform prediction using the YOLO model.
+
+ Args:
+ source (str | int | PIL | np.ndarray): The source of the image to make predictions on.
+ Accepts all source types accepted by the YOLO model.
+ stream (bool): Whether to stream the predictions or not. Defaults to False.
+ **kwargs : Additional keyword arguments passed to the predictor.
+ Check the 'configuration' section in the documentation for all available options.
+
+ Returns:
+ (List[ultralytics.yolo.engine.results.Results]): The prediction results.
+ """
+ if source is None:
+ source = ROOT / 'assets' if is_git_dir() else 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+ LOGGER.warning(f"WARNING ⚠️ 'source' is missing. Using 'source={source}'.")
+ overrides = self.overrides.copy()
+ overrides['conf'] = 0.25
+ overrides.update(kwargs) # prefer kwargs
+ overrides['mode'] = kwargs.get('mode', 'predict')
+ assert overrides['mode'] in ['track', 'predict']
+ overrides['save'] = kwargs.get('save', False) # do not save by default if called in Python
+ self.predictor = FastSAMPredictor(overrides=overrides)
+ self.predictor.setup_model(model=self.model, verbose=False)
+
+ return self.predictor(source, stream=stream)
+
+ def train(self, **kwargs):
+ """Function trains models but raises an error as FastSAM models do not support training."""
+ raise NotImplementedError("FastSAM models don't support training")
+
+ def val(self, **kwargs):
+ """Run validation given dataset."""
+ overrides = dict(task='segment', mode='val')
+ overrides.update(kwargs) # prefer kwargs
+ args = get_cfg(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, overrides=overrides)
+ args.imgsz = check_imgsz(args.imgsz, max_dim=1)
+ validator = FastSAM(args=args)
+ validator(model=self.model)
+ self.metrics = validator.metrics
+ return validator.metrics
+
+ @smart_inference_mode()
+ def export(self, **kwargs):
+ """
+ Export model.
+
+ Args:
+ **kwargs : Any other args accepted by the predictors. To see all args check 'configuration' section in docs
+ """
+ overrides = dict(task='detect')
+ overrides.update(kwargs)
+ overrides['mode'] = 'export'
+ args = get_cfg(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, overrides=overrides)
+ args.task = self.task
+ if args.imgsz == DEFAULT_CFG.imgsz:
+ args.imgsz = self.model.args['imgsz'] # use trained imgsz unless custom value is passed
+ if args.batch == DEFAULT_CFG.batch:
+ args.batch = 1 # default to 1 if not modified
+ return Exporter(overrides=args)(model=self.model)
+
+ def info(self, detailed=False, verbose=True):
+ """
+ Logs model info.
+
+ Args:
+ detailed (bool): Show detailed information about model.
+ verbose (bool): Controls verbosity.
+ """
+ return model_info(self.model, detailed=detailed, verbose=verbose, imgsz=640)
+
+ def __call__(self, source=None, stream=False, **kwargs):
+ """Calls the 'predict' function with given arguments to perform object detection."""
+ return self.predict(source, stream, **kwargs)
+
+ def __getattr__(self, attr):
+ """Raises error if object has no requested attribute."""
+ name = self.__class__.__name__
+ raise AttributeError(f"'{name}' object has no attribute '{attr}'. See valid attributes below.\n{self.__doc__}")
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/predict.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/predict.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0a6ac277c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/predict.py
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+
+import torch
+
+from ultralytics.yolo.engine.results import Results
+from ultralytics.yolo.fastsam.utils import bbox_iou
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import DEFAULT_CFG, ops
+from ultralytics.yolo.v8.detect.predict import DetectionPredictor
+
+
+class FastSAMPredictor(DetectionPredictor):
+
+ def __init__(self, cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, overrides=None, _callbacks=None):
+ super().__init__(cfg, overrides, _callbacks)
+ self.args.task = 'segment'
+
+ def postprocess(self, preds, img, orig_imgs):
+ """TODO: filter by classes."""
+ p = ops.non_max_suppression(preds[0],
+ self.args.conf,
+ self.args.iou,
+ agnostic=self.args.agnostic_nms,
+ max_det=self.args.max_det,
+ nc=len(self.model.names),
+ classes=self.args.classes)
+ full_box = torch.zeros_like(p[0][0])
+ full_box[2], full_box[3], full_box[4], full_box[6:] = img.shape[3], img.shape[2], 1.0, 1.0
+ full_box = full_box.view(1, -1)
+ critical_iou_index = bbox_iou(full_box[0][:4], p[0][:, :4], iou_thres=0.9, image_shape=img.shape[2:])
+ if critical_iou_index.numel() != 0:
+ full_box[0][4] = p[0][critical_iou_index][:, 4]
+ full_box[0][6:] = p[0][critical_iou_index][:, 6:]
+ p[0][critical_iou_index] = full_box
+ results = []
+ proto = preds[1][-1] if len(preds[1]) == 3 else preds[1] # second output is len 3 if pt, but only 1 if exported
+ for i, pred in enumerate(p):
+ orig_img = orig_imgs[i] if isinstance(orig_imgs, list) else orig_imgs
+ path = self.batch[0]
+ img_path = path[i] if isinstance(path, list) else path
+ if not len(pred): # save empty boxes
+ results.append(Results(orig_img=orig_img, path=img_path, names=self.model.names, boxes=pred[:, :6]))
+ continue
+ if self.args.retina_masks:
+ if not isinstance(orig_imgs, torch.Tensor):
+ pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape)
+ masks = ops.process_mask_native(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape[:2]) # HWC
+ else:
+ masks = ops.process_mask(proto[i], pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], img.shape[2:], upsample=True) # HWC
+ if not isinstance(orig_imgs, torch.Tensor):
+ pred[:, :4] = ops.scale_boxes(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], orig_img.shape)
+ results.append(
+ Results(orig_img=orig_img, path=img_path, names=self.model.names, boxes=pred[:, :6], masks=masks))
+ return results
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/prompt.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/prompt.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d34968d8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/prompt.py
@@ -0,0 +1,406 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+
+import os
+
+import cv2
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+from PIL import Image
+
+
+class FastSAMPrompt:
+
+ def __init__(self, img_path, results, device='cuda') -> None:
+ # self.img_path = img_path
+ self.device = device
+ self.results = results
+ self.img_path = img_path
+ self.ori_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
+
+ # Import and assign clip
+ try:
+ import clip # for linear_assignment
+ except ImportError:
+ from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_requirements
+ check_requirements('git+https://github.com/openai/CLIP.git') # required before installing lap from source
+ import clip
+ self.clip = clip
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _segment_image(image, bbox):
+ image_array = np.array(image)
+ segmented_image_array = np.zeros_like(image_array)
+ x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
+ segmented_image_array[y1:y2, x1:x2] = image_array[y1:y2, x1:x2]
+ segmented_image = Image.fromarray(segmented_image_array)
+ black_image = Image.new('RGB', image.size, (255, 255, 255))
+ # transparency_mask = np.zeros_like((), dtype=np.uint8)
+ transparency_mask = np.zeros((image_array.shape[0], image_array.shape[1]), dtype=np.uint8)
+ transparency_mask[y1:y2, x1:x2] = 255
+ transparency_mask_image = Image.fromarray(transparency_mask, mode='L')
+ black_image.paste(segmented_image, mask=transparency_mask_image)
+ return black_image
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _format_results(result, filter=0):
+ annotations = []
+ n = len(result.masks.data)
+ for i in range(n):
+ mask = result.masks.data[i] == 1.0
+
+ if torch.sum(mask) < filter:
+ continue
+ annotation = {
+ 'id': i,
+ 'segmentation': mask.cpu().numpy(),
+ 'bbox': result.boxes.data[i],
+ 'score': result.boxes.conf[i]}
+ annotation['area'] = annotation['segmentation'].sum()
+ annotations.append(annotation)
+ return annotations
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def filter_masks(annotations): # filter the overlap mask
+ annotations.sort(key=lambda x: x['area'], reverse=True)
+ to_remove = set()
+ for i in range(len(annotations)):
+ a = annotations[i]
+ for j in range(i + 1, len(annotations)):
+ b = annotations[j]
+ if i != j and j not in to_remove and b['area'] < a['area'] and \
+ (a['segmentation'] & b['segmentation']).sum() / b['segmentation'].sum() > 0.8:
+ to_remove.add(j)
+
+ return [a for i, a in enumerate(annotations) if i not in to_remove], to_remove
+
+ @staticmethod
+ def _get_bbox_from_mask(mask):
+ mask = mask.astype(np.uint8)
+ contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
+ x1, y1, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[0])
+ x2, y2 = x1 + w, y1 + h
+ if len(contours) > 1:
+ for b in contours:
+ x_t, y_t, w_t, h_t = cv2.boundingRect(b)
+ # 将多个bbox合并成一个
+ x1 = min(x1, x_t)
+ y1 = min(y1, y_t)
+ x2 = max(x2, x_t + w_t)
+ y2 = max(y2, y_t + h_t)
+ h = y2 - y1
+ w = x2 - x1
+ return [x1, y1, x2, y2]
+
+ def plot(self,
+ annotations,
+ output,
+ bbox=None,
+ points=None,
+ point_label=None,
+ mask_random_color=True,
+ better_quality=True,
+ retina=False,
+ withContours=True):
+ if isinstance(annotations[0], dict):
+ annotations = [annotation['segmentation'] for annotation in annotations]
+ result_name = os.path.basename(self.img_path)
+ image = self.ori_img
+ image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
+ original_h = image.shape[0]
+ original_w = image.shape[1]
+ # for macOS only
+ # plt.switch_backend('TkAgg')
+ plt.figure(figsize=(original_w / 100, original_h / 100))
+ # Add subplot with no margin.
+ plt.subplots_adjust(top=1, bottom=0, right=1, left=0, hspace=0, wspace=0)
+ plt.margins(0, 0)
+ plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator())
+ plt.gca().yaxis.set_major_locator(plt.NullLocator())
+
+ plt.imshow(image)
+ if better_quality:
+ if isinstance(annotations[0], torch.Tensor):
+ annotations = np.array(annotations.cpu())
+ for i, mask in enumerate(annotations):
+ mask = cv2.morphologyEx(mask.astype(np.uint8), cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8))
+ annotations[i] = cv2.morphologyEx(mask.astype(np.uint8), cv2.MORPH_OPEN, np.ones((8, 8), np.uint8))
+ if self.device == 'cpu':
+ annotations = np.array(annotations)
+ self.fast_show_mask(
+ annotations,
+ plt.gca(),
+ random_color=mask_random_color,
+ bbox=bbox,
+ points=points,
+ pointlabel=point_label,
+ retinamask=retina,
+ target_height=original_h,
+ target_width=original_w,
+ )
+ else:
+ if isinstance(annotations[0], np.ndarray):
+ annotations = torch.from_numpy(annotations)
+ self.fast_show_mask_gpu(
+ annotations,
+ plt.gca(),
+ random_color=mask_random_color,
+ bbox=bbox,
+ points=points,
+ pointlabel=point_label,
+ retinamask=retina,
+ target_height=original_h,
+ target_width=original_w,
+ )
+ if isinstance(annotations, torch.Tensor):
+ annotations = annotations.cpu().numpy()
+ if withContours:
+ contour_all = []
+ temp = np.zeros((original_h, original_w, 1))
+ for i, mask in enumerate(annotations):
+ if type(mask) == dict:
+ mask = mask['segmentation']
+ annotation = mask.astype(np.uint8)
+ if not retina:
+ annotation = cv2.resize(
+ annotation,
+ (original_w, original_h),
+ interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST,
+ )
+ contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(annotation, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
+ contour_all.extend(iter(contours))
+ cv2.drawContours(temp, contour_all, -1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
+ color = np.array([0 / 255, 0 / 255, 1.0, 0.8])
+ contour_mask = temp / 255 * color.reshape(1, 1, -1)
+ plt.imshow(contour_mask)
+
+ save_path = output
+ if not os.path.exists(save_path):
+ os.makedirs(save_path)
+ plt.axis('off')
+ fig = plt.gcf()
+ plt.draw()
+
+ try:
+ buf = fig.canvas.tostring_rgb()
+ except AttributeError:
+ fig.canvas.draw()
+ buf = fig.canvas.tostring_rgb()
+ cols, rows = fig.canvas.get_width_height()
+ img_array = np.frombuffer(buf, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(rows, cols, 3)
+ cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(save_path, result_name), cv2.cvtColor(img_array, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
+
+ # CPU post process
+ def fast_show_mask(
+ self,
+ annotation,
+ ax,
+ random_color=False,
+ bbox=None,
+ points=None,
+ pointlabel=None,
+ retinamask=True,
+ target_height=960,
+ target_width=960,
+ ):
+ msak_sum = annotation.shape[0]
+ height = annotation.shape[1]
+ weight = annotation.shape[2]
+ # 将annotation 按照面积 排序
+ areas = np.sum(annotation, axis=(1, 2))
+ sorted_indices = np.argsort(areas)
+ annotation = annotation[sorted_indices]
+
+ index = (annotation != 0).argmax(axis=0)
+ if random_color:
+ color = np.random.random((msak_sum, 1, 1, 3))
+ else:
+ color = np.ones((msak_sum, 1, 1, 3)) * np.array([30 / 255, 144 / 255, 1.0])
+ transparency = np.ones((msak_sum, 1, 1, 1)) * 0.6
+ visual = np.concatenate([color, transparency], axis=-1)
+ mask_image = np.expand_dims(annotation, -1) * visual
+
+ show = np.zeros((height, weight, 4))
+ h_indices, w_indices = np.meshgrid(np.arange(height), np.arange(weight), indexing='ij')
+ indices = (index[h_indices, w_indices], h_indices, w_indices, slice(None))
+ # 使用向量化索引更新show的值
+ show[h_indices, w_indices, :] = mask_image[indices]
+ if bbox is not None:
+ x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
+ ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((x1, y1), x2 - x1, y2 - y1, fill=False, edgecolor='b', linewidth=1))
+ # draw point
+ if points is not None:
+ plt.scatter(
