Add `speed_estimation` and `distance_calculation` in ultralytics solutions (#7325)
Co-authored-by: Glenn Jocher <glenn.jocher@ultralytics.com>pull/7319/head^2
parent
2f9ec8c0b4
commit
61fa12460d
12 changed files with 642 additions and 23 deletions
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@ |
||||
--- |
||||
comments: true |
||||
description: Distance Calculation Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
||||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Object Detection, Distance Calculation, Object Tracking, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Distance Calculation using Ultralytics YOLOv8 🚀 |
||||
|
||||
## What is Distance Calculation? |
||||
|
||||
Measuring the gap between two objects is known as distance calculation within a specified space. In the case of [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics), the bounding box centroid is employed to calculate the distance for bounding boxes highlighted by the user. |
||||
|
||||
## Advantages of Distance Calculation? |
||||
|
||||
- **Localization Precision:** Enhances accurate spatial positioning in computer vision tasks. |
||||
- **Size Estimation:** Allows estimation of physical sizes for better contextual understanding. |
||||
- **Scene Understanding:** Contributes to a 3D understanding of the environment for improved decision-making. |
||||
|
||||
???+ tip "Distance Calculation" |
||||
|
||||
- Click on any two bounding boxes with Left Mouse click for distance calculation |
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Distance Calculation using YOLOv8 Example" |
||||
|
||||
=== "Video Stream" |
||||
```python |
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO |
||||
from ultralytics.solutions import distance_calculation |
||||
import cv2 |
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") |
||||
names = model.model.names |
||||
|
||||
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4") |
||||
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file" |
||||
|
||||
# Video writer |
||||
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("distance_calculation.avi", |
||||
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), |
||||
int(cap.get(5)), |
||||
(int(cap.get(3)), int(cap.get(4)))) |
||||
|
||||
# Init distance-calculation obj |
||||
dist_obj = distance_calculation.DistanceCalculation() |
||||
dist_obj.set_args(names=names, view_img=True) |
||||
|
||||
while cap.isOpened(): |
||||
success, im0 = cap.read() |
||||
if not success: |
||||
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.") |
||||
break |
||||
|
||||
tracks = model.track(im0, persist=True, show=False) |
||||
im0 = dist_obj.start_process(im0, tracks) |
||||
video_writer.write(im0) |
||||
|
||||
cap.release() |
||||
video_writer.release() |
||||
cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
???+ tip "Note" |
||||
|
||||
- Mouse Right Click will delete all drawn points |
||||
- Mouse Left Click can be used to draw points |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Optional Arguments `set_args` |
||||
|
||||
| Name | Type | Default | Description | |
||||
|----------------|--------|-----------------|--------------------------------------------------------| |
||||
| names | `dict` | `None` | Classes names | |
||||
| view_img | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts | |
||||
| line_thickness | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness | |
||||
| line_color | `RGB` | `(255, 255, 0)` | Line Color for centroids mapping on two bounding boxes | |
||||
| centroid_color | `RGB` | `(255, 0, 255)` | Centroid color for each bounding box | |
||||
|
||||
### Arguments `model.track` |
||||
|
||||
| Name | Type | Default | Description | |
||||
|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| |
||||
| `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | |
||||
| `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | |
||||
| `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | |
||||
| `conf` | `float` | `0.3` | Confidence Threshold | |
||||
