if:(github.event.comment.body == 'recheck' || github.event.comment.body == 'I have read the CLA Document and I sign the CLA') || github.event_name == 'pull_request_target'
diff = response.text if response.status_code == 200 else f"Failed to get diff: {response.content}"
# Set up client
client = openai.AzureOpenAI(
api_key=OPENAI_AZURE_API_KEY,
api_version=OPENAI_AZURE_API_VERSION,
azure_endpoint=OPENAI_AZURE_ENDPOINT
)
# Get summary
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are an Ultralytics AI assistant skilled in software development and technical communication. Your task is to summarize GitHub releases from Ultralytics in a way that is detailed, accurate, and understandable to both expert developers and non-expert users. Focus on highlighting the key changes and their impact in simple and intuitive terms."
"content": "You are an Ultralytics AI assistant skilled in software development and technical communication. Your task is to summarize GitHub releases in a way that is detailed, accurate, and understandable to both expert developers and non-expert users. Focus on highlighting the key changes and their impact in simple and intuitive terms."
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Summarize the updates made in the [Ultralytics](https://ultralytics.com) '{latest_tag}' tag, focusing on major changes, their purpose, and potential impact. Keep the summary clear and suitable for a broad audience. Add emojis to enliven the summary. Reply directly with a summary along these example guidelines, though feel free to adjust as appropriate:\n\n"
"content": f"Summarize the updates made in the '{latest_tag}' tag, focusing on major changes, their purpose, and potential impact. Keep the summary clear and suitable for a broad audience. Add emojis to enliven the summary. Reply directly with a summary along these example guidelines, though feel free to adjust as appropriate:\n\n"
f"## 🌟 Summary (single-line synopsis)\n"
f"## 📊 Key Changes (bullet points highlighting any major changes)\n"
f"## 🎯 Purpose & Impact (bullet points explaining any benefits and potential impact to users)\n"
f"\n\nHere's the release diff:\n\n{diff[:300000]}",
@ -153,14 +153,18 @@ Each subset comprises images categorized into 10 classes, with their annotations
If you use the CIFAR-10 dataset in your research or development projects, make sure to cite the following paper:
```bibtex
@TECHREPORT{Krizhevsky09learningmultiple,
author={Alex Krizhevsky},
title={Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images},
institution={},
year={2009}
}
```
!!! Quote ""
=== "BibTeX"
```bibtex
@TECHREPORT{Krizhevsky09learningmultiple,
author={Alex Krizhevsky},
title={Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images},
institution={},
year={2009}
}
```
Acknowledging the dataset's creators helps support continued research and development in the field. For more details, see the [citations and acknowledgments](#citations-and-acknowledgments) section.
It's important to note that using smaller images will likely yield lower performance in terms of classification accuracy. However, it's an excellent way to iterate quickly in the early stages of model development and prototyping.
The [VisDrone Dataset](https://github.com/VisDrone/VisDrone-Dataset) is a large-scale benchmark created by the AISKYEYE team at the Lab of Machine Learning and Data Mining, Tianjin University, China. It contains carefully annotated ground truth data for various computer vision tasks related to drone-based image and video analysis.
<strong>Watch:</strong> How to Train Ultralytics YOLO Models on the VisDrone Dataset for Drone Image Analysis
</p>
VisDrone is composed of 288 video clips with 261,908 frames and 10,209 static images, captured by various drone-mounted cameras. The dataset covers a wide range of aspects, including location (14 different cities across China), environment (urban and rural), objects (pedestrians, vehicles, bicycles, etc.), and density (sparse and crowded scenes). The dataset was collected using various drone platforms under different scenarios and weather and lighting conditions. These frames are manually annotated with over 2.6 million bounding boxes of targets such as pedestrians, cars, bicycles, and tricycles. Attributes like scene visibility, object class, and occlusion are also provided for better data utilization.