+ [point[0] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 1],
+ [point[1] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 1],
+ s=20,
+ c='y',
+ )
+ plt.scatter(
+ [point[0] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 0],
+ [point[1] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 0],
+ s=20,
+ c='m',
+ )
+
+ if not retinamask:
+ show = cv2.resize(show, (target_width, target_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
+ ax.imshow(show)
+
+ def fast_show_mask_gpu(
+ self,
+ annotation,
+ ax,
+ random_color=False,
+ bbox=None,
+ points=None,
+ pointlabel=None,
+ retinamask=True,
+ target_height=960,
+ target_width=960,
+ ):
+ msak_sum = annotation.shape[0]
+ height = annotation.shape[1]
+ weight = annotation.shape[2]
+ areas = torch.sum(annotation, dim=(1, 2))
+ sorted_indices = torch.argsort(areas, descending=False)
+ annotation = annotation[sorted_indices]
+ # 找每个位置第一个非零值下标
+ index = (annotation != 0).to(torch.long).argmax(dim=0)
+ if random_color:
+ color = torch.rand((msak_sum, 1, 1, 3)).to(annotation.device)
+ else:
+ color = torch.ones((msak_sum, 1, 1, 3)).to(annotation.device) * torch.tensor([30 / 255, 144 / 255, 1.0]).to(
+ annotation.device)
+ transparency = torch.ones((msak_sum, 1, 1, 1)).to(annotation.device) * 0.6
+ visual = torch.cat([color, transparency], dim=-1)
+ mask_image = torch.unsqueeze(annotation, -1) * visual
+ # 按index取数,index指每个位置选哪个batch的数,把mask_image转成一个batch的形式
+ show = torch.zeros((height, weight, 4)).to(annotation.device)
+ h_indices, w_indices = torch.meshgrid(torch.arange(height), torch.arange(weight), indexing='ij')
+ indices = (index[h_indices, w_indices], h_indices, w_indices, slice(None))
+ # 使用向量化索引更新show的值
+ show[h_indices, w_indices, :] = mask_image[indices]
+ show_cpu = show.cpu().numpy()
+ if bbox is not None:
+ x1, y1, x2, y2 = bbox
+ ax.add_patch(plt.Rectangle((x1, y1), x2 - x1, y2 - y1, fill=False, edgecolor='b', linewidth=1))
+ # draw point
+ if points is not None:
+ plt.scatter(
+ [point[0] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 1],
+ [point[1] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 1],
+ s=20,
+ c='y',
+ )
+ plt.scatter(
+ [point[0] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 0],
+ [point[1] for i, point in enumerate(points) if pointlabel[i] == 0],
+ s=20,
+ c='m',
+ )
+ if not retinamask:
+ show_cpu = cv2.resize(show_cpu, (target_width, target_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
+ ax.imshow(show_cpu)
+
+ # clip
+ @torch.no_grad()
+ def retrieve(self, model, preprocess, elements, search_text: str, device) -> int:
+ preprocessed_images = [preprocess(image).to(device) for image in elements]
+ tokenized_text = self.clip.tokenize([search_text]).to(device)
+ stacked_images = torch.stack(preprocessed_images)
+ image_features = model.encode_image(stacked_images)
+ text_features = model.encode_text(tokenized_text)
+ image_features /= image_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
+ text_features /= text_features.norm(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
+ probs = 100.0 * image_features @ text_features.T
+ return probs[:, 0].softmax(dim=0)
+
+ def _crop_image(self, format_results):
+
+ image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(self.ori_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
+ ori_w, ori_h = image.size
+ annotations = format_results
+ mask_h, mask_w = annotations[0]['segmentation'].shape
+ if ori_w != mask_w or ori_h != mask_h:
+ image = image.resize((mask_w, mask_h))
+ cropped_boxes = []
+ cropped_images = []
+ not_crop = []
+ filter_id = []
+ # annotations, _ = filter_masks(annotations)
+ # filter_id = list(_)
+ for _, mask in enumerate(annotations):
+ if np.sum(mask['segmentation']) <= 100:
+ filter_id.append(_)
+ continue
+ bbox = self._get_bbox_from_mask(mask['segmentation']) # mask 的 bbox
+ cropped_boxes.append(self._segment_image(image, bbox)) # 保存裁剪的图片
+ # cropped_boxes.append(segment_image(image,mask["segmentation"]))
+ cropped_images.append(bbox) # 保存裁剪的图片的bbox
+
+ return cropped_boxes, cropped_images, not_crop, filter_id, annotations
+
+ def box_prompt(self, bbox):
+
+ assert (bbox[2] != 0 and bbox[3] != 0)
+ masks = self.results[0].masks.data
+ target_height = self.ori_img.shape[0]
+ target_width = self.ori_img.shape[1]
+ h = masks.shape[1]
+ w = masks.shape[2]
+ if h != target_height or w != target_width:
+ bbox = [
+ int(bbox[0] * w / target_width),
+ int(bbox[1] * h / target_height),
+ int(bbox[2] * w / target_width),
+ int(bbox[3] * h / target_height), ]
+ bbox[0] = max(round(bbox[0]), 0)
+ bbox[1] = max(round(bbox[1]), 0)
+ bbox[2] = min(round(bbox[2]), w)
+ bbox[3] = min(round(bbox[3]), h)
+
+ # IoUs = torch.zeros(len(masks), dtype=torch.float32)
+ bbox_area = (bbox[3] - bbox[1]) * (bbox[2] - bbox[0])
+
+ masks_area = torch.sum(masks[:, bbox[1]:bbox[3], bbox[0]:bbox[2]], dim=(1, 2))
+ orig_masks_area = torch.sum(masks, dim=(1, 2))
+
+ union = bbox_area + orig_masks_area - masks_area
+ IoUs = masks_area / union
+ max_iou_index = torch.argmax(IoUs)
+
+ return np.array([masks[max_iou_index].cpu().numpy()])
+
+ def point_prompt(self, points, pointlabel): # numpy 处理
+
+ masks = self._format_results(self.results[0], 0)
+ target_height = self.ori_img.shape[0]
+ target_width = self.ori_img.shape[1]
+ h = masks[0]['segmentation'].shape[0]
+ w = masks[0]['segmentation'].shape[1]
+ if h != target_height or w != target_width:
+ points = [[int(point[0] * w / target_width), int(point[1] * h / target_height)] for point in points]
+ onemask = np.zeros((h, w))
+ for i, annotation in enumerate(masks):
+ mask = annotation['segmentation'] if type(annotation) == dict else annotation
+ for i, point in enumerate(points):
+ if mask[point[1], point[0]] == 1 and pointlabel[i] == 1:
+ onemask += mask
+ if mask[point[1], point[0]] == 1 and pointlabel[i] == 0:
+ onemask -= mask
+ onemask = onemask >= 1
+ return np.array([onemask])
+
+ def text_prompt(self, text):
+ format_results = self._format_results(self.results[0], 0)
+ cropped_boxes, cropped_images, not_crop, filter_id, annotations = self._crop_image(format_results)
+ clip_model, preprocess = self.clip.load('ViT-B/32', device=self.device)
+ scores = self.retrieve(clip_model, preprocess, cropped_boxes, text, device=self.device)
+ max_idx = scores.argsort()
+ max_idx = max_idx[-1]
+ max_idx += sum(np.array(filter_id) <= int(max_idx))
+ return np.array([annotations[max_idx]['segmentation']])
+
+ def everything_prompt(self):
+ return self.results[0].masks.data
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/utils.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/utils.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c5b6cc235
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/utils.py
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+
+import torch
+
+
+def adjust_bboxes_to_image_border(boxes, image_shape, threshold=20):
+ """
+ Adjust bounding boxes to stick to image border if they are within a certain threshold.
+
+ Args:
+ boxes: (n, 4)
+ image_shape: (height, width)
+ threshold: pixel threshold
+
+ Returns:
+ adjusted_boxes: adjusted bounding boxes
+ """
+
+ # Image dimensions
+ h, w = image_shape
+
+ # Adjust boxes
+ boxes[boxes[:, 0] < threshold, 0] = 0 # x1
+ boxes[boxes[:, 1] < threshold, 1] = 0 # y1
+ boxes[boxes[:, 2] > w - threshold, 2] = w # x2
+ boxes[boxes[:, 3] > h - threshold, 3] = h # y2
+ return boxes
+
+
+def bbox_iou(box1, boxes, iou_thres=0.9, image_shape=(640, 640), raw_output=False):
+ """
+ Compute the Intersection-Over-Union of a bounding box with respect to an array of other bounding boxes.
+
+ Args:
+ box1: (4, )
+ boxes: (n, 4)
+
+ Returns:
+ high_iou_indices: Indices of boxes with IoU > thres
+ """
+ boxes = adjust_bboxes_to_image_border(boxes, image_shape)
+ # obtain coordinates for intersections
+ x1 = torch.max(box1[0], boxes[:, 0])
+ y1 = torch.max(box1[1], boxes[:, 1])
+ x2 = torch.min(box1[2], boxes[:, 2])
+ y2 = torch.min(box1[3], boxes[:, 3])
+
+ # compute the area of intersection
+ intersection = (x2 - x1).clamp(0) * (y2 - y1).clamp(0)
+
+ # compute the area of both individual boxes
+ box1_area = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
+ box2_area = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1])
+
+ # compute the area of union
+ union = box1_area + box2_area - intersection
+
+ # compute the IoU
+ iou = intersection / union # Should be shape (n, )
+ if raw_output:
+ return 0 if iou.numel() == 0 else iou
+
+ # return indices of boxes with IoU > thres
+ return torch.nonzero(iou > iou_thres).flatten()
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/val.py b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/val.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..250bd5e41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/fastsam/val.py
@@ -0,0 +1,244 @@
+# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+
+from multiprocessing.pool import ThreadPool
+from pathlib import Path
+
+import numpy as np
+import torch
+import torch.nn.functional as F
+
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LOGGER, NUM_THREADS, ops
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_requirements
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.metrics import SegmentMetrics, box_iou, mask_iou
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils.plotting import output_to_target, plot_images
+from ultralytics.yolo.v8.detect import DetectionValidator
+
+
+class FastSAMValidator(DetectionValidator):
+
+ def __init__(self, dataloader=None, save_dir=None, pbar=None, args=None, _callbacks=None):
+ """Initialize SegmentationValidator and set task to 'segment', metrics to SegmentMetrics."""
+ super().__init__(dataloader, save_dir, pbar, args, _callbacks)
+ self.args.task = 'segment'
+ self.metrics = SegmentMetrics(save_dir=self.save_dir, on_plot=self.on_plot)
+
+ def preprocess(self, batch):
+ """Preprocesses batch by converting masks to float and sending to device."""
+ batch = super().preprocess(batch)
+ batch['masks'] = batch['masks'].to(self.device).float()
+ return batch
+
+ def init_metrics(self, model):
+ """Initialize metrics and select mask processing function based on save_json flag."""
+ super().init_metrics(model)
+ self.plot_masks = []
+ if self.args.save_json:
+ check_requirements('pycocotools>=2.0.6')
+ self.process = ops.process_mask_upsample # more accurate
+ else:
+ self.process = ops.process_mask # faster
+
+ def get_desc(self):
+ """Return a formatted description of evaluation metrics."""
+ return ('%22s' + '%11s' * 10) % ('Class', 'Images', 'Instances', 'Box(P', 'R', 'mAP50', 'mAP50-95)', 'Mask(P',
+ 'R', 'mAP50', 'mAP50-95)')
+
+ def postprocess(self, preds):
+ """Postprocesses YOLO predictions and returns output detections with proto."""
+ p = ops.non_max_suppression(preds[0],
+ self.args.conf,
+ self.args.iou,
+ labels=self.lb,
+ multi_label=True,
+ agnostic=self.args.single_cls,
+ max_det=self.args.max_det,
+ nc=self.nc)
+ proto = preds[1][-1] if len(preds[1]) == 3 else preds[1] # second output is len 3 if pt, but only 1 if exported
+ return p, proto
+
+ def update_metrics(self, preds, batch):
+ """Metrics."""
+ for si, (pred, proto) in enumerate(zip(preds[0], preds[1])):
+ idx = batch['batch_idx'] == si
+ cls = batch['cls'][idx]
+ bbox = batch['bboxes'][idx]
+ nl, npr = cls.shape[0], pred.shape[0] # number of labels, predictions
+ shape = batch['ori_shape'][si]
+ correct_masks = torch.zeros(npr, self.niou, dtype=torch.bool, device=self.device) # init
+ correct_bboxes = torch.zeros(npr, self.niou, dtype=torch.bool, device=self.device) # init
+ self.seen += 1
+
+ if npr == 0:
+ if nl:
+ self.stats.append((correct_bboxes, correct_masks, *torch.zeros(
+ (2, 0), device=self.device), cls.squeeze(-1)))
+ if self.args.plots:
+ self.confusion_matrix.process_batch(detections=None, labels=cls.squeeze(-1))
+ continue
+
+ # Masks
+ midx = [si] if self.args.overlap_mask else idx
+ gt_masks = batch['masks'][midx]
+ pred_masks = self.process(proto, pred[:, 6:], pred[:, :4], shape=batch['img'][si].shape[1:])
+
+ # Predictions
+ if self.args.single_cls:
+ pred[:, 5] = 0
+ predn = pred.clone()
+ ops.scale_boxes(batch['img'][si].shape[1:], predn[:, :4], shape,
+ ratio_pad=batch['ratio_pad'][si]) # native-space pred
+
+ # Evaluate
+ if nl:
+ height, width = batch['img'].shape[2:]
+ tbox = ops.xywh2xyxy(bbox) * torch.tensor(
+ (width, height, width, height), device=self.device) # target boxes
+ ops.scale_boxes(batch['img'][si].shape[1:], tbox, shape,
+ ratio_pad=batch['ratio_pad'][si]) # native-space labels
+ labelsn = torch.cat((cls, tbox), 1) # native-space labels
+ correct_bboxes = self._process_batch(predn, labelsn)
+ # TODO: maybe remove these `self.` arguments as they already are member variable
+ correct_masks = self._process_batch(predn,
+ labelsn,
+ pred_masks,
+ gt_masks,
+ overlap=self.args.overlap_mask,
+ masks=True)
+ if self.args.plots:
+ self.confusion_matrix.process_batch(predn, labelsn)
+
+ # Append correct_masks, correct_boxes, pconf, pcls, tcls
+ self.stats.append((correct_bboxes, correct_masks, pred[:, 4], pred[:, 5], cls.squeeze(-1)))
+
+ pred_masks = torch.as_tensor(pred_masks, dtype=torch.uint8)
+ if self.args.plots and self.batch_i < 3:
+ self.plot_masks.append(pred_masks[:15].cpu()) # filter top 15 to plot
+
+ # Save
+ if self.args.save_json:
+ pred_masks = ops.scale_image(pred_masks.permute(1, 2, 0).contiguous().cpu().numpy(),
+ shape,
+ ratio_pad=batch['ratio_pad'][si])
+ self.pred_to_json(predn, batch['im_file'][si], pred_masks)
+ # if self.args.save_txt:
+ # save_one_txt(predn, save_conf, shape, file=save_dir / 'labels' / f'{path.stem}.txt')
+
+ def finalize_metrics(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ """Sets speed and confusion matrix for evaluation metrics."""