| `iou` | `float` | `0.5` | IOU Threshold | |
||||
| `classes` | `list` | `None` | filter results by class, i.e. classes=0, or classes=[0,2,3] | |
||||
| `verbose` | `bool` | `True` | Display the object tracking results | |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@ |
||||
--- |
||||
comments: true |
||||
description: Speed Estimation Using Ultralytics YOLOv8 |
||||
keywords: Ultralytics, YOLOv8, Object Detection, Speed Estimation, Object Tracking, Notebook, IPython Kernel, CLI, Python SDK |
||||
--- |
||||
|
||||
# Speed Estimation using Ultralytics YOLOv8 🚀 |
||||
|
||||
## What is Speed Estimation? |
||||
|
||||
Speed estimation is the process of calculating the rate of movement of an object within a given context, often employed in computer vision applications. Using [Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) you can now calculate the speed of object using [object tracking](https://docs.ultralytics.com/modes/track/) alongside distance and time data, crucial for tasks like traffic and surveillance. The accuracy of speed estimation directly influences the efficiency and reliability of various applications, making it a key component in the advancement of intelligent systems and real-time decision-making processes. |
||||
|
||||
## Advantages of Speed Estimation? |
||||
|
||||
- **Efficient Traffic Control:** Accurate speed estimation aids in managing traffic flow, enhancing safety, and reducing congestion on roadways. |
||||
- **Precise Autonomous Navigation:** In autonomous systems like self-driving cars, reliable speed estimation ensures safe and accurate vehicle navigation. |
||||
- **Enhanced Surveillance Security:** Speed estimation in surveillance analytics helps identify unusual behaviors or potential threats, improving the effectiveness of security measures. |
||||
|
||||
## Real World Applications |
||||
|
||||
| Transportation | Transportation | |
||||
|:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:| |
||||
|  | 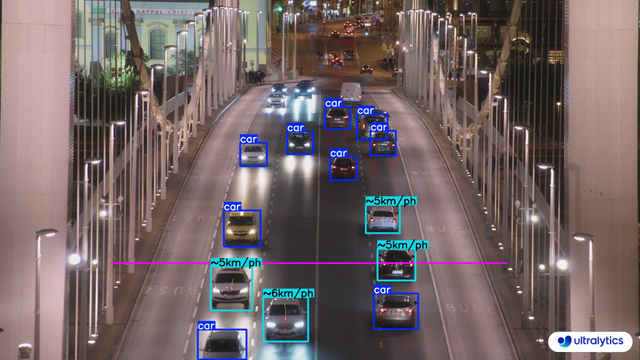 | |
||||
| Speed Estimation on Road using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | Speed Estimation on Bridge using Ultralytics YOLOv8 | |
||||
|
||||
!!! Example "Speed Estimation using YOLOv8 Example" |
||||
|
||||
=== "Speed Estimation" |
||||
```python |
||||
from ultralytics import YOLO |
||||
from ultralytics.solutions import speed_estimation |
||||
import cv2 |
||||
|
||||
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") |
||||
names = model.model.names |
||||
|
||||
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4") |
||||
assert cap.isOpened(), "Error reading video file" |
||||
|
||||
# Video writer |
||||
video_writer = cv2.VideoWriter("speed_estimation.avi", |
||||
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v'), |
||||
int(cap.get(5)), |
||||
(int(cap.get(3)), int(cap.get(4)))) |
||||
|
||||
line_pts = [(0, 360), (1280, 360)] |
||||
|
||||
# Init speed-estimation obj |
||||
speed_obj = speed_estimation.SpeedEstimator() |
||||
speed_obj.set_args(reg_pts=line_pts, |
||||
names=names, |
||||
view_img=True) |
||||
|
||||
while cap.isOpened(): |
||||
|
||||
success, im0 = cap.read() |
||||
if not success: |
||||
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.") |
||||
break |
||||
|
||||
tracks = model.track(im0, persist=True, show=False) |
||||
|
||||
im0 = speed_obj.estimate_speed(im0, tracks) |
||||
video_writer.write(im0) |
||||
|
||||
cap.release() |
||||
video_writer.release() |
||||
cv2.destroyAllWindows() |
||||
|
||||
``` |
||||
|
||||
???+ warning "Speed is Estimate" |
||||
|
||||
Speed will be an estimate and may not be completely accurate. Additionally, the estimation can vary depending on GPU speed. |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Optional Arguments `set_args` |
||||
|
||||
| Name | Type | Default | Description | |
||||
|---------------------|-------------|----------------------------|---------------------------------------------------| |
||||
| reg_pts | `list` | `[(20, 400), (1260, 400)]` | Points defining the Region Area | |
||||