## Dataset Structure
@ -148,16 +159,19 @@ The configuration file for the VisDrone dataset, `VisDrone.yaml`, can be found i
If you use the VisDrone dataset in your research or development work, please cite the following paper:
!!! Quote "BibTeX"
```bibtex
@ARTICLE{9573394,
author={Zhu, Pengfei and Wen, Longyin and Du, Dawei and Bian, Xiao and Fan, Heng and Hu, Qinghua and Ling, Haibin},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
title={Detection and Tracking Meet Drones Challenge},
year={2021},
volume={},
number={},
pages={1-1},
doi={10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3119563}}
```
!!! Quote ""
=== "BibTeX"
```bibtex
@ARTICLE{9573394,
author={Zhu, Pengfei and Wen, Longyin and Du, Dawei and Bian, Xiao and Fan, Heng and Hu, Qinghua and Ling, Haibin},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence},
title={Detection and Tracking Meet Drones Challenge},
Parking management with [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) ensures efficient and safe parking by organizing spaces and monitoring availability. YOLOv8 can improve parking lot management through real-time vehicle detection, and insights into parking occupancy.
@ -98,6 +98,18 @@ Next, [train a model](./models.md#train-model) on your dataset.
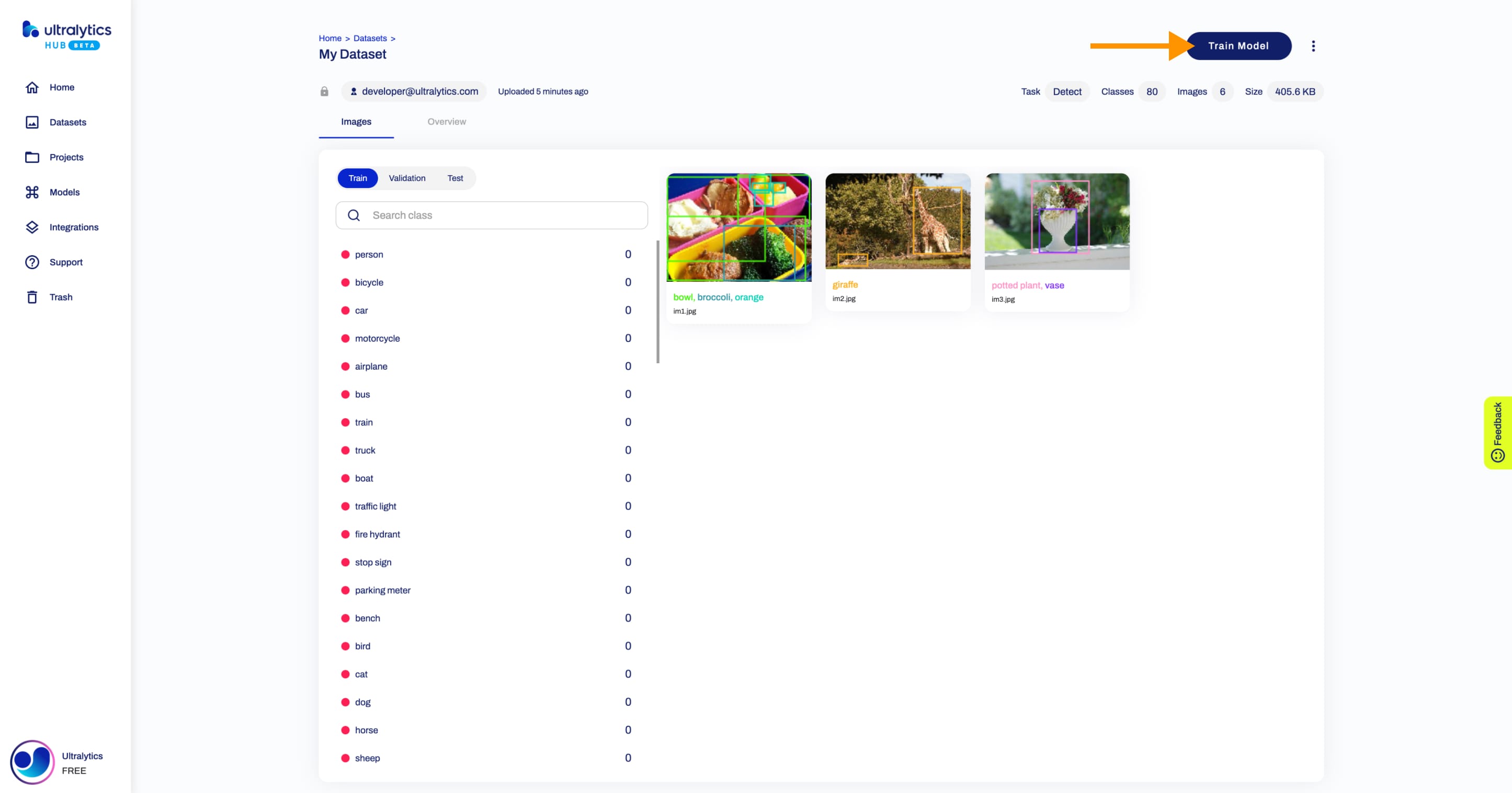
## Download Dataset
Navigate to the Dataset page of the dataset you want to download, open the dataset actions dropdown and click on the **Download** option. This action will start downloading your dataset.