+ self.metrics.speed = self.speed
+ self.metrics.confusion_matrix = self.confusion_matrix
+
+ def _process_batch(self, detections, labels, pred_masks=None, gt_masks=None, overlap=False, masks=False):
+ """
+ Return correct prediction matrix
+ Arguments:
+ detections (array[N, 6]), x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, class
+ labels (array[M, 5]), class, x1, y1, x2, y2
+ Returns:
+ correct (array[N, 10]), for 10 IoU levels
+ """
+ if masks:
+ if overlap:
+ nl = len(labels)
+ index = torch.arange(nl, device=gt_masks.device).view(nl, 1, 1) + 1
+ gt_masks = gt_masks.repeat(nl, 1, 1) # shape(1,640,640) -> (n,640,640)
+ gt_masks = torch.where(gt_masks == index, 1.0, 0.0)
+ if gt_masks.shape[1:] != pred_masks.shape[1:]:
+ gt_masks = F.interpolate(gt_masks[None], pred_masks.shape[1:], mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0]
+ gt_masks = gt_masks.gt_(0.5)
+ iou = mask_iou(gt_masks.view(gt_masks.shape[0], -1), pred_masks.view(pred_masks.shape[0], -1))
+ else: # boxes
+ iou = box_iou(labels[:, 1:], detections[:, :4])
+
+ correct = np.zeros((detections.shape[0], self.iouv.shape[0])).astype(bool)
+ correct_class = labels[:, 0:1] == detections[:, 5]
+ for i in range(len(self.iouv)):
+ x = torch.where((iou >= self.iouv[i]) & correct_class) # IoU > threshold and classes match
+ if x[0].shape[0]:
+ matches = torch.cat((torch.stack(x, 1), iou[x[0], x[1]][:, None]),
+ 1).cpu().numpy() # [label, detect, iou]
+ if x[0].shape[0] > 1:
+ matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
+ matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 1], return_index=True)[1]]
+ # matches = matches[matches[:, 2].argsort()[::-1]]
+ matches = matches[np.unique(matches[:, 0], return_index=True)[1]]
+ correct[matches[:, 1].astype(int), i] = True
+ return torch.tensor(correct, dtype=torch.bool, device=detections.device)
+
+ def plot_val_samples(self, batch, ni):
+ """Plots validation samples with bounding box labels."""
+ plot_images(batch['img'],
+ batch['batch_idx'],
+ batch['cls'].squeeze(-1),
+ batch['bboxes'],
+ batch['masks'],
+ paths=batch['im_file'],
+ fname=self.save_dir / f'val_batch{ni}_labels.jpg',
+ names=self.names,
+ on_plot=self.on_plot)
+
+ def plot_predictions(self, batch, preds, ni):
+ """Plots batch predictions with masks and bounding boxes."""
+ plot_images(
+ batch['img'],
+ *output_to_target(preds[0], max_det=15), # not set to self.args.max_det due to slow plotting speed
+ torch.cat(self.plot_masks, dim=0) if len(self.plot_masks) else self.plot_masks,
+ paths=batch['im_file'],
+ fname=self.save_dir / f'val_batch{ni}_pred.jpg',
+ names=self.names,
+ on_plot=self.on_plot) # pred
+ self.plot_masks.clear()
+
+ def pred_to_json(self, predn, filename, pred_masks):
+ """Save one JSON result."""
+ # Example result = {"image_id": 42, "category_id": 18, "bbox": [258.15, 41.29, 348.26, 243.78], "score": 0.236}
+ from pycocotools.mask import encode # noqa
+
+ def single_encode(x):
+ """Encode predicted masks as RLE and append results to jdict."""
+ rle = encode(np.asarray(x[:, :, None], order='F', dtype='uint8'))[0]
+ rle['counts'] = rle['counts'].decode('utf-8')
+ return rle
+
+ stem = Path(filename).stem
+ image_id = int(stem) if stem.isnumeric() else stem
+ box = ops.xyxy2xywh(predn[:, :4]) # xywh
+ box[:, :2] -= box[:, 2:] / 2 # xy center to top-left corner
+ pred_masks = np.transpose(pred_masks, (2, 0, 1))
+ with ThreadPool(NUM_THREADS) as pool:
+ rles = pool.map(single_encode, pred_masks)
+ for i, (p, b) in enumerate(zip(predn.tolist(), box.tolist())):
+ self.jdict.append({
+ 'image_id': image_id,
+ 'category_id': self.class_map[int(p[5])],
+ 'bbox': [round(x, 3) for x in b],
+ 'score': round(p[4], 5),
+ 'segmentation': rles[i]})
+
+ def eval_json(self, stats):
+ """Return COCO-style object detection evaluation metrics."""
+ if self.args.save_json and self.is_coco and len(self.jdict):
+ anno_json = self.data['path'] / 'annotations/instances_val2017.json' # annotations
+ pred_json = self.save_dir / 'predictions.json' # predictions
+ LOGGER.info(f'\nEvaluating pycocotools mAP using {pred_json} and {anno_json}...')
+ try: # https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi/blob/master/PythonAPI/pycocoEvalDemo.ipynb
+ check_requirements('pycocotools>=2.0.6')
+ from pycocotools.coco import COCO # noqa
+ from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval # noqa
+
+ for x in anno_json, pred_json:
+ assert x.is_file(), f'{x} file not found'
+ anno = COCO(str(anno_json)) # init annotations api
+ pred = anno.loadRes(str(pred_json)) # init predictions api (must pass string, not Path)
+ for i, eval in enumerate([COCOeval(anno, pred, 'bbox'), COCOeval(anno, pred, 'segm')]):
+ if self.is_coco:
+ eval.params.imgIds = [int(Path(x).stem) for x in self.dataloader.dataset.im_files] # im to eval
+ eval.evaluate()
+ eval.accumulate()
+ eval.summarize()
+ idx = i * 4 + 2
+ stats[self.metrics.keys[idx + 1]], stats[
+ self.metrics.keys[idx]] = eval.stats[:2] # update mAP50-95 and mAP50
+ except Exception as e:
+ LOGGER.warning(f'pycocotools unable to run: {e}')
+ return stats
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/__init__.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/__init__.py
index 1e3d0a287..bcfce51eb 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/__init__.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/__init__.py
@@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ VERBOSE = str(os.getenv('YOLO_VERBOSE', True)).lower() == 'true' # global verbo
TQDM_BAR_FORMAT = '{l_bar}{bar:10}{r_bar}' # tqdm bar format
LOGGING_NAME = 'ultralytics'
MACOS, LINUX, WINDOWS = (platform.system() == x for x in ['Darwin', 'Linux', 'Windows']) # environment booleans
+ARM64 = platform.machine() in ('arm64', 'aarch64') # ARM64 booleans
HELP_MSG = \
"""
Usage examples for running YOLOv8:
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/benchmarks.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/benchmarks.py
index a277d6b7c..e84a1a6fd 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/benchmarks.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/benchmarks.py
@@ -21,6 +21,7 @@ TensorFlow Lite | `tflite` | yolov8n.tflite
TensorFlow Edge TPU | `edgetpu` | yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite
TensorFlow.js | `tfjs` | yolov8n_web_model/
PaddlePaddle | `paddle` | yolov8n_paddle_model/
+ncnn | `ncnn` | yolov8n_ncnn_model/
"""
import glob
@@ -33,6 +34,7 @@ import torch.cuda
from tqdm import tqdm
from ultralytics import YOLO
+from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import TASK2DATA, TASK2METRIC
from ultralytics.yolo.engine.exporter import export_formats
from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LINUX, LOGGER, MACOS, ROOT, SETTINGS
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.checks import check_requirements, check_yolo
@@ -96,6 +98,7 @@ def benchmark(model=Path(SETTINGS['weights_dir']) / 'yolov8n.pt',
emoji = '❎' # indicates export succeeded
# Predict
+ assert model.task != 'pose' or i != 7, 'GraphDef Pose inference is not supported'
assert i not in (9, 10), 'inference not supported' # Edge TPU and TF.js are unsupported
assert i != 5 or platform.system() == 'Darwin', 'inference only supported on macOS>=10.13' # CoreML
if not (ROOT / 'assets/bus.jpg').exists():
@@ -103,15 +106,8 @@ def benchmark(model=Path(SETTINGS['weights_dir']) / 'yolov8n.pt',
export.predict(ROOT / 'assets/bus.jpg', imgsz=imgsz, device=device, half=half)
# Validate
- if model.task == 'detect':
- data, key = 'coco8.yaml', 'metrics/mAP50-95(B)'
- elif model.task == 'segment':
- data, key = 'coco8-seg.yaml', 'metrics/mAP50-95(M)'
- elif model.task == 'classify':
- data, key = 'imagenet100', 'metrics/accuracy_top5'
- elif model.task == 'pose':
- data, key = 'coco8-pose.yaml', 'metrics/mAP50-95(P)'
-
+ data = TASK2DATA[model.task] # task to dataset, i.e. coco8.yaml for task=detect
+ key = TASK2METRIC[model.task] # task to metric, i.e. metrics/mAP50-95(B) for task=detect
results = export.val(data=data,
batch=1,
imgsz=imgsz,
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/dvc.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/dvc.py
index 63ec36875..138100c8d 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/dvc.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/dvc.py
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ def on_pretrain_routine_start(trainer):
try:
global live
if not _logger_disabled():
- live = dvclive.Live(save_dvc_exp=True)
+ live = dvclive.Live(save_dvc_exp=True, cache_images=True)
LOGGER.info(
'DVCLive is detected and auto logging is enabled (can be disabled with `ULTRALYTICS_DVC_DISABLED=true`).'
)
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/mlflow.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/mlflow.py
index 1c2ed7472..6c4b798b9 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/mlflow.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/mlflow.py
@@ -26,7 +26,8 @@ def on_pretrain_routine_end(trainer):
mlflow_location = os.environ['MLFLOW_TRACKING_URI'] # "http://192.168.xxx.xxx:5000"
mlflow.set_tracking_uri(mlflow_location)
- experiment_name = trainer.args.project or '/Shared/YOLOv8'
+ experiment_name = os.environ.get('MLFLOW_EXPERIMENT_NAME') or trainer.args.project or '/Shared/YOLOv8'
+ run_name = os.environ.get('MLFLOW_RUN') or trainer.args.name
experiment = mlflow.get_experiment_by_name(experiment_name)
if experiment is None:
mlflow.create_experiment(experiment_name)
@@ -36,7 +37,7 @@ def on_pretrain_routine_end(trainer):
try:
run, active_run = mlflow, mlflow.active_run()
if not active_run:
- active_run = mlflow.start_run(experiment_id=experiment.experiment_id)
+ active_run = mlflow.start_run(experiment_id=experiment.experiment_id, run_name=run_name)
run_id = active_run.info.run_id
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix}Using run_id({run_id}) at {mlflow_location}')
run.log_params(vars(trainer.model.args))
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/wb.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/wb.py
index 827f79734..4b4c29b77 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/wb.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/callbacks/wb.py
@@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ def on_train_end(trainer):
art = wb.Artifact(type='model', name=f'run_{wb.run.id}_model')
if trainer.best.exists():
art.add_file(trainer.best)
- wb.run.log_artifact(art)
+ wb.run.log_artifact(art, aliases=['best'])
callbacks = {
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/checks.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/checks.py
index eb30da1bf..0ea860c10 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/checks.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/checks.py
@@ -8,6 +8,7 @@ import platform
import re
import shutil
import subprocess
+import time
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Optional
@@ -20,8 +21,8 @@ import torch
from matplotlib import font_manager
from ultralytics.yolo.utils import (AUTOINSTALL, LOGGER, ONLINE, ROOT, USER_CONFIG_DIR, TryExcept, clean_url, colorstr,
- downloads, emojis, is_colab, is_docker, is_kaggle, is_online, is_pip_package,
- url2file)
+ downloads, emojis, is_colab, is_docker, is_jupyter, is_kaggle, is_online,
+ is_pip_package, url2file)
def is_ascii(s) -> bool:
@@ -222,25 +223,29 @@ def check_requirements(requirements=ROOT.parent / 'requirements.txt', exclude=()
s = '' # console string
n = 0 # number of packages updates
for r in requirements:
+ rmin = r.split('/')[-1].replace('.git', '') # replace git+https://org/repo.git -> 'repo'
try:
- pkg.require(r)
+ pkg.require(rmin)
except (pkg.VersionConflict, pkg.DistributionNotFound): # exception if requirements not met
try: # attempt to import (slower but more accurate)
import importlib
- importlib.import_module(next(pkg.parse_requirements(r)).name)
+ importlib.import_module(next(pkg.parse_requirements(rmin)).name)
except ImportError:
s += f'"{r}" '
n += 1
if s:
if install and AUTOINSTALL: # check environment variable
- LOGGER.info(f"{prefix} Ultralytics requirement{'s' * (n > 1)} {s}not found, attempting AutoUpdate...")
+ pkgs = file or requirements # missing packages
+ LOGGER.info(f"{prefix} Ultralytics requirement{'s' * (n > 1)} {pkgs} not found, attempting AutoUpdate...")
try:
+ t = time.time()
assert is_online(), 'AutoUpdate skipped (offline)'
LOGGER.info(subprocess.check_output(f'pip install --no-cache {s} {cmds}', shell=True).decode())
- s = f"{prefix} {n} package{'s' * (n > 1)} updated per {file or requirements}\n" \
- f"{prefix} ⚠️ {colorstr('bold', 'Restart runtime or rerun command for updates to take effect')}\n"
- LOGGER.info(s)
+ dt = time.time() - t
+ LOGGER.info(
+ f"{prefix} AutoUpdate success ✅ {dt:.1f}s, installed {n} package{'s' * (n > 1)}: {pkgs}\n"
+ f"{prefix} ⚠️ {colorstr('bold', 'Restart runtime or rerun command for updates to take effect')}\n")
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.warning(f'{prefix} ❌ {e}')
return False
@@ -325,8 +330,11 @@ def check_yolo(verbose=True, device=''):
"""Return a human-readable YOLO software and hardware summary."""
from ultralytics.yolo.utils.torch_utils import select_device
- if is_colab():
- shutil.rmtree('sample_data', ignore_errors=True) # remove colab /sample_data directory
+ if is_jupyter():
+ if check_requirements('wandb', install=False):
+ os.system('pip uninstall -y wandb') # uninstall wandb: unwanted account creation prompt with infinite hang
+ if is_colab():
+ shutil.rmtree('sample_data', ignore_errors=True) # remove colab /sample_data directory
if verbose:
# System info
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/downloads.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/downloads.py
index c69b18ffb..53f58cfdd 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/downloads.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/downloads.py
@@ -18,7 +18,9 @@ from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LOGGER, checks, clean_url, emojis, is_online,
GITHUB_ASSET_NAMES = [f'yolov8{k}{suffix}.pt' for k in 'nsmlx' for suffix in ('', '6', '-cls', '-seg', '-pose')] + \
[f'yolov5{k}u.pt' for k in 'nsmlx'] + \
[f'yolov3{k}u.pt' for k in ('', '-spp', '-tiny')] + \
+ [f'yolo_nas_{k}.pt' for k in 'sml'] + \
[f'sam_{k}.pt' for k in 'bl'] + \
+ [f'FastSAM-{k}.pt' for k in 'sx'] + \
[f'rtdetr-{k}.pt' for k in 'lx']
GITHUB_ASSET_STEMS = [Path(k).stem for k in GITHUB_ASSET_NAMES]
@@ -36,7 +38,7 @@ def is_url(url, check=True):
return False
-def unzip_file(file, path=None, exclude=('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX')):
+def unzip_file(file, path=None, exclude=('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX'), exist_ok=False):
"""
Unzips a *.zip file to the specified path, excluding files containing strings in the exclude list.