| names | `dict` | `None` | Classes names | |
||||
| view_img | `bool` | `False` | Display frames with counts | |
||||
| line_thickness | `int` | `2` | Increase bounding boxes thickness | |
||||
| region_thickness | `int` | `5` | Thickness for object counter region or line | |
||||
| spdl_dist_thresh | `int` | `10` | Euclidean Distance threshold for speed check line | |
||||
|
||||
### Arguments `model.track` |
||||
|
||||
| Name | Type | Default | Description | |
||||
|-----------|---------|----------------|-------------------------------------------------------------| |
||||
| `source` | `im0` | `None` | source directory for images or videos | |
||||
| `persist` | `bool` | `False` | persisting tracks between frames | |
||||
| `tracker` | `str` | `botsort.yaml` | Tracking method 'bytetrack' or 'botsort' | |
||||
| `conf` | `float` | `0.3` | Confidence Threshold | |
||||
| `iou` | `float` | `0.5` | IOU Threshold | |
||||
| `classes` | `list` | `None` | filter results by class, i.e. classes=0, or classes=[0,2,3] | |
||||
| `verbose` | `bool` | `True` | Display the object tracking results | |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,187 @@ |
||||
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license |
||||
|
||||
import math |
||||
|
||||
import cv2 |
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DistanceCalculation: |
||||
"""A class to calculate distance between two objects in real-time video stream based on their tracks.""" |
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self): |
||||
"""Initializes the distance calculation class with default values for Visual, Image, track and distance |
||||
parameters. |
||||
""" |
||||
|
||||
# Visual & im0 information |
||||
self.im0 = None |
||||
self.annotator = None |
||||
self.view_img = False |
||||
self.line_color = (255, 255, 0) |
||||
self.centroid_color = (255, 0, 255) |
||||
|
||||
# Predict/track information |
||||
self.clss = None |
||||
self.names = None |
||||
self.boxes = None |
||||
self.line_thickness = 2 |
||||
self.trk_ids = None |
||||
|
||||
# Distance calculation information |
||||
self.centroids = [] |
||||
self.pixel_per_meter = 10 |
||||
|
||||
# Mouse event |
||||
self.left_mouse_count = 0 |
||||
self.selected_boxes = {} |
||||
|
||||
def set_args(self, |
||||
names, |
||||
pixels_per_meter=10, |
||||
view_img=False, |
||||
line_thickness=2, |
||||
line_color=(255, 255, 0), |
||||
centroid_color=(255, 0, 255)): |
||||
""" |
||||
Configures the distance calculation and display parameters. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
names (dict): object detection classes names |
||||
pixels_per_meter (int): Number of pixels in meter |
||||
view_img (bool): Flag indicating frame display |
||||
line_thickness (int): Line thickness for bounding boxes. |
||||
line_color (RGB): color of centroids line |
||||
centroid_color (RGB): colors of bbox centroids |
||||
""" |
||||
self.names = names |
||||
self.pixel_per_meter = pixels_per_meter |
||||
self.view_img = view_img |
||||
self.line_thickness = line_thickness |
||||
self.line_color = line_color |
||||
self.centroid_color = centroid_color |
||||
|
||||
def mouse_event_for_distance(self, event, x, y, flags, param): |
||||
""" |
||||
This function is designed to move region with mouse events in a real-time video stream. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
event (int): The type of mouse event (e.g., cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE, cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN, etc.). |
||||
x (int): The x-coordinate of the mouse pointer. |
||||
y (int): The y-coordinate of the mouse pointer. |
||||
flags (int): Any flags associated with the event (e.g., cv2.EVENT_FLAG_CTRLKEY, |
||||
cv2.EVENT_FLAG_SHIFTKEY, etc.). |
||||
param (dict): Additional parameters you may want to pass to the function. |
||||
""" |
||||
global selected_boxes |
||||
global left_mouse_count |
||||
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN: |
||||
self.left_mouse_count += 1 |
||||
if self.left_mouse_count <= 2: |
||||