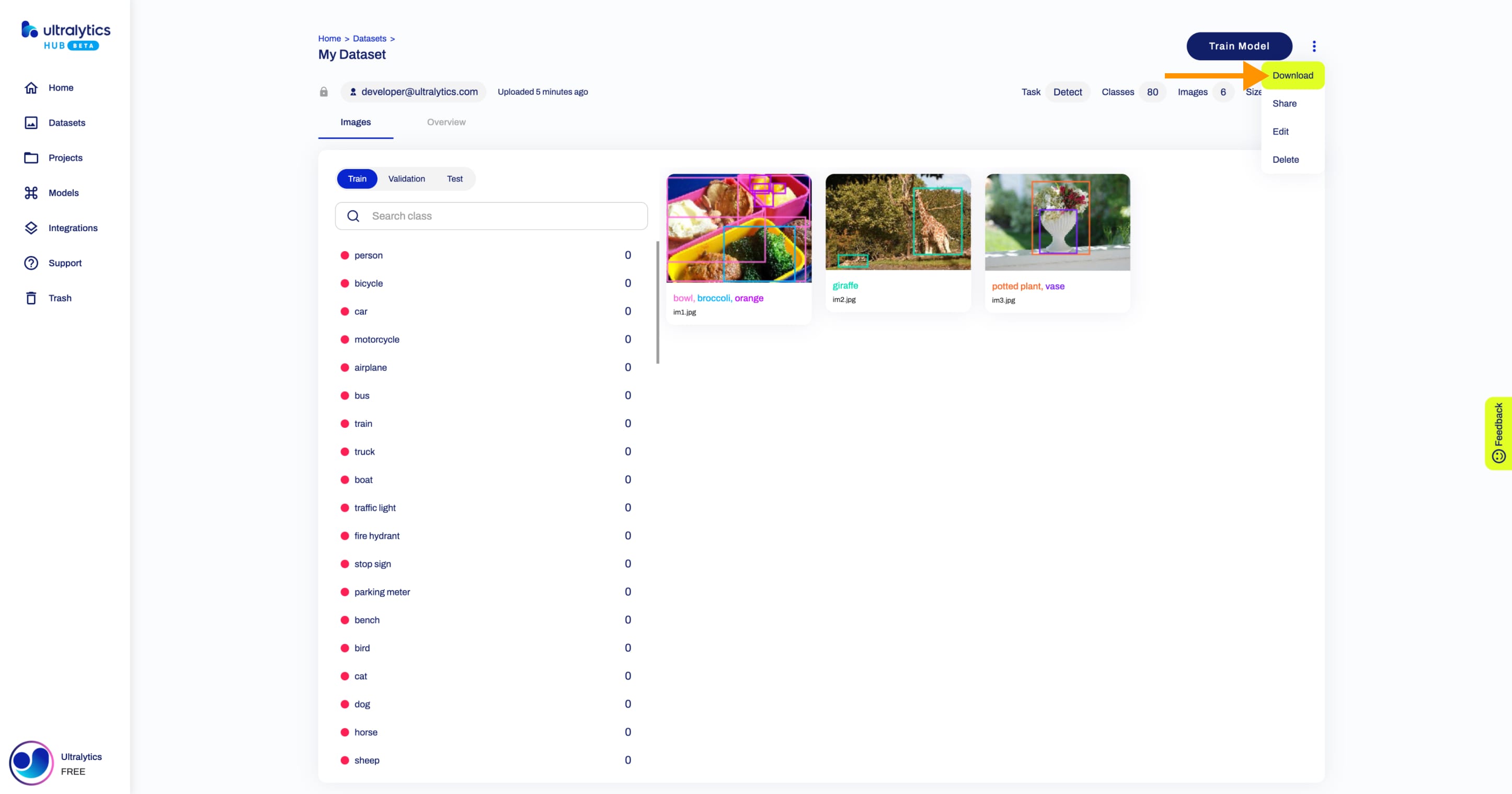
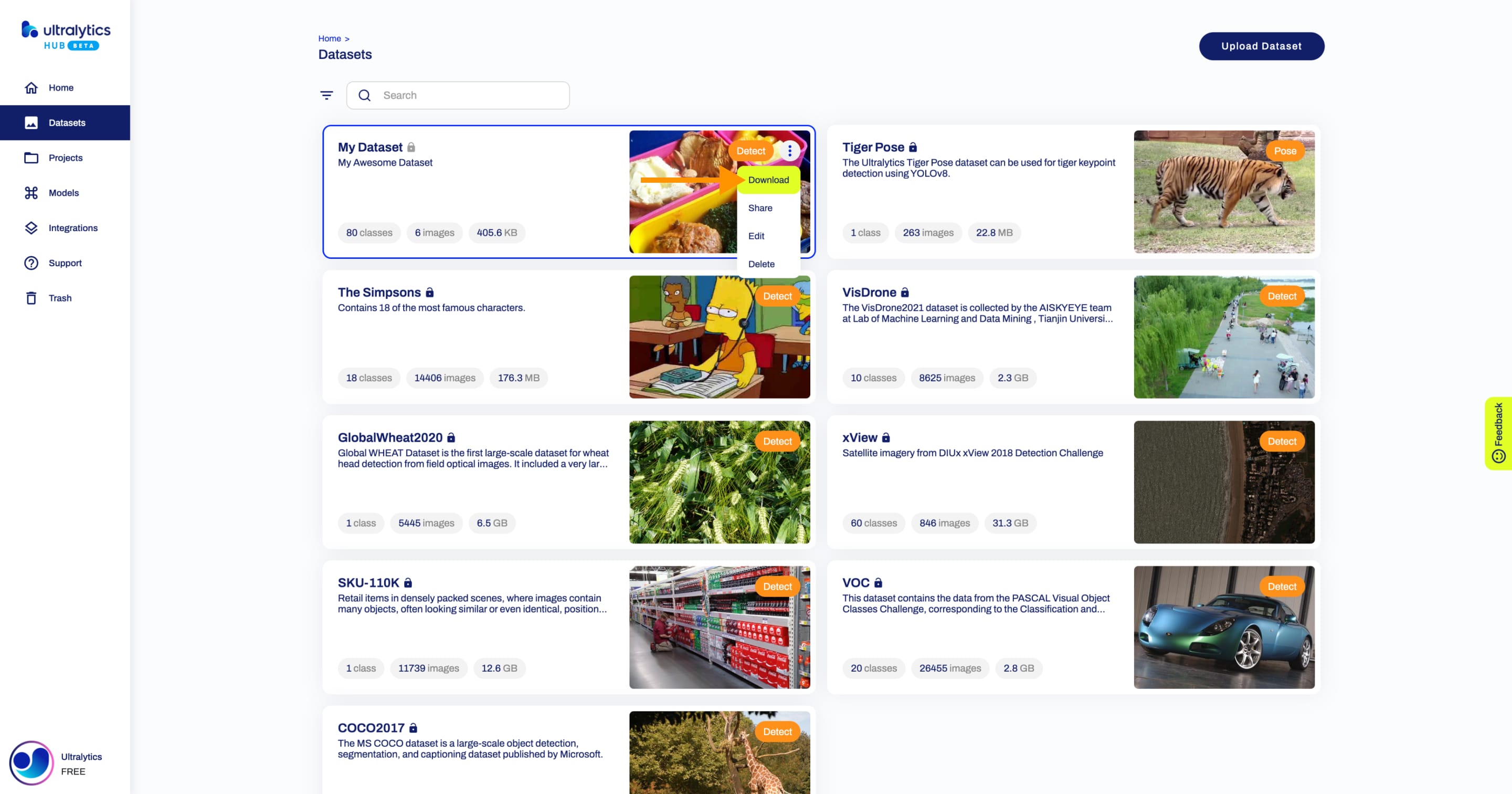
??? tip "Tip"
You can download a dataset directly from the [Datasets](https://hub.ultralytics.com/datasets) page.