@@ -48,6 +50,7 @@ def unzip_file(file, path=None, exclude=('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX')):
file (str): The path to the zipfile to be extracted.
path (str, optional): The path to extract the zipfile to. Defaults to None.
exclude (tuple, optional): A tuple of filename strings to be excluded. Defaults to ('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX').
+ exist_ok (bool, optional): Whether to overwrite existing contents if they exist. Defaults to False.
Raises:
BadZipFile: If the provided file does not exist or is not a valid zipfile.
@@ -60,6 +63,7 @@ def unzip_file(file, path=None, exclude=('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX')):
if path is None:
path = Path(file).parent # default path
+ # Unzip the file contents
with ZipFile(file) as zipObj:
file_list = [f for f in zipObj.namelist() if all(x not in f for x in exclude)]
top_level_dirs = {Path(f).parts[0] for f in file_list}
@@ -67,6 +71,13 @@ def unzip_file(file, path=None, exclude=('.DS_Store', '__MACOSX')):
if len(top_level_dirs) > 1 or not file_list[0].endswith('/'):
path = Path(path) / Path(file).stem # define new unzip directory
+ # Check if destination directory already exists and contains files
+ extract_path = Path(path) / list(top_level_dirs)[0]
+ if extract_path.exists() and any(extract_path.iterdir()) and not exist_ok:
+ # If it exists and is not empty, return the path without unzipping
+ LOGGER.info(f'Skipping {file} unzip (already unzipped)')
+ return path
+
for f in file_list:
zipObj.extract(f, path=path)
@@ -178,7 +189,7 @@ def safe_download(url,
if unzip and f.exists() and f.suffix in ('', '.zip', '.tar', '.gz'):
unzip_dir = dir or f.parent # unzip to dir if provided else unzip in place
- LOGGER.info(f'Unzipping {f} to {unzip_dir}...')
+ LOGGER.info(f'Unzipping {f} to {unzip_dir.absolute()}...')
if is_zipfile(f):
unzip_dir = unzip_file(file=f, path=unzip_dir) # unzip
elif f.suffix == '.tar':
@@ -190,17 +201,18 @@ def safe_download(url,
return unzip_dir
+def get_github_assets(repo='ultralytics/assets', version='latest'):
+ """Return GitHub repo tag and assets (i.e. ['yolov8n.pt', 'yolov8s.pt', ...])."""
+ if version != 'latest':
+ version = f'tags/{version}' # i.e. tags/v6.2
+ response = requests.get(f'https://api.github.com/repos/{repo}/releases/{version}').json() # github api
+ return response['tag_name'], [x['name'] for x in response['assets']] # tag, assets
+
+
def attempt_download_asset(file, repo='ultralytics/assets', release='v0.0.0'):
"""Attempt file download from GitHub release assets if not found locally. release = 'latest', 'v6.2', etc."""
from ultralytics.yolo.utils import SETTINGS # scoped for circular import
- def github_assets(repository, version='latest'):
- """Return GitHub repo tag and assets (i.e. ['yolov8n.pt', 'yolov8s.pt', ...])."""
- if version != 'latest':
- version = f'tags/{version}' # i.e. tags/v6.2
- response = requests.get(f'https://api.github.com/repos/{repository}/releases/{version}').json() # github api
- return response['tag_name'], [x['name'] for x in response['assets']] # tag, assets
-
# YOLOv3/5u updates
file = str(file)
file = checks.check_yolov5u_filename(file)
@@ -224,10 +236,10 @@ def attempt_download_asset(file, repo='ultralytics/assets', release='v0.0.0'):
# GitHub assets
assets = GITHUB_ASSET_NAMES
try:
- tag, assets = github_assets(repo, release)
+ tag, assets = get_github_assets(repo, release)
except Exception:
try:
- tag, assets = github_assets(repo) # latest release
+ tag, assets = get_github_assets(repo) # latest release
except Exception:
try:
tag = subprocess.check_output(['git', 'tag']).decode().split()[-1]
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/metrics.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/metrics.py
index 8544adf51..cd903213f 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/metrics.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/metrics.py
@@ -204,7 +204,7 @@ class ConfusionMatrix:
"""
preds, targets = torch.cat(preds)[:, 0], torch.cat(targets)
for p, t in zip(preds.cpu().numpy(), targets.cpu().numpy()):
- self.matrix[t][p] += 1
+ self.matrix[p][t] += 1
def process_batch(self, detections, labels):
"""
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/ops.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/ops.py
index b998df443..9135117ff 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/ops.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/ops.py
@@ -200,12 +200,15 @@ def non_max_suppression(
multi_label &= nc > 1 # multiple labels per box (adds 0.5ms/img)
merge = False # use merge-NMS
+ prediction = prediction.transpose(-1, -2) # shape(1,84,6300) to shape(1,6300,84)
+ prediction[..., :4] = xywh2xyxy(prediction[..., :4]) # xywh to xyxy
+
t = time.time()
output = [torch.zeros((0, 6 + nm), device=prediction.device)] * bs
for xi, x in enumerate(prediction): # image index, image inference
# Apply constraints
# x[((x[:, 2:4] < min_wh) | (x[:, 2:4] > max_wh)).any(1), 4] = 0 # width-height
- x = x.transpose(0, -1)[xc[xi]] # confidence
+ x = x[xc[xi]] # confidence
# Cat apriori labels if autolabelling
if labels and len(labels[xi]):
@@ -221,9 +224,9 @@ def non_max_suppression(
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
box, cls, mask = x.split((4, nc, nm), 1)
- box = xywh2xyxy(box) # center_x, center_y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
+
if multi_label:
- i, j = (cls > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).T
+ i, j = torch.where(cls > conf_thres)
x = torch.cat((box[i], x[i, 4 + j, None], j[:, None].float(), mask[i]), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = cls.max(1, keepdim=True)
@@ -241,7 +244,8 @@ def non_max_suppression(
n = x.shape[0] # number of boxes
if not n: # no boxes
continue
- x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
+ if n > max_nms: # excess boxes
+ x = x[x[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)[:max_nms]] # sort by confidence and remove excess boxes
# Batched NMS
c = x[:, 5:6] * (0 if agnostic else max_wh) # classes
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/plotting.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/plotting.py
index 9061ca1d7..893206213 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/plotting.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/plotting.py
@@ -2,6 +2,7 @@
import contextlib
import math
+import warnings
from pathlib import Path
import cv2
@@ -233,6 +234,9 @@ def plot_labels(boxes, cls, names=(), save_dir=Path(''), on_plot=None):
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sn
+ # Filter matplotlib>=3.7.2 warning
+ warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=UserWarning, message='The figure layout has changed to tight')
+
# Plot dataset labels
LOGGER.info(f"Plotting labels to {save_dir / 'labels.jpg'}... ")
b = boxes.transpose() # classes, boxes
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/torch_utils.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/torch_utils.py
index a9d79178d..e5a62dc5e 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/torch_utils.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/torch_utils.py
@@ -319,9 +319,9 @@ def init_seeds(seed=0, deterministic=False):
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) # for Multi-GPU, exception safe
# torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True # AutoBatch problem https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/issues/9287
- if deterministic: # https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/8213
+ if deterministic:
if TORCH_2_0:
- torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True)
+ torch.use_deterministic_algorithms(True, warn_only=True) # warn if deterministic is not possible
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
os.environ['CUBLAS_WORKSPACE_CONFIG'] = ':4096:8'
os.environ['PYTHONHASHSEED'] = str(seed)
diff --git a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/tuner.py b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/tuner.py
index 9f57677a5..54f10b054 100644
--- a/ultralytics/yolo/utils/tuner.py
+++ b/ultralytics/yolo/utils/tuner.py
@@ -1,44 +1,120 @@
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license
+from ultralytics.yolo.cfg import TASK2DATA, TASK2METRIC
+from ultralytics.yolo.utils import DEFAULT_CFG_DICT, LOGGER, NUM_THREADS
-from ultralytics.yolo.utils import LOGGER
-
-try:
- from ray import tune
- from ray.air import RunConfig, session # noqa
- from ray.air.integrations.wandb import WandbLoggerCallback # noqa
- from ray.tune.schedulers import ASHAScheduler # noqa
- from ray.tune.schedulers import AsyncHyperBandScheduler as AHB # noqa
-
-except ImportError:
- LOGGER.info("Tuning hyperparameters requires ray/tune. Install using `pip install 'ray[tune]'`")
- tune = None
-
-default_space = {
- # 'optimizer': tune.choice(['SGD', 'Adam', 'AdamW', 'NAdam', 'RAdam', 'RMSProp']),
- 'lr0': tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1),
- 'lrf': tune.uniform(0.01, 1.0), # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
- 'momentum': tune.uniform(0.6, 0.98), # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
- 'weight_decay': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.001), # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
- 'warmup_epochs': tune.uniform(0.0, 5.0), # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
- 'warmup_momentum': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.95), # warmup initial momentum
- 'box': tune.uniform(0.02, 0.2), # box loss gain
- 'cls': tune.uniform(0.2, 4.0), # cls loss gain (scale with pixels)
- 'hsv_h': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.1), # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
- 'hsv_s': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
- 'hsv_v': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
- 'degrees': tune.uniform(0.0, 45.0), # image rotation (+/- deg)
- 'translate': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image translation (+/- fraction)
- 'scale': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image scale (+/- gain)
- 'shear': tune.uniform(0.0, 10.0), # image shear (+/- deg)
- 'perspective': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.001), # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
- 'flipud': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image flip up-down (probability)
- 'fliplr': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image flip left-right (probability)
- 'mosaic': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
- 'mixup': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
- 'copy_paste': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0)} # segment copy-paste (probability)
-
-task_metric_map = {
- 'detect': 'metrics/mAP50-95(B)',
- 'segment': 'metrics/mAP50-95(M)',
- 'classify': 'metrics/accuracy_top1',
- 'pose': 'metrics/mAP50-95(P)'}
+
+def run_ray_tune(model,
+ space: dict = None,
+ grace_period: int = 10,
+ gpu_per_trial: int = None,
+ max_samples: int = 10,
+ **train_args):
+ """
+ Runs hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune.
+
+ Args:
+ model (YOLO): Model to run the tuner on.
+ space (dict, optional): The hyperparameter search space. Defaults to None.
+ grace_period (int, optional): The grace period in epochs of the ASHA scheduler. Defaults to 10.
+ gpu_per_trial (int, optional): The number of GPUs to allocate per trial. Defaults to None.
+ max_samples (int, optional): The maximum number of trials to run. Defaults to 10.
+ train_args (dict, optional): Additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method. Defaults to {}.
+
+ Returns:
+ (dict): A dictionary containing the results of the hyperparameter search.
+
+ Raises:
+ ModuleNotFoundError: If Ray Tune is not installed.
+ """
+ if train_args is None:
+ train_args = {}
+
+ try:
+ from ray import tune
+ from ray.air import RunConfig
+ from ray.air.integrations.wandb import WandbLoggerCallback
+ from ray.tune.schedulers import ASHAScheduler
+ except ImportError:
+ raise ModuleNotFoundError("Tuning hyperparameters requires Ray Tune. Install with: pip install 'ray[tune]'")
+
+ try:
+ import wandb
+
+ assert hasattr(wandb, '__version__')
+ except (ImportError, AssertionError):
+ wandb = False
+
+ default_space = {
+ # 'optimizer': tune.choice(['SGD', 'Adam', 'AdamW', 'NAdam', 'RAdam', 'RMSProp']),
+ 'lr0': tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1),
+ 'lrf': tune.uniform(0.01, 1.0), # final OneCycleLR learning rate (lr0 * lrf)
+ 'momentum': tune.uniform(0.6, 0.98), # SGD momentum/Adam beta1
+ 'weight_decay': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.001), # optimizer weight decay 5e-4
+ 'warmup_epochs': tune.uniform(0.0, 5.0), # warmup epochs (fractions ok)
+ 'warmup_momentum': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.95), # warmup initial momentum
+ 'box': tune.uniform(0.02, 0.2), # box loss gain
+ 'cls': tune.uniform(0.2, 4.0), # cls loss gain (scale with pixels)
+ 'hsv_h': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.1), # image HSV-Hue augmentation (fraction)
+ 'hsv_s': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Saturation augmentation (fraction)
+ 'hsv_v': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image HSV-Value augmentation (fraction)
+ 'degrees': tune.uniform(0.0, 45.0), # image rotation (+/- deg)
+ 'translate': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image translation (+/- fraction)
+ 'scale': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.9), # image scale (+/- gain)
+ 'shear': tune.uniform(0.0, 10.0), # image shear (+/- deg)
+ 'perspective': tune.uniform(0.0, 0.001), # image perspective (+/- fraction), range 0-0.001
+ 'flipud': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image flip up-down (probability)
+ 'fliplr': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image flip left-right (probability)
+ 'mosaic': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
+ 'mixup': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0), # image mixup (probability)
+ 'copy_paste': tune.uniform(0.0, 1.0)} # segment copy-paste (probability)
+
+ def _tune(config):
+ """
+ Trains the YOLO model with the specified hyperparameters and additional arguments.
+
+ Args:
+ config (dict): A dictionary of hyperparameters to use for training.
+
+ Returns:
+ None.
+ """
+ model._reset_callbacks()
+ config.update(train_args)
+ model.train(**config)
+
+ # Get search space
+ if not space:
+ space = default_space
+ LOGGER.warning('WARNING ⚠️ search space not provided, using default search space.')
+
+ # Get dataset
+ data = train_args.get('data', TASK2DATA[model.task])
+ space['data'] = data
+ if 'data' not in train_args:
+ LOGGER.warning(f'WARNING ⚠️ data not provided, using default "data={data}".')
+
+ # Define the trainable function with allocated resources
+ trainable_with_resources = tune.with_resources(_tune, {'cpu': NUM_THREADS, 'gpu': gpu_per_trial or 0})
+
+ # Define the ASHA scheduler for hyperparameter search
+ asha_scheduler = ASHAScheduler(time_attr='epoch',
+ metric=TASK2METRIC[model.task],
+ mode='max',
+ max_t=train_args.get('epochs') or DEFAULT_CFG_DICT['epochs'] or 100,
+ grace_period=grace_period,
+ reduction_factor=3)
+
+ # Define the callbacks for the hyperparameter search
+ tuner_callbacks = [WandbLoggerCallback(project='YOLOv8-tune')] if wandb else []
+
+ # Create the Ray Tune hyperparameter search tuner
+ tuner = tune.Tuner(trainable_with_resources,
+ param_space=space,
+ tune_config=tune.TuneConfig(scheduler=asha_scheduler, num_samples=max_samples),
+ run_config=RunConfig(callbacks=tuner_callbacks, storage_path='./runs/tune'))
+
+ # Run the hyperparameter search
+ tuner.fit()
+
+ # Return the results of the hyperparameter search
+ return tuner.get_results()
联系方式
-对于 YOLOv8 的错误报告和功能请求,请访问 [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues),并加入我们的 [Discord](https://discord.gg/7aegy5d8) 社区进行问题和讨论!