put indicates that TensorBoard is now actively monitoring your YOLOv8 training session. You can access the TensorBoard dashboard by visiting the provided URL (http://localhost:6006/) to view real-time training metrics and model performance. For users working in Google Colab, the TensorBoard will be displayed in the same cell where you executed the TensorBoard configuration commands.
information related to the model training process, be sure to check our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md). If you are interested in learning more about logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management, read our [usage guide on configuration](../usage/cfg.md).
standing Your TensorBoard for YOLOv8 Training
's focus on understanding the various features and components of TensorBoard in the context of YOLOv8 training. The three key sections of the TensorBoard are Time Series, Scalars, and Graphs.
Series
Upon running the usage code snippet above, you can expect the following output:
Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspective of various training metrics over time for YOLOv8 models. It focuses on the progression and trends of metrics across training epochs. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
er Tags and Pinned Cards**: This functionality allows users to filter specific metrics and pin cards for quick comparison and access. It's particularly useful for focusing on specific aspects of the training process.
iled Metric Cards**: Time Series divides metrics into different categories like learning rate (lr), training (train), and validation (val) metrics, each represented by individual cards.
```bash
TensorBoard: Start with 'tensorboard --logdir path_to_your_tensorboard_logs', view at http://localhost:6006/
```
hical Display**: Each card in the Time Series section shows a detailed graph of a specific metric over the course of training. This visual representation aids in identifying trends, patterns, or anomalies in the training process.
This output indicates that TensorBoard is now actively monitoring your YOLOv8 training session. You can access the TensorBoard dashboard by visiting the provided URL (http://localhost:6006/) to view real-time training metrics and model performance. For users working in Google Colab, the TensorBoard will be displayed in the same cell where you executed the TensorBoard configuration commands.
epth Analysis**: Time Series provides an in-depth analysis of each metric. For instance, different learning rate segments are shown, offering insights into how adjustments in learning rate impact the model's learning curve.
For more information related to the model training process, be sure to check our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md). If you are interested in learning more about logging, checkpoints, plotting, and file management, read our [usage guide on configuration](../usage/cfg.md).
ortance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
## Understanding Your TensorBoard for YOLOv8 Training
Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metrics progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
Now, let's focus on understanding the various features and components of TensorBoard in the context of YOLOv8 training. The three key sections of the TensorBoard are Time Series, Scalars, and Graphs.
ars
### Time Series
in the TensorBoard are crucial for plotting and analyzing simple metrics like loss and accuracy during the training of YOLOv8 models. They offer a clear and concise view of how these metrics evolve with each training epoch, providing insights into the model's learning effectiveness and stability. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
The Time Series feature in the TensorBoard offers a dynamic and detailed perspective of various training metrics over time for YOLOv8 models. It focuses on the progression and trends of metrics across training epochs. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
ning Rate (lr) Tags**: These tags show the variations in the learning rate across different segments (e.g., `pg0`, `pg1`, `pg2`). This helps us understand the impact of learning rate adjustments on the training process.
- **Filter Tags and Pinned Cards**: This functionality allows users to filter specific metrics and pin cards for quick comparison and access. It's particularly useful for focusing on specific aspects of the training process.
ics Tags**: Scalars include performance indicators such as:
- **Detailed Metric Cards**: Time Series divides metrics into different categories like learning rate (lr), training (train), and validation (val) metrics, each represented by individual cards.
AP50 (B)`: Mean Average Precision at 50% Intersection over Union (IoU), crucial for assessing object detection accuracy.
- **Graphical Display**: Each card in the Time Series section shows a detailed graph of a specific metric over the course of training. This visual representation aids in identifying trends, patterns, or anomalies in the training process.
AP50-95 (B)`: Mean Average Precision calculated over a range of IoU thresholds, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of accuracy.
- **In-Depth Analysis**: Time Series provides an in-depth analysis of each metric. For instance, different learning rate segments are shown, offering insights into how adjustments in learning rate impact the model's learning curve.
recision (B)`: Indicates the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations, key to understanding prediction accuracy.
#### Importance of Time Series in YOLOv8 Training
ecall (B)`: Important for models where missing a detection is significant, this metric measures the ability to detect all relevant instances.
The Time Series section is essential for a thorough analysis of the YOLOv8 model's training progress. It lets you track the metrics in real time to promptly identify and solve issues. It also offers a detailed view of each metrics progression, which is crucial for fine-tuning the model and enhancing its performance.
learn more about the different metrics, read our guide on [performance metrics](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md).
### Scalars
ning and Validation Tags (`train`, `val`)**: These tags display metrics specifically for the training and validation datasets, allowing for a comparative analysis of model performance across different data sets.
Scalars in the TensorBoard are crucial for plotting and analyzing simple metrics like loss and accuracy during the training of YOLOv8 models. They offer a clear and concise view of how these metrics evolve with each training epoch, providing insights into the model's learning effectiveness and stability. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
g scalar metrics is crucial for fine-tuning the YOLOv8 model. Variations in these metrics, such as spikes or irregular patterns in loss graphs, can highlight potential issues such as overfitting, underfitting, or inappropriate learning rate settings. By closely monitoring these scalars, you can make informed decisions to optimize the training process, ensuring that the model learns effectively and achieves the desired performance.
#### Key Features of Scalars in TensorBoard
erence Between Scalars and Time Series
- **Learning Rate (lr) Tags**: These tags show the variations in the learning rate across different segments (e.g., `pg0`, `pg1`, `pg2`). This helps us understand the impact of learning rate adjustments on the training process.
th Scalars and Time Series in TensorBoard are used for tracking metrics, they serve slightly different purposes. Scalars focus on plotting simple metrics such as loss and accuracy as scalar values. They provide a high-level overview of how these metrics change with each training epoch. While, the time-series section of the TensorBoard offers a more detailed timeline view of various metrics. It is particularly useful for monitoring the progression and trends of metrics over time, providing a deeper dive into the specifics of the training process.
- **Metrics Tags**: Scalars include performance indicators such as:
hs
- `mAP50 (B)`: Mean Average Precision at 50% Intersection over Union (IoU), crucial for assessing object detection accuracy.
hs section of the TensorBoard visualizes the computational graph of the YOLOv8 model, showing how operations and data flow within the model. It's a powerful tool for understanding the model's structure, ensuring that all layers are connected correctly, and for identifying any potential bottlenecks in data flow. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
- `mAP50-95 (B)`: Mean Average Precision calculated over a range of IoU thresholds, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of accuracy.
- `Precision (B)`: Indicates the ratio of correctly predicted positive observations, key to understanding prediction accuracy.
re particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex architectures typical in deep learning models like YOLOv8. They help in verifying layer connections and the overall design of the model.