+对于 YOLOv8 的错误报告和功能请求,请访问 [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues),并加入我们的 [Discord](https://discord.gg/2wNGbc6g9X) 社区进行问题和讨论!
diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile b/docker/Dockerfile index 4fca588d2..2f86bb858 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile +++ b/docker/Dockerfile @@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ RUN pip install --no-cache nvidia-tensorrt --index-url https://pypi.ngc.nvidia.c ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y gcc git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 b/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 index bd5432394..3a91abd47 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-arm64 @@ -9,8 +9,9 @@ FROM arm64v8/ubuntu:22.10 ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ - && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop gcc libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev + && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop gcc libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 # Create working directory diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-cpu b/docker/Dockerfile-cpu index c58e4233c..3bf0339c1 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-cpu +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-cpu @@ -3,13 +3,13 @@ # Image is CPU-optimized for ONNX, OpenVINO and PyTorch YOLOv8 deployments # Start FROM Ubuntu image https://hub.docker.com/_/ubuntu -FROM ubuntu:22.10 +FROM ubuntu:lunar-20230615 # Downloads to user config dir ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y python3-pip git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 @@ -23,6 +23,9 @@ WORKDIR /usr/src/ultralytics RUN git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics /usr/src/ultralytics ADD https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/yolov8n.pt /usr/src/ultralytics/ +# Remove python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED or use 'pip install --break-system-packages' avoid 'externally-managed-environment' Ubuntu nightly error +RUN rm -rf /usr/lib/python3.11/EXTERNALLY-MANAGED + # Install pip packages RUN python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip wheel RUN pip install --no-cache -e . thop --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu diff --git a/docker/Dockerfile-jetson b/docker/Dockerfile-jetson index 0182f2c26..785ca8938 100644 --- a/docker/Dockerfile-jetson +++ b/docker/Dockerfile-jetson @@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/l4t-pytorch:r35.2.1-pth2.0-py3 ADD https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.ttf https://ultralytics.com/assets/Arial.Unicode.ttf /root/.config/Ultralytics/ # Install linux packages -# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' package +# g++ required to build 'tflite_support' and 'lap' packages RUN apt update \ && apt install --no-install-recommends -y gcc git zip curl htop libgl1-mesa-glx libglib2.0-0 libpython3-dev gnupg g++ # RUN alias python=python3 diff --git a/docs/datasets/classify/index.md b/docs/datasets/classify/index.md index fd902882d..ab6ca5cff 100644 --- a/docs/datasets/classify/index.md +++ b/docs/datasets/classify/index.md @@ -97,9 +97,24 @@ In this example, the `train` directory contains subdirectories for each class in ```bash # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model - yolo detect train data=path/to/data model=yolov8n-seg.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 + yolo detect train data=path/to/data model=yolov8n-cls.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 ``` ## Supported Datasets -TODO \ No newline at end of file +Ultralytics supports the following datasets with automatic download: + +* [Caltech 101](caltech101.md): A dataset containing images of 101 object categories for image classification tasks. +* [Caltech 256](caltech256.md): An extended version of Caltech 101 with 256 object categories and more challenging images. +* [CIFAR-10](cifar10.md): A dataset of 60K 32x32 color images in 10 classes, with 6K images per class. +* [CIFAR-100](cifar100.md): An extended version of CIFAR-10 with 100 object categories and 600 images per class. +* [Fashion-MNIST](fashion-mnist.md): A dataset consisting of 70,000 grayscale images of 10 fashion categories for image classification tasks. +* [ImageNet](imagenet.md): A large-scale dataset for object detection and image classification with over 14 million images and 20,000 categories. +* [ImageNet-10](imagenet10.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet with 10 categories for faster experimentation and testing. +* [Imagenette](imagenette.md): A smaller subset of ImageNet that contains 10 easily distinguishable classes for quicker training and testing. +* [Imagewoof](imagewoof.md): A more challenging subset of ImageNet containing 10 dog breed categories for image classification tasks. +* [MNIST](mnist.md): A dataset of 70,000 grayscale images of handwritten digits for image classification tasks. + +### Adding your own dataset + +If you have your own dataset and would like to use it for training classification models with Ultralytics, ensure that it follows the format specified above under "Dataset format" and then point your `data` argument to the dataset directory. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/datasets/detect/index.md b/docs/datasets/detect/index.md index 7eec93cd9..6a9cd614d 100644 --- a/docs/datasets/detect/index.md +++ b/docs/datasets/detect/index.md @@ -1,82 +1,53 @@ --- comments: true -description: Learn about supported dataset formats for training YOLO detection models, including Ultralytics YOLO and COCO, in this Object Detection Datasets Overview. -keywords: object detection, datasets, formats, Ultralytics YOLO, label format, dataset file format, dataset definition, YOLO dataset, model configuration +description: Explore supported dataset formats for training YOLO detection models, including Ultralytics YOLO and COCO. This guide covers various dataset formats and their specific configurations for effective object detection training. +keywords: object detection, datasets, formats, Ultralytics YOLO, COCO, label format, dataset file format, dataset definition, YOLO dataset, model configuration --- # Object Detection Datasets Overview +Training a robust and accurate object detection model requires a comprehensive dataset. This guide introduces various formats of datasets that are compatible with the Ultralytics YOLO model and provides insights into their structure, usage, and how to convert between different formats. + ## Supported Dataset Formats ### Ultralytics YOLO format -** Label Format ** - -The dataset format used for training YOLO detection models is as follows: - -1. One text file per image: Each image in the dataset has a corresponding text file with the same name as the image file and the ".txt" extension. -2. One row per object: Each row in the text file corresponds to one object instance in the image. -3. Object information per row: Each row contains the following information about the object instance: - - Object class index: An integer representing the class of the object (e.g., 0 for person, 1 for car, etc.). - - Object center coordinates: The x and y coordinates of the center of the object, normalized to be between 0 and 1. - - Object width and height: The width and height of the object, normalized to be between 0 and 1. - -The format for a single row in the detection dataset file is as follows: - -``` -

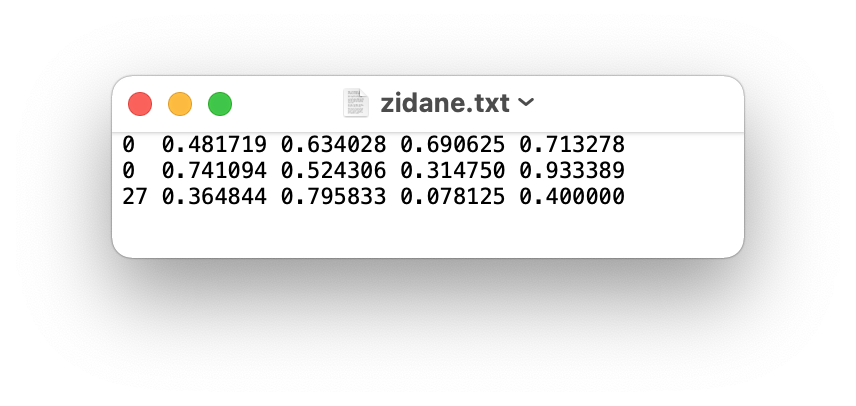
 @@ -84,4 +84,5 @@ i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/predict.md b/docs/modes/predict.md
index 581d4221d..8708933e6 100644
--- a/docs/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/modes/predict.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
comments: true
-description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
+description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
keywords: YOLOv8, predict mode, generator, streaming mode, input sources, video formats, arguments customization
---
@@ -12,60 +12,279 @@ passing `stream=True` in the predictor's call method.
!!! example "Predict"
- === "Return a list with `Stream=False`"
+ === "Return a list with `stream=False`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs) # list of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg']) # return a list of Results objects
+ # Process results list
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
- === "Return a generator with `Stream=True`"
+ === "Return a generator with `stream=True`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg'], stream=True) # return a generator of Results objects
+ # Process results generator
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
-!!! tip "Tip"
-
- Streaming mode with `stream=True` should be used for long videos or large predict sources, otherwise results will accumuate in memory and will eventually cause out-of-memory errors.
+## Inference Sources
-## Sources
+YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in the table below. The sources include static images, video streams, and various data formats. The table also indicates whether each source can be used in streaming mode with the argument `stream=True` ✅. Streaming mode is beneficial for processing videos or live streams as it creates a generator of results instead of loading all frames into memory.
-YOLOv8 can accept various input sources, as shown in the table below. This includes images, URLs, PIL images, OpenCV,
-numpy arrays, torch tensors, CSV files, videos, directories, globs, YouTube videos, and streams. The table indicates
-whether each source can be used in streaming mode with `stream=True` ✅ and an example argument for each source.
+!!! tip "Tip"
-| source | model(arg) | type | notes |
-|-------------|--------------------------------------------|----------------|------------------|
-| image | `'im.jpg'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | |
-| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | |
-| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC, RGB |
-| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC, BGR |
-| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC |
-| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW, RGB |
-| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str`, `Path` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
-| video ✅ | `'vid.mp4'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Use `*` operator |
-| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | |
-| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
+ Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
+
+| Source | Argument | Type | Notes |
+|-------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. |
+| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. |
+| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. |
+| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. |
+| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` of `float32 (0.0-1.0)` | BCHW format with RGB channels. |
+| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. |
+| video ✅ | `'video.mp4'` | `str` or `Path` | Video file in formats like MP4, AVI, etc. |
+| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str` or `Path` | Path to a directory containing images or videos. |
+| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Glob pattern to match multiple files. Use the `*` character as a wildcard. |
+| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | URL to a YouTube video. |
+| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | URL for streaming protocols such as RTSP, RTMP, or an IP address. |
+
+Below are code examples for using each source type:
+
+!!! example "Prediction sources"
+
+ === "image"
+ Run inference on an image file.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to the image file
+ source = 'path/to/image.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "screenshot"
+ Run inference on the current screen content as a screenshot.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define current screenshot as source
+ source = 'screen'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "URL"
+ Run inference on an image or video hosted remotely via URL.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define remote image or video URL
+ source = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "PIL"
+ Run inference on an image opened with Python Imaging Library (PIL).
+ ```python
+ from PIL import Image
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Open an image using PIL
+ source = Image.open('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "OpenCV"
+ Run inference on an image read with OpenCV.
+ ```python
+ import cv2
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Read an image using OpenCV
+ source = cv2.imread('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "numpy"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a numpy array.
+ ```python
+ import numpy as np
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random numpy array of HWC shape (640, 640, 3) with values in range [0, 255] and type uint8
+ source = np.random.randint(low=0, high=255, size=(640, 640, 3), dtype='uint8')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "torch"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a PyTorch tensor.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
+ source = torch.rand(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "CSV"
+ Run inference on a collection of images, URLs, videos and directories listed in a CSV file.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a path to a CSV file with images, URLs, videos and directories
+ source = 'path/to/file.csv'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "video"
+ Run inference on a video file. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to video file
+ source = 'path/to/video.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "directory"
+ Run inference on all images and videos in a directory. To also capture images and videos in subdirectories use a glob pattern, i.e. `path/to/dir/**/*`.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to directory containing images and videos for inference
+ source = 'path/to/dir'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "glob"
+ Run inference on all images and videos that match a glob expression with `*` characters.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a glob search for all JPG files in a directory
+ source = 'path/to/dir/*.jpg'
+
+ # OR define a recursive glob search for all JPG files including subdirectories
+ source = 'path/to/dir/**/*.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "YouTube"
+ Run inference on a YouTube video. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage for long videos.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as YouTube video URL
+ source = 'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "Stream"
+ Run inference on remote streaming sources using RTSP, RTMP, and IP address protocols.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as RTSP, RTMP or IP streaming address
+ source = 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
-## Arguments
+## Inference Arguments
`model.predict` accepts multiple arguments that control the prediction operation. These arguments can be passed directly to `model.predict`:
!!! example
- ```
+ ```python
model.predict(source, save=True, imgsz=320, conf=0.5)
```
@@ -97,12 +316,12 @@ All supported arguments:
## Image and Video Formats
-YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified
-in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the
-tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
+YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Image Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
+
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .bmp | `yolo predict source=image.bmp` | [Microsoft BMP File Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format) |
@@ -118,6 +337,8 @@ tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Video Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics video formats.
+
| Video Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .asf | `yolo predict source=video.asf` | [Advanced Systems Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Systems_Format) |
diff --git a/docs/modes/train.md b/docs/modes/train.md
index 882c0d1f1..16c32ef84 100644
--- a/docs/modes/train.md
+++ b/docs/modes/train.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, train mode, train a custom YOLOv8 model, hyperparameters, trai
@@ -84,4 +84,5 @@ i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
+| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/modes/predict.md b/docs/modes/predict.md
index 581d4221d..8708933e6 100644
--- a/docs/modes/predict.md
+++ b/docs/modes/predict.md
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
---
comments: true
-description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
+description: Get started with YOLOv8 Predict mode and input sources. Accepts various input sources such as images, videos, and directories.
keywords: YOLOv8, predict mode, generator, streaming mode, input sources, video formats, arguments customization
---
@@ -12,60 +12,279 @@ passing `stream=True` in the predictor's call method.
!!! example "Predict"
- === "Return a list with `Stream=False`"
+ === "Return a list with `stream=False`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs) # list of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg']) # return a list of Results objects
+ # Process results list
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
- === "Return a generator with `Stream=True`"
+ === "Return a generator with `stream=True`"
```python
- inputs = [img, img] # list of numpy arrays
- results = model(inputs, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # pretrained YOLOv8n model
+
+ # Run batched inference on a list of images
+ results = model(['im1.jpg', 'im2.jpg'], stream=True) # return a generator of Results objects
+ # Process results generator
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes # Boxes object for bbox outputs
masks = result.masks # Masks object for segmentation masks outputs
+ keypoints = result.keypoints # Keypoints object for pose outputs
probs = result.probs # Class probabilities for classification outputs
```
-!!! tip "Tip"
-
- Streaming mode with `stream=True` should be used for long videos or large predict sources, otherwise results will accumuate in memory and will eventually cause out-of-memory errors.
+## Inference Sources
-## Sources
+YOLOv8 can process different types of input sources for inference, as shown in the table below. The sources include static images, video streams, and various data formats. The table also indicates whether each source can be used in streaming mode with the argument `stream=True` ✅. Streaming mode is beneficial for processing videos or live streams as it creates a generator of results instead of loading all frames into memory.
-YOLOv8 can accept various input sources, as shown in the table below. This includes images, URLs, PIL images, OpenCV,
-numpy arrays, torch tensors, CSV files, videos, directories, globs, YouTube videos, and streams. The table indicates
-whether each source can be used in streaming mode with `stream=True` ✅ and an example argument for each source.