- `Recall (B)`: Important for models where missing a detection is significant, this metric measures the ability to detect all relevant instances.
ry
-Tolearnmoreabout the different metrics, read our guide on [performance metrics](../guides/yolo-performance-metrics.md).
de aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
- **Training and Validation Tags (`train`, `val`)**: These tags display metrics specifically for the training and validation datasets, allowing for a comparative analysis of model performance across different data sets.
re detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow's official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
#### Importance of Monitoring Scalars
learn more about the various integrations of Ultralytics? Check out the [Ultralytics integrations guide page](../integrations/index.md) to see what other exciting capabilities are waiting to be discovered!
Observing scalar metrics is crucial for fine-tuning the YOLOv8 model. Variations in these metrics, such as spikes or irregular patterns in loss graphs, can highlight potential issues such as overfitting, underfitting, or inappropriate learning rate settings. By closely monitoring these scalars, you can make informed decisions to optimize the training process, ensuring that the model learns effectively and achieves the desired performance.
## FAQ
### Difference Between Scalars and Time Series
do I integrate YOLOv8 with TensorBoard for real-time visualization?
While both Scalars and Time Series in TensorBoard are used for tracking metrics, they serve slightly different purposes. Scalars focus on plotting simple metrics such as loss and accuracy as scalar values. They provide a high-level overview of how these metrics change with each training epoch. While, the time-series section of the TensorBoard offers a more detailed timeline view of various metrics. It is particularly useful for monitoring the progression and trends of metrics over time, providing a deeper dive into the specifics of the training process.
ing YOLOv8 with TensorBoard allows for real-time visual insights during model training. First, install the necessary package:
### Graphs
ple "Installation"
The Graphs section of the TensorBoard visualizes the computational graph of the YOLOv8 model, showing how operations and data flow within the model. It's a powerful tool for understanding the model's structure, ensuring that all layers are connected correctly, and for identifying any potential bottlenecks in data flow. Here's an example of what you can expect to see.
"CLI"
```bash
# Install the required package for YOLOv8 and Tensorboard
Next, configure TensorBoard to log your training runs, then start TensorBoard:
Graphs are particularly useful for debugging the model, especially in complex architectures typical in deep learning models like YOLOv8. They help in verifying layer connections and the overall design of the model.
!!! Example "Configure TensorBoard for Google Colab"
## Summary
=== "Python"
This guide aims to help you use TensorBoard with YOLOv8 for visualization and analysis of machine learning model training. It focuses on explaining how key TensorBoard features can provide insights into training metrics and model performance during YOLOv8 training sessions.
```ipython
%load_ext tensorboard
%tensorboard --logdir path/to/runs
```
For a more detailed exploration of these features and effective utilization strategies, you can refer to TensorFlow's official [TensorBoard documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/tensorboard/get_started) and their [GitHub repository](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard).
Finally, during training, YOLOv8 automatically logs metrics like loss and accuracy to TensorBoard. You can monitor these metrics by visiting [http://localhost:6006/](http://localhost:6006/).
Want to learn more about the various integrations of Ultralytics? Check out the [Ultralytics integrations guide page](../integrations/index.md) to see what other exciting capabilities are waiting to be discovered!
For a comprehensive guide, refer to our [YOLOv8 Model Training guide](../modes/train.md).
## FAQ
### What benefits does using TensorBoard with YOLOv8 offer?
@ -225,16 +198,16 @@ Yes, you can use TensorBoard in a Google Colab environment to train YOLOv8 model
TensorBoard will visualize the training progress within Colab, providing real-time insights into metrics like loss and accuracy. For additional details on configuring YOLOv8 training, see our detailed [YOLOv8 Installation guide](../quickstart.md).
@ -82,6 +82,19 @@ Note (2): Due to ONNX Runtime, we need to use CUDA 11 and cuDNN 8. Keep in mind
cmake ..
```
**Notice**:
If you encounter an error indicating that the `ONNXRUNTIME_ROOT` variable is not set correctly, you can resolve this by building the project using the appropriate command tailored to your system.