+!!! tip "Tip"
-| source | model(arg) | type | notes |
-|-------------|--------------------------------------------|----------------|------------------|
-| image | `'im.jpg'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | |
-| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | |
-| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC, RGB |
-| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` | HWC, BGR |
-| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` | HWC |
-| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` | BCHW, RGB |
-| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str`, `Path` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
-| video ✅ | `'vid.mp4'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str`, `Path` | |
-| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Use `*` operator |
-| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | |
-| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | RTSP, RTMP, HTTP |
+ Use `stream=True` for processing long videos or large datasets to efficiently manage memory. When `stream=False`, the results for all frames or data points are stored in memory, which can quickly add up and cause out-of-memory errors for large inputs. In contrast, `stream=True` utilizes a generator, which only keeps the results of the current frame or data point in memory, significantly reducing memory consumption and preventing out-of-memory issues.
+
+| Source | Argument | Type | Notes |
+|-------------|--------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| image | `'image.jpg'` | `str` or `Path` | Single image file. |
+| URL | `'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'` | `str` | URL to an image. |
+| screenshot | `'screen'` | `str` | Capture a screenshot. |
+| PIL | `Image.open('im.jpg')` | `PIL.Image` | HWC format with RGB channels. |
+| OpenCV | `cv2.imread('im.jpg')` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| numpy | `np.zeros((640,1280,3))` | `np.ndarray` of `uint8 (0-255)` | HWC format with BGR channels. |
+| torch | `torch.zeros(16,3,320,640)` | `torch.Tensor` of `float32 (0.0-1.0)` | BCHW format with RGB channels. |
+| CSV | `'sources.csv'` | `str` or `Path` | CSV file containing paths to images, videos, or directories. |
+| video ✅ | `'video.mp4'` | `str` or `Path` | Video file in formats like MP4, AVI, etc. |
+| directory ✅ | `'path/'` | `str` or `Path` | Path to a directory containing images or videos. |
+| glob ✅ | `'path/*.jpg'` | `str` | Glob pattern to match multiple files. Use the `*` character as a wildcard. |
+| YouTube ✅ | `'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'` | `str` | URL to a YouTube video. |
+| stream ✅ | `'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'` | `str` | URL for streaming protocols such as RTSP, RTMP, or an IP address. |
+
+Below are code examples for using each source type:
+
+!!! example "Prediction sources"
+
+ === "image"
+ Run inference on an image file.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to the image file
+ source = 'path/to/image.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "screenshot"
+ Run inference on the current screen content as a screenshot.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define current screenshot as source
+ source = 'screen'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "URL"
+ Run inference on an image or video hosted remotely via URL.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define remote image or video URL
+ source = 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "PIL"
+ Run inference on an image opened with Python Imaging Library (PIL).
+ ```python
+ from PIL import Image
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Open an image using PIL
+ source = Image.open('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "OpenCV"
+ Run inference on an image read with OpenCV.
+ ```python
+ import cv2
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Read an image using OpenCV
+ source = cv2.imread('path/to/image.jpg')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "numpy"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a numpy array.
+ ```python
+ import numpy as np
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random numpy array of HWC shape (640, 640, 3) with values in range [0, 255] and type uint8
+ source = np.random.randint(low=0, high=255, size=(640, 640, 3), dtype='uint8')
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "torch"
+ Run inference on an image represented as a PyTorch tensor.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Create a random torch tensor of BCHW shape (1, 3, 640, 640) with values in range [0, 1] and type float32
+ source = torch.rand(1, 3, 640, 640, dtype=torch.float32)
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "CSV"
+ Run inference on a collection of images, URLs, videos and directories listed in a CSV file.
+ ```python
+ import torch
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a path to a CSV file with images, URLs, videos and directories
+ source = 'path/to/file.csv'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source) # list of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "video"
+ Run inference on a video file. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to video file
+ source = 'path/to/video.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "directory"
+ Run inference on all images and videos in a directory. To also capture images and videos in subdirectories use a glob pattern, i.e. `path/to/dir/**/*`.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define path to directory containing images and videos for inference
+ source = 'path/to/dir'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "glob"
+ Run inference on all images and videos that match a glob expression with `*` characters.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define a glob search for all JPG files in a directory
+ source = 'path/to/dir/*.jpg'
+
+ # OR define a recursive glob search for all JPG files including subdirectories
+ source = 'path/to/dir/**/*.jpg'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "YouTube"
+ Run inference on a YouTube video. By using `stream=True`, you can create a generator of Results objects to reduce memory usage for long videos.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as YouTube video URL
+ source = 'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
+
+ === "Stream"
+ Run inference on remote streaming sources using RTSP, RTMP, and IP address protocols.
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a pretrained YOLOv8n model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt')
+
+ # Define source as RTSP, RTMP or IP streaming address
+ source = 'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4'
+
+ # Run inference on the source
+ results = model(source, stream=True) # generator of Results objects
+ ```
-## Arguments
+## Inference Arguments
`model.predict` accepts multiple arguments that control the prediction operation. These arguments can be passed directly to `model.predict`:
!!! example
- ```
+ ```python
model.predict(source, save=True, imgsz=320, conf=0.5)
```
@@ -97,12 +316,12 @@ All supported arguments:
## Image and Video Formats
-YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified
-in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the
-tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
+YOLOv8 supports various image and video formats, as specified in [yolo/data/utils.py](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/ultralytics/yolo/data/utils.py). See the tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Image Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics image formats.
+
| Image Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .bmp | `yolo predict source=image.bmp` | [Microsoft BMP File Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BMP_file_format) |
@@ -118,6 +337,8 @@ tables below for the valid suffixes and example predict commands.
### Video Suffixes
+The below table contains valid Ultralytics video formats.
+
| Video Suffixes | Example Predict Command | Reference |
|----------------|----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| .asf | `yolo predict source=video.asf` | [Advanced Systems Format](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Advanced_Systems_Format) |
diff --git a/docs/modes/train.md b/docs/modes/train.md
index 882c0d1f1..16c32ef84 100644
--- a/docs/modes/train.md
+++ b/docs/modes/train.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: YOLOv8, train mode, train a custom YOLOv8 model, hyperparameters, trai
 -**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the
-specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can
-accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
+**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,10 +14,11 @@ accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
## Usage Examples
-Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of
-training arguments.
+Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of training arguments.
-!!! example ""
+!!! example "Single-GPU and CPU Training Example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise training will start on CPU.
=== "Python"
@@ -47,14 +46,95 @@ training arguments.
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml pretrained=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
```
+### Multi-GPU Training
+
+The training device can be specified using the `device` argument. If no argument is passed GPU `device=0` will be used if available, otherwise `device=cpu` will be used.
+
+!!! example "Multi-GPU Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device=[0, 1])
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=0,1
+ ```
+
+### Apple M1 and M2 MPS Training
+
+With the support for Apple M1 and M2 chips integrated in the Ultralytics YOLO models, it's now possible to train your models on devices utilizing the powerful Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) framework. The MPS offers a high-performance way of executing computation and image processing tasks on Apple's custom silicon.
+
+To enable training on Apple M1 and M2 chips, you should specify 'mps' as your device when initiating the training process. Below is an example of how you could do this in Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "MPS Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device='mps')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=mps
+ ```
+
+While leveraging the computational power of the M1/M2 chips, this enables more efficient processing of the training tasks. For more detailed guidance and advanced configuration options, please refer to the [PyTorch MPS documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html).
+
+### Resuming Interrupted Trainings
+
+Resuming training from a previously saved state is a crucial feature when working with deep learning models. This can come in handy in various scenarios, like when the training process has been unexpectedly interrupted, or when you wish to continue training a model with new data or for more epochs.
+
+When training is resumed, Ultralytics YOLO loads the weights from the last saved model and also restores the optimizer state, learning rate scheduler, and the epoch number. This allows you to continue the training process seamlessly from where it was left off.
+
+You can easily resume training in Ultralytics YOLO by setting the `resume` argument to `True` when calling the `train` method, and specifying the path to the `.pt` file containing the partially trained model weights.
+
+Below is an example of how to resume an interrupted training using Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "Resume Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('path/to/last.pt') # load a partially trained model
+
+ # Resume training
+ model.train(resume=True)
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Resume an interrupted training
+ yolo train resume model=path/to/last.pt
+ ```
+
+By setting `resume=True`, the `train` function will continue training from where it left off, using the state stored in the 'path/to/last.pt' file. If the `resume` argument is omitted or set to `False`, the `train` function will start a new training session.
+
+Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at fixed interval using the `save_period` argument, so you must complete at least 1 epoch to resume a training run.
+
## Arguments
-Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a
-dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings
-include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process
-include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given
-task.
+Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given task.
| Key | Value | Description |
|-------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/modes/val.md b/docs/modes/val.md
index 79fdf6f8e..4ffff738d 100644
--- a/docs/modes/val.md
+++ b/docs/modes/val.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, YOLOv8, Val, Validation, Hyperparameters, Performan
-**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the
-specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can
-accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
+**Train mode** is used for training a YOLOv8 model on a custom dataset. In this mode, the model is trained using the specified dataset and hyperparameters. The training process involves optimizing the model's parameters so that it can accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,10 +14,11 @@ accurately predict the classes and locations of objects in an image.
## Usage Examples
-Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of
-training arguments.
+Train YOLOv8n on the COCO128 dataset for 100 epochs at image size 640. See Arguments section below for a full list of training arguments.
-!!! example ""
+!!! example "Single-GPU and CPU Training Example"
+
+ Device is determined automatically. If a GPU is available then it will be used, otherwise training will start on CPU.
=== "Python"
@@ -47,14 +46,95 @@ training arguments.
yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.yaml pretrained=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640
```
+### Multi-GPU Training
+
+The training device can be specified using the `device` argument. If no argument is passed GPU `device=0` will be used if available, otherwise `device=cpu` will be used.
+
+!!! example "Multi-GPU Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device=[0, 1])
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=0,1
+ ```
+
+### Apple M1 and M2 MPS Training
+
+With the support for Apple M1 and M2 chips integrated in the Ultralytics YOLO models, it's now possible to train your models on devices utilizing the powerful Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) framework. The MPS offers a high-performance way of executing computation and image processing tasks on Apple's custom silicon.
+
+To enable training on Apple M1 and M2 chips, you should specify 'mps' as your device when initiating the training process. Below is an example of how you could do this in Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "MPS Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load a pretrained model (recommended for training)
+
+ # Train the model with 2 GPUs
+ model.train(data='coco128.yaml', epochs=100, imgsz=640, device='mps')
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Start training from a pretrained *.pt model using GPUs 0 and 1
+ yolo detect train data=coco128.yaml model=yolov8n.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 device=mps
+ ```
+
+While leveraging the computational power of the M1/M2 chips, this enables more efficient processing of the training tasks. For more detailed guidance and advanced configuration options, please refer to the [PyTorch MPS documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html).
+
+### Resuming Interrupted Trainings
+
+Resuming training from a previously saved state is a crucial feature when working with deep learning models. This can come in handy in various scenarios, like when the training process has been unexpectedly interrupted, or when you wish to continue training a model with new data or for more epochs.
+
+When training is resumed, Ultralytics YOLO loads the weights from the last saved model and also restores the optimizer state, learning rate scheduler, and the epoch number. This allows you to continue the training process seamlessly from where it was left off.
+
+You can easily resume training in Ultralytics YOLO by setting the `resume` argument to `True` when calling the `train` method, and specifying the path to the `.pt` file containing the partially trained model weights.
+
+Below is an example of how to resume an interrupted training using Python and via the command line:
+
+!!! example "Resume Training Example"
+
+ === "Python"
+
+ ```python
+ from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+ # Load a model
+ model = YOLO('path/to/last.pt') # load a partially trained model
+
+ # Resume training
+ model.train(resume=True)
+ ```
+ === "CLI"
+
+ ```bash
+ # Resume an interrupted training
+ yolo train resume model=path/to/last.pt
+ ```
+
+By setting `resume=True`, the `train` function will continue training from where it left off, using the state stored in the 'path/to/last.pt' file. If the `resume` argument is omitted or set to `False`, the `train` function will start a new training session.
+
+Remember that checkpoints are saved at the end of every epoch by default, or at fixed interval using the `save_period` argument, so you must complete at least 1 epoch to resume a training run.
+
## Arguments
-Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a
-dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings
-include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process
-include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given
-task.
+Training settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to train the model on a dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO training settings include the batch size, learning rate, momentum, and weight decay. Other factors that may affect the training process include the choice of optimizer, the choice of loss function, and the size and composition of the training dataset. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to achieve the best possible performance for a given task.
| Key | Value | Description |
|-------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
diff --git a/docs/modes/val.md b/docs/modes/val.md
index 79fdf6f8e..4ffff738d 100644
--- a/docs/modes/val.md
+++ b/docs/modes/val.md
@@ -6,9 +6,7 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, YOLOv8, Val, Validation, Hyperparameters, Performan
 -**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a
-validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters
-of the model to improve its performance.
+**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters of the model to improve its performance.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,8 +14,7 @@ of the model to improve its performance.
## Usage Examples
-Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's
-training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
+Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
!!! example ""
@@ -46,13 +43,7 @@ training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below f
## Arguments
-Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to
-evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and
-accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed
-during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation
-process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the
-validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
+Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| Key | Value | Description |
|---------------|---------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|
@@ -70,23 +61,4 @@ validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| `plots` | `False` | show plots during training |
| `rect` | `False` | rectangular val with each batch collated for minimum padding |
| `split` | `val` | dataset split to use for validation, i.e. 'val', 'test' or 'train' |
-
-## Export Formats
-
-Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument,
-i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
-
-| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
-| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
-| [OpenVINO](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
-| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
-| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
-| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
-| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+|
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/quickstart.md b/docs/quickstart.md
index b762e5ab4..cd8d63054 100644
--- a/docs/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/quickstart.md
@@ -4,27 +4,74 @@ description: Install and use YOLOv8 via CLI or Python. Run single-line commands
keywords: YOLOv8, object detection, segmentation, classification, pip, git, CLI, Python
---
-## Install
+## Install Ultralytics
-Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning
-the [https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) repository for the most
-up-to-date version.
+Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Docker. Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning the [Ultralytics GitHub repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) for the most up-to-date version. Docker can be used to execute the package in an isolated container, avoiding local installation.
!!! example "Install"
- === "pip install (recommended)"
+ === "Pip install (recommended)"
+ Install the `ultralytics` package using pip, or update an existing installation by running `pip install -U ultralytics`. Visit the Python Package Index (PyPI) for more details on the `ultralytics` package: [https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/).
+
+ [](https://badge.fury.io/py/ultralytics) [](https://pepy.tech/project/ultralytics)
+
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using pip
pip install ultralytics
```
+
+ === "Conda install"
+ Conda is an alternative package manager to pip which may also be used for installation. Visit Anaconda for more details at [https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics). Ultralytics feedstock repository for updating the conda package is at [https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/](https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/).
+
+
+ [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics)
- === "git clone (for development)"
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using conda
+ conda install ultralytics
+ ```
+
+ === "Git clone"
+ Clone the `ultralytics` repository if you are interested in contributing to the development or wish to experiment with the latest source code. After cloning, navigate into the directory and install the package in editable mode `-e` using pip.
+ ```bash
+ # Clone the ultralytics repository
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
+
+ # Navigate to the cloned directory
cd ultralytics
+
+ # Install the package in editable mode for development
pip install -e .
```
-See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that `pip` automatically installs all required dependencies.
+ === "Docker"
+ Utilize Docker to execute the `ultralytics` package in an isolated container. By employing the official `ultralytics` image from [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics), you can avoid local installation. Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
+
+
-**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a
-validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters
-of the model to improve its performance.
+**Val mode** is used for validating a YOLOv8 model after it has been trained. In this mode, the model is evaluated on a validation set to measure its accuracy and generalization performance. This mode can be used to tune the hyperparameters of the model to improve its performance.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -16,8 +14,7 @@ of the model to improve its performance.
## Usage Examples
-Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's
-training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
+Validate trained YOLOv8n model accuracy on the COCO128 dataset. No argument need to passed as the `model` retains it's training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below for a full list of export arguments.
!!! example ""
@@ -46,13 +43,7 @@ training `data` and arguments as model attributes. See Arguments section below f
## Arguments
-Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to
-evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and
-accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed
-during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation
-process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It
-is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the
-validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
+Validation settings for YOLO models refer to the various hyperparameters and configurations used to evaluate the model's performance on a validation dataset. These settings can affect the model's performance, speed, and accuracy. Some common YOLO validation settings include the batch size, the frequency with which validation is performed during training, and the metrics used to evaluate the model's performance. Other factors that may affect the validation process include the size and composition of the validation dataset and the specific task the model is being used for. It is important to carefully tune and experiment with these settings to ensure that the model is performing well on the validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| Key | Value | Description |
|---------------|---------|--------------------------------------------------------------------|
@@ -70,23 +61,4 @@ validation dataset and to detect and prevent overfitting.
| `plots` | `False` | show plots during training |
| `rect` | `False` | rectangular val with each batch collated for minimum padding |
| `split` | `val` | dataset split to use for validation, i.e. 'val', 'test' or 'train' |
-
-## Export Formats
-
-Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can export to any format using the `format` argument,
-i.e. `format='onnx'` or `format='engine'`.
-
-| Format | `format` Argument | Model | Metadata | Arguments |
-|--------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------|---------------------------|----------|-----------------------------------------------------|
-| [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) | - | `yolov8n.pt` | ✅ | - |
-| [TorchScript](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/jit.html) | `torchscript` | `yolov8n.torchscript` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `optimize` |
-| [ONNX](https://onnx.ai/) | `onnx` | `yolov8n.onnx` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `opset` |
-| [OpenVINO](https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html) | `openvino` | `yolov8n_openvino_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` |
-| [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) | `engine` | `yolov8n.engine` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `dynamic`, `simplify`, `workspace` |
-| [CoreML](https://github.com/apple/coremltools) | `coreml` | `yolov8n.mlmodel` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8`, `nms` |
-| [TF SavedModel](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model) | `saved_model` | `yolov8n_saved_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `keras` |
-| [TF GraphDef](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Graph) | `pb` | `yolov8n.pb` | ❌ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite) | `tflite` | `yolov8n.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half`, `int8` |
-| [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
-| [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` |
\ No newline at end of file
+|
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/quickstart.md b/docs/quickstart.md
index b762e5ab4..cd8d63054 100644
--- a/docs/quickstart.md
+++ b/docs/quickstart.md
@@ -4,27 +4,74 @@ description: Install and use YOLOv8 via CLI or Python. Run single-line commands
keywords: YOLOv8, object detection, segmentation, classification, pip, git, CLI, Python
---
-## Install
+## Install Ultralytics
-Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning
-the [https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) repository for the most
-up-to-date version.
+Ultralytics provides various installation methods including pip, conda, and Docker. Install YOLOv8 via the `ultralytics` pip package for the latest stable release or by cloning the [Ultralytics GitHub repository](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics) for the most up-to-date version. Docker can be used to execute the package in an isolated container, avoiding local installation.
!!! example "Install"
- === "pip install (recommended)"
+ === "Pip install (recommended)"
+ Install the `ultralytics` package using pip, or update an existing installation by running `pip install -U ultralytics`. Visit the Python Package Index (PyPI) for more details on the `ultralytics` package: [https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/](https://pypi.org/project/ultralytics/).
+
+ [](https://badge.fury.io/py/ultralytics) [](https://pepy.tech/project/ultralytics)
+
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using pip
pip install ultralytics
```
+
+ === "Conda install"
+ Conda is an alternative package manager to pip which may also be used for installation. Visit Anaconda for more details at [https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics). Ultralytics feedstock repository for updating the conda package is at [https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/](https://github.com/conda-forge/ultralytics-feedstock/).
+
+
+ [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics) [](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/ultralytics)
- === "git clone (for development)"
```bash
+ # Install the ultralytics package using conda
+ conda install ultralytics
+ ```
+
+ === "Git clone"
+ Clone the `ultralytics` repository if you are interested in contributing to the development or wish to experiment with the latest source code. After cloning, navigate into the directory and install the package in editable mode `-e` using pip.
+ ```bash
+ # Clone the ultralytics repository
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
+
+ # Navigate to the cloned directory
cd ultralytics
+
+ # Install the package in editable mode for development
pip install -e .
```
-See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that `pip` automatically installs all required dependencies.
+ === "Docker"
+ Utilize Docker to execute the `ultralytics` package in an isolated container. By employing the official `ultralytics` image from [Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/ultralytics/ultralytics), you can avoid local installation. Below are the commands to get the latest image and execute it:
+
+  +
+ ```bash
+ # Set image name as a variable
+ t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
+
+ # Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
+ sudo docker pull $t
+
+ # Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t
+ ```
+
+ The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
+
+ Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
+ ```
+
+ Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
+
+See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -34,9 +81,9 @@ See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralyt
+
+ ```bash
+ # Set image name as a variable
+ t=ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
+
+ # Pull the latest ultralytics image from Docker Hub
+ sudo docker pull $t
+
+ # Run the ultralytics image in a container with GPU support
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all $t
+ ```
+
+ The above command initializes a Docker container with the latest `ultralytics` image. The `-it` flag assigns a pseudo-TTY and maintains stdin open, enabling you to interact with the container. The `--ipc=host` flag sets the IPC (Inter-Process Communication) namespace to the host, which is essential for sharing memory between processes. The `--gpus all` flag enables access to all available GPUs inside the container, which is crucial for tasks that require GPU computation.
+
+ Note: To work with files on your local machine within the container, use Docker volumes for mounting a local directory into the container:
+
+ ```bash
+ # Mount local directory to a directory inside the container
+ sudo docker run -it --ipc=host --gpus all -v /path/on/host:/path/in/container $t
+ ```
+
+ Alter `/path/on/host` with the directory path on your local machine, and `/path/in/container` with the desired path inside the Docker container for accessibility.
+
+See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/blob/main/requirements.txt) file for a list of dependencies. Note that all examples above install all required dependencies.
!!! tip "Tip"
@@ -34,9 +81,9 @@ See the `ultralytics` [requirements.txt](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralyt
 -## Use with CLI
+## Use Ultralytics with CLI
-The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
+The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! example
@@ -103,7 +150,7 @@ CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button .md-button--primary}
-## Use with Python
+## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
index c979186ea..f4446087c 100644
--- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
+++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
@@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETR, Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, speed, accuracy, implemen
## RTDETR
---
### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.model.RTDETR
-
-## Use with CLI
+## Use Ultralytics with CLI
-The YOLO command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
+The Ultralytics command line interface (CLI) allows for simple single-line commands without the need for a Python environment.
CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from the terminal with the `yolo` command. Check out the [CLI Guide](usage/cli.md) to learn more about using YOLOv8 from the command line.
!!! example
@@ -103,7 +150,7 @@ CLI requires no customization or Python code. You can simply run all tasks from
[CLI Guide](usage/cli.md){ .md-button .md-button--primary}
-## Use with Python
+## Use Ultralytics with Python
YOLOv8's Python interface allows for seamless integration into your Python projects, making it easy to load, run, and process the model's output. Designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind, the Python interface enables users to quickly implement object detection, segmentation, and classification in their projects. This makes YOLOv8's Python interface an invaluable tool for anyone looking to incorporate these functionalities into their Python projects.
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
index c979186ea..f4446087c 100644
--- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
+++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/model.md
@@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETR, Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, speed, accuracy, implemen
## RTDETR
---
### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.model.RTDETR
-\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md index c5b5420a4..032c2da59 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/predict.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRPredictor, object detection, vision transformer, Ultralytics YOL ## RTDETRPredictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.predict.RTDETRPredictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md index b7bb384eb..03f33f7c8 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/train.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRTrainer, Ultralytics YOLO Docs, object detection, VIT-based RTDE ## train --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.train.train -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md index 43c1898b3..32359b32f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/rtdetr/val.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: RTDETRDataset, RTDETRValidator, data validation, documentation ## RTDETRValidator --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.rtdetr.val.RTDETRValidator -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md index 82c66e8b1..a5b5e4f82 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/amg.md @@ -86,4 +86,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, SAM, MaskData, mask_to_rle_pytorch, area_from_rle, genera ## batched_mask_to_box --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.amg.batched_mask_to_box -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md index cbb0ca7c0..ca84d37f6 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/autosize.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: ResizeLongestSide, Ultralytics YOLO, automatic image resizing, image r ## ResizeLongestSide --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.autosize.ResizeLongestSide -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md index faa26eead..6c3962112 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/build.md @@ -26,4 +26,4 @@ keywords: SAM, VIT, computer vision models, build SAM models, build VIT models, ## build_sam --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.build.build_sam -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md index 7d924d4a9..4149847fc 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/model.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, VIT, SAM, object detection, computer vision, deep learnin ## SAM --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.model.SAM -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md index e89ca9d68..940d720c6 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/decoders.md @@ -1,3 +1,8 @@ +--- +description: Learn about Ultralytics YOLO's MaskDecoder, Transformer architecture, MLP, mask prediction, and quality prediction. +keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, MaskDecoder, Transformer architecture, mask prediction, image embeddings, prompt embeddings, multi-mask output, MLP, mask quality prediction +--- + ## MaskDecoder --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.decoders.MaskDecoder diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md index 8c338bc6d..bd5760a97 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/encoders.md @@ -51,4 +51,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, ViT Encoder, Position Embeddings, Attention, Window ## add_decomposed_rel_pos --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.encoders.add_decomposed_rel_pos -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md index e2e1251c1..beec1d3f0 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/mask_generator.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: SamAutomaticMaskGenerator, Ultralytics YOLO, automatic mask generator, ## SamAutomaticMaskGenerator --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.mask_generator.SamAutomaticMaskGenerator -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md index f7e3b3713..00de169ef 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/prompt_predictor.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: PromptPredictor, Ultralytics, YOLO, VIT SAM, image captioning, deep le ## PromptPredictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.prompt_predictor.PromptPredictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md index acd467b19..7ead8cb7f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/sam.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics VIT, Sam module, PyTorch vision library, image classificat ## Sam --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.sam.Sam -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md index 994b98455..e0d8eeb86 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/modules/transformer.md @@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, Attention module, TwoWayTransformer module, Object D ## Attention --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.modules.transformer.Attention -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md b/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md index 836d91e3c..35479518b 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/sam/predict.md @@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, VIT SAM Predictor, object detection, YOLO ## Predictor --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.sam.predict.Predictor -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md b/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md index 3eb366ed3..cd45d5f5f 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/utils/loss.md @@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ keywords: DETRLoss, RTDETRDetectionLoss, Ultralytics, object detection, image cl ## RTDETRDetectionLoss --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.utils.loss.RTDETRDetectionLoss -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md b/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md index f4b7c8176..e4660f094 100644 --- a/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md +++ b/docs/reference/vit/utils/ops.md @@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ keywords: Ultralytics, YOLO, object detection, HungarianMatcher, inverse_sigmoid ## inverse_sigmoid --- ### ::: ultralytics.vit.utils.ops.inverse_sigmoid -
\ No newline at end of file +
diff --git a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md index dd07646c1..3e06f8f34 100644 --- a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md +++ b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/downloads.md @@ -23,6 +23,11 @@ keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, downloads, trained models, datasets, weights, deep l ### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.safe_download
+## get_github_assets +--- +### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.get_github_assets +
+ ## attempt_download_asset --- ### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.downloads.attempt_download_asset diff --git a/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md new file mode 100644 index 000000000..bf9300089 --- /dev/null +++ b/docs/reference/yolo/utils/tuner.md @@ -0,0 +1,9 @@ +--- +description: Optimize YOLO models' hyperparameters with Ultralytics YOLO's `run_ray_tune` function using Ray Tune and ASHA scheduler. +keywords: Ultralytics YOLO, Hyperparameter Tuning, Ray Tune, ASHAScheduler, Optimization, Object Detection +--- + +## run_ray_tune +--- +### ::: ultralytics.yolo.utils.tuner.run_ray_tune +
diff --git a/docs/tasks/classify.md b/docs/tasks/classify.md index fe0b939b3..8d71093d8 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/classify.md +++ b/docs/tasks/classify.md @@ -176,5 +176,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-cls.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your mo | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-cls_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-cls_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-cls_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-cls_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/detect.md b/docs/tasks/detect.md index 35a3d444c..6573b75b9 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/detect.md +++ b/docs/tasks/detect.md @@ -167,5 +167,6 @@ Available YOLOv8 export formats are in the table below. You can predict or valid | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/pose.md b/docs/tasks/pose.md index 094f95b87..ef8495dc7 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/pose.md +++ b/docs/tasks/pose.md @@ -181,5 +181,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-pose.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your m | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-pose_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-pose_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-pose_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-pose_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/tasks/segment.md b/docs/tasks/segment.md index 4f9192ffc..659ac8267 100644 --- a/docs/tasks/segment.md +++ b/docs/tasks/segment.md @@ -181,5 +181,6 @@ i.e. `yolo predict model=yolov8n-seg.onnx`. Usage examples are shown for your mo | [TF Edge TPU](https://coral.ai/docs/edgetpu/models-intro/) | `edgetpu` | `yolov8n-seg_edgetpu.tflite` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [TF.js](https://www.tensorflow.org/js) | `tfjs` | `yolov8n-seg_web_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | | [PaddlePaddle](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle) | `paddle` | `yolov8n-seg_paddle_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz` | +| [ncnn](https://github.com/Tencent/ncnn) | `ncnn` | `yolov8n-seg_ncnn_model/` | ✅ | `imgsz`, `half` | See full `export` details in the [Export](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/export/) page. \ No newline at end of file diff --git a/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md b/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md index 06a384144..1b25ade16 100644 --- a/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md +++ b/docs/usage/hyperparameter_tuning.md @@ -1,29 +1,26 @@ --- comments: true -description: Discover how to integrate hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune and Ultralytics YOLOv8. Speed up the tuning process and optimize your model's performance. +description: Learn to integrate hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune with Ultralytics YOLOv8, and optimize your model's performance efficiently. keywords: yolov8, ray tune, hyperparameter tuning, hyperparameter optimization, machine learning, computer vision, deep learning, image recognition --- -# Hyperparameter Tuning with Ray Tune and YOLOv8 +# Efficient Hyperparameter Tuning with Ray Tune and YOLOv8 -Hyperparameter tuning (or hyperparameter optimization) is the process of determining the right combination of hyperparameters that maximizes model performance. It works by running multiple trials in a single training process, evaluating the performance of each trial, and selecting the best hyperparameter values based on the evaluation results. +Hyperparameter tuning is vital in achieving peak model performance by discovering the optimal set of hyperparameters. This involves running trials with different hyperparameters and evaluating each trial’s performance. -## Ultralytics YOLOv8 and Ray Tune Integration +## Accelerate Tuning with Ultralytics YOLOv8 and Ray Tune -[Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) YOLOv8 integrates hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune, allowing you to easily optimize your YOLOv8 model's hyperparameters. By using Ray Tune, you can leverage advanced search algorithms, parallelism, and early stopping to speed up the tuning process and achieve better model performance. +[Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://ultralytics.com) incorporates Ray Tune for hyperparameter tuning, streamlining the optimization of YOLOv8 model hyperparameters. With Ray Tune, you can utilize advanced search strategies, parallelism, and early stopping to expedite the tuning process. ### Ray Tune -
-
- -
-
+
-[Ray Tune](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html) is a powerful and flexible hyperparameter tuning library for machine learning models. It provides an efficient way to optimize hyperparameters by supporting various search algorithms, parallelism, and early stopping strategies. Ray Tune's flexible architecture enables seamless integration with popular machine learning frameworks, including Ultralytics YOLOv8.
+[Ray Tune](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html) is a hyperparameter tuning library designed for efficiency and flexibility. It supports various search strategies, parallelism, and early stopping strategies, and seamlessly integrates with popular machine learning frameworks, including Ultralytics YOLOv8.
-### Weights & Biases
+### Integration with Weights & Biases
-YOLOv8 also supports optional integration with [Weights & Biases](https://wandb.ai/site) (wandb) for tracking the tuning progress.
+YOLOv8 also allows optional integration with [Weights & Biases](https://wandb.ai/site) for monitoring the tuning process.
## Installation
@@ -32,8 +29,11 @@ To install the required packages, run:
!!! tip "Installation"
```bash
- pip install -U ultralytics "ray[tune]" # install and/or update
- pip install wandb # optional
+ # Install and update Ultralytics and Ray Tune pacakges
+ pip install -U ultralytics 'ray[tune]'
+
+ # Optionally install W&B for logging
+ pip install wandb
```
## Usage
@@ -44,21 +44,21 @@ To install the required packages, run:
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
- results = model.tune(data="coco128.yaml")
+ result_grid = model.tune(data="coco128.yaml")
```
## `tune()` Method Parameters
The `tune()` method in YOLOv8 provides an easy-to-use interface for hyperparameter tuning with Ray Tune. It accepts several arguments that allow you to customize the tuning process. Below is a detailed explanation of each parameter:
-| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
-|-----------------|----------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
-| `data` | str | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
-| `space` | dict, optional | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
-| `grace_period` | int, optional | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler]https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api/schedulers.html) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
-| `gpu_per_trial` | int, optional | The number of GPUs to allocate per trial during tuning. This helps manage GPU usage, particularly in multi-GPU environments. If not provided, the tuner will use all available GPUs. | None |
-| `max_samples` | int, optional | The maximum number of trials to run during tuning. This parameter helps control the total number of hyperparameter combinations tested, ensuring the tuning process does not run indefinitely. | 10 |
-| `train_args` | dict, optional | A dictionary of additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method during tuning. These arguments can include settings like the number of training epochs, batch size, and other training-specific configurations. | {} |
+| Parameter | Type | Description | Default Value |
+|-----------------|----------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
+| `data` | str | The dataset configuration file (in YAML format) to run the tuner on. This file should specify the training and validation data paths, as well as other dataset-specific settings. | |
+| `space` | dict, optional | A dictionary defining the hyperparameter search space for Ray Tune. Each key corresponds to a hyperparameter name, and the value specifies the range of values to explore during tuning. If not provided, YOLOv8 uses a default search space with various hyperparameters. | |
+| `grace_period` | int, optional | The grace period in epochs for the [ASHA scheduler](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api/schedulers.html) in Ray Tune. The scheduler will not terminate any trial before this number of epochs, allowing the model to have some minimum training before making a decision on early stopping. | 10 |
+| `gpu_per_trial` | int, optional | The number of GPUs to allocate per trial during tuning. This helps manage GPU usage, particularly in multi-GPU environments. If not provided, the tuner will use all available GPUs. | None |
+| `max_samples` | int, optional | The maximum number of trials to run during tuning. This parameter helps control the total number of hyperparameter combinations tested, ensuring the tuning process does not run indefinitely. | 10 |
+| `**train_args` | dict, optional | Additional arguments to pass to the `train()` method during tuning. These arguments can include settings like the number of training epochs, batch size, and other training-specific configurations. | {} |
By customizing these parameters, you can fine-tune the hyperparameter optimization process to suit your specific needs and available computational resources.
@@ -98,14 +98,72 @@ In this example, we demonstrate how to use a custom search space for hyperparame
```python
from ultralytics import YOLO
- from ray import tune
-
+
+ # Define a YOLO model
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
- result = model.tune(
- data="coco128.yaml",
- space={"lr0": tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1)},
- train_args={"epochs": 50}
- )
+
+ # Run Ray Tune on the model
+ result_grid = model.tune(data="coco128.yaml",
+ space={"lr0": tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1)},
+ epochs=50)
```
-In the code snippet above, we create a YOLO model with the "yolov8n.pt" pretrained weights. Then, we call the `tune()` method, specifying the dataset configuration with "coco128.yaml". We provide a custom search space for the initial learning rate `lr0` using a dictionary with the key "lr0" and the value `tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1)`. Finally, we pass additional training arguments, such as the number of epochs, using the `train_args` parameter.
\ No newline at end of file
+In the code snippet above, we create a YOLO model with the "yolov8n.pt" pretrained weights. Then, we call the `tune()` method, specifying the dataset configuration with "coco128.yaml". We provide a custom search space for the initial learning rate `lr0` using a dictionary with the key "lr0" and the value `tune.uniform(1e-5, 1e-1)`. Finally, we pass additional training arguments, such as the number of epochs directly to the tune method as `epochs=50`.
+
+# Processing Ray Tune Results
+
+After running a hyperparameter tuning experiment with Ray Tune, you might want to perform various analyses on the obtained results. This guide will take you through common workflows for processing and analyzing these results.
+
+## Loading Tune Experiment Results from a Directory
+
+After running the tuning experiment with `tuner.fit()`, you can load the results from a directory. This is useful, especially if you're performing the analysis after the initial training script has exited.
+
+```python
+experiment_path = f"{storage_path}/{exp_name}"
+print(f"Loading results from {experiment_path}...")
+
+restored_tuner = tune.Tuner.restore(experiment_path, trainable=train_mnist)
+result_grid = restored_tuner.get_results()
+```
+
+## Basic Experiment-Level Analysis
+
+Get an overview of how trials performed. You can quickly check if there were any errors during the trials.
+
+```python
+if result_grid.errors:
+ print("One or more trials failed!")
+else:
+ print("No errors!")
+```
+
+## Basic Trial-Level Analysis
+
+Access individual trial hyperparameter configurations and the last reported metrics.
+
+```python
+for i, result in enumerate(result_grid):
+ print(f"Trial #{i}: Configuration: {result.config}, Last Reported Metrics: {result.metrics}")
+```
+
+## Plotting the Entire History of Reported Metrics for a Trial
+
+You can plot the history of reported metrics for each trial to see how the metrics evolved over time.
+
+```python
+import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
+
+for result in result_grid:
+ plt.plot(result.metrics_dataframe["training_iteration"], result.metrics_dataframe["mean_accuracy"], label=f"Trial {i}")
+
+plt.xlabel('Training Iterations')
+plt.ylabel('Mean Accuracy')
+plt.legend()
+plt.show()
+```
+
+## Summary
+
+In this documentation, we covered common workflows to analyze the results of experiments run with Ray Tune using Ultralytics. The key steps include loading the experiment results from a directory, performing basic experiment-level and trial-level analysis and plotting metrics.
+
+Explore further by looking into Ray Tune’s [Analyze Results](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/examples/tune_analyze_results.html) docs page to get the most out of your hyperparameter tuning experiments.
diff --git a/docs/yolov5/index.md b/docs/yolov5/index.md
index 8c666a2b9..74f8feee4 100644
--- a/docs/yolov5/index.md
+++ b/docs/yolov5/index.md
@@ -85,6 +85,6 @@ This badge signifies that all [YOLOv5 GitHub Actions](https://github.com/ultraly
 -
-
 -
+
-
+
 \ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/README.md b/examples/README.md
index d2c27c13d..120c04be5 100644
--- a/examples/README.md
+++ b/examples/README.md
@@ -8,9 +8,12 @@ This repository features a collection of real-world applications and walkthrough
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------- |
| [YOLO ONNX Detection Inference with C++](./YOLOv8-CPP-Inference) | C++/ONNX | [Justas Bartnykas](https://github.com/JustasBart) |
| [YOLO OpenCV ONNX Detection Python](./YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python) | OpenCV/Python/ONNX | [Farid Inawan](https://github.com/frdteknikelektro) |
+| [YOLOv8 .NET ONNX ImageSharp](https://github.com/dme-compunet/YOLOv8) | C#/ONNX/ImageSharp | [Compunet](https://github.com/dme-compunet) |
| [YOLO .Net ONNX Detection C#](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Yolov8.Net) | C# .Net | [Samuel Stainback](https://github.com/sstainba) |
| [YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson(TensorRT and DeepStream)](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/YOLOv8-DeepStream-TRT-Jetson/) | Python | [Lakshantha](https://github.com/lakshanthad) |
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
+| [YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP) | C++/ONNXRuntime | [DennisJcy](https://github.com/DennisJcy) |
+| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime C#](https://github.com/Kayzwer/yolo-cs/blob/master/RTDETR.cs) | C#/ONNX | [Kayzwer](https://github.com/Kayzwer) |
### How to Contribute
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c49866497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+# YOLOv8 OnnxRuntime C++
+
+This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 in C++ with ONNX Runtime and OpenCV's API.
+
+We recommend using Visual Studio to build the project.
+
+## Benefits
+
+- Friendly for deployment in the industrial sector.
+- Faster than OpenCV's DNN inference on both CPU and GPU.
+- Supports CUDA acceleration.
+- Easy to add FP16 inference (using template functions).
+
+## Exporting YOLOv8 Models
+
+To export YOLOv8 models, use the following Python script:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+# Load a YOLOv8 model
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
+
+# Export the model
+model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
+```
+
+## Dependencies
+
+| Dependency | Version |
+| ----------------------- | -------- |
+| Onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu | >=1.14.1 |
+| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
+| C++ | >=17 |
+
+Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
+
+## Usage
+
+```c++
+// CPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, false};
+// GPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, true};
+
+// Load your image
+cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
+
+char* ret = p1->CreateSession(params);
+
+ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
+```
+
+This repository should also work for YOLOv5, which needs a permute operator for the output of the YOLOv5 model, but this has not been implemented yet.
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5af395dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+#include "inference.h"
+#include
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/examples/README.md b/examples/README.md
index d2c27c13d..120c04be5 100644
--- a/examples/README.md
+++ b/examples/README.md
@@ -8,9 +8,12 @@ This repository features a collection of real-world applications and walkthrough
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------ | --------------------------------------------------- |
| [YOLO ONNX Detection Inference with C++](./YOLOv8-CPP-Inference) | C++/ONNX | [Justas Bartnykas](https://github.com/JustasBart) |
| [YOLO OpenCV ONNX Detection Python](./YOLOv8-OpenCV-ONNX-Python) | OpenCV/Python/ONNX | [Farid Inawan](https://github.com/frdteknikelektro) |
+| [YOLOv8 .NET ONNX ImageSharp](https://github.com/dme-compunet/YOLOv8) | C#/ONNX/ImageSharp | [Compunet](https://github.com/dme-compunet) |
| [YOLO .Net ONNX Detection C#](https://www.nuget.org/packages/Yolov8.Net) | C# .Net | [Samuel Stainback](https://github.com/sstainba) |
| [YOLOv8 on NVIDIA Jetson(TensorRT and DeepStream)](https://wiki.seeedstudio.com/YOLOv8-DeepStream-TRT-Jetson/) | Python | [Lakshantha](https://github.com/lakshanthad) |
| [YOLOv8 ONNXRuntime Python](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime) | Python/ONNXRuntime | [Semih Demirel](https://github.com/semihhdemirel) |
+| [YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP](./YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP) | C++/ONNXRuntime | [DennisJcy](https://github.com/DennisJcy) |
+| [RTDETR ONNXRuntime C#](https://github.com/Kayzwer/yolo-cs/blob/master/RTDETR.cs) | C#/ONNX | [Kayzwer](https://github.com/Kayzwer) |
### How to Contribute
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c49866497
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+# YOLOv8 OnnxRuntime C++
+
+This example demonstrates how to perform inference using YOLOv8 in C++ with ONNX Runtime and OpenCV's API.
+
+We recommend using Visual Studio to build the project.
+
+## Benefits
+
+- Friendly for deployment in the industrial sector.
+- Faster than OpenCV's DNN inference on both CPU and GPU.
+- Supports CUDA acceleration.
+- Easy to add FP16 inference (using template functions).
+
+## Exporting YOLOv8 Models
+
+To export YOLOv8 models, use the following Python script:
+
+```python
+from ultralytics import YOLO
+
+# Load a YOLOv8 model
+model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt")
+
+# Export the model
+model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
+```
+
+## Dependencies
+
+| Dependency | Version |
+| ----------------------- | -------- |
+| Onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu | >=1.14.1 |
+| OpenCV | >=4.0.0 |
+| C++ | >=17 |
+
+Note: The dependency on C++17 is due to the usage of the C++17 filesystem feature.
+
+## Usage
+
+```c++
+// CPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, false};
+// GPU inference
+DCSP_INIT_PARAM params{ model_path, YOLO_ORIGIN_V8, {imgsz_w, imgsz_h}, class_num, 0.1, 0.5, true};
+
+// Load your image
+cv::Mat img = cv::imread(img_path);
+
+char* ret = p1->CreateSession(params);
+
+ret = p->RunSession(img, res);
+```
+
+This repository should also work for YOLOv5, which needs a permute operator for the output of the YOLOv5 model, but this has not been implemented yet.
diff --git a/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5af395dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/examples/YOLOv8-ONNXRuntime-CPP/inference.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,271 @@
+#include "inference.h"
+#include