for box, track_id in zip(self.boxes, self.trk_ids): |
||||
if box[0] < x < box[2] and box[1] < y < box[3]: |
||||
if track_id not in self.selected_boxes: |
||||
self.selected_boxes[track_id] = [] |
||||
self.selected_boxes[track_id] = box |
||||
|
||||
if event == cv2.EVENT_RBUTTONDOWN: |
||||
self.selected_boxes = {} |
||||
self.left_mouse_count = 0 |
||||
|
||||
def extract_tracks(self, tracks): |
||||
""" |
||||
Extracts results from the provided data. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
tracks (list): List of tracks obtained from the object tracking process. |
||||
""" |
||||
self.boxes = tracks[0].boxes.xyxy.cpu() |
||||
self.clss = tracks[0].boxes.cls.cpu().tolist() |
||||
self.trk_ids = tracks[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist() |
||||
|
||||
def calculate_centroid(self, box): |
||||
""" |
||||
Calculate the centroid of bounding box |
||||
Args: |
||||
box (list): Bounding box data |
||||
""" |
||||
return int((box[0] + box[2]) // 2), int((box[1] + box[3]) // 2) |
||||
|
||||
def calculate_distance(self, centroid1, centroid2): |
||||
""" |
||||
Calculate distance between two centroids |
||||
Args: |
||||
centroid1 (point): First bounding box data |
||||
centroid2 (point): Second bounding box data |
||||
""" |
||||
pixel_distance = math.sqrt((centroid1[0] - centroid2[0]) ** 2 + (centroid1[1] - centroid2[1]) ** 2) |
||||
return pixel_distance / self.pixel_per_meter |
||||
|
||||
def plot_distance_and_line(self, distance): |
||||
""" |
||||
Plot the distance and line on frame |
||||
Args: |
||||
distance (float): Distance between two centroids |
||||
""" |
||||
cv2.rectangle(self.im0, (15, 25), (280, 70), (255, 255, 255), -1) |
||||
cv2.putText(self.im0, f'Distance : {distance:.2f}m', (20, 55), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, (0, 0, 0), 2, |
||||
cv2.LINE_AA) |
||||
cv2.line(self.im0, self.centroids[0], self.centroids[1], self.line_color, 3) |
||||
cv2.circle(self.im0, self.centroids[0], 6, self.centroid_color, -1) |
||||
cv2.circle(self.im0, self.centroids[1], 6, self.centroid_color, -1) |
||||
|
||||
def start_process(self, im0, tracks): |
||||
""" |
||||
Calculate distance between two bounding boxes based on tracking data |
||||
Args: |
||||
im0 (nd array): Image |
||||
tracks (list): List of tracks obtained from the object tracking process. |
||||
""" |
||||
self.im0 = im0 |
||||
if tracks[0].boxes.id is None: |
||||
if self.view_img: |
||||
self.display_frames() |
||||
return |
||||
else: |
||||
return |
||||
|
||||
self.extract_tracks(tracks) |
||||
|
||||
self.annotator = Annotator(self.im0, line_width=2) |
||||
|
||||
for box, cls, track_id in zip(self.boxes, self.clss, self.trk_ids): |
||||
self.annotator.box_label(box, color=colors(int(cls), True), label=self.names[int(cls)]) |
||||
|
||||
if len(self.selected_boxes) == 2: |
||||
for trk_id, _ in self.selected_boxes.items(): |
||||
if trk_id == track_id: |
||||
self.selected_boxes[track_id] = box |
||||
|
||||
if len(self.selected_boxes) == 2: |
||||
for trk_id, box in self.selected_boxes.items(): |
||||
centroid = self.calculate_centroid(self.selected_boxes[trk_id]) |
||||
self.centroids.append(centroid) |
||||
|
||||
distance = self.calculate_distance(self.centroids[0], self.centroids[1]) |
||||
self.plot_distance_and_line(distance) |
||||
|
||||
self.centroids = [] |
||||
|
||||
if self.view_img: |
||||
self.display_frames() |
||||
|
||||
return im0 |
||||
|
||||
def display_frames(self): |
||||
"""Display frame.""" |
||||
cv2.namedWindow('Ultralytics Distance Estimation') |
||||
cv2.setMouseCallback('Ultralytics Distance Estimation', self.mouse_event_for_distance) |
||||
cv2.imshow('Ultralytics Distance Estimation', self.im0) |
||||
|
||||
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): |
||||
return |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__': |
||||
DistanceCalculation() |
||||
@ -0,0 +1,203 @@ |
||||
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license |
||||
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict |
||||
from time import time |
||||
|
||||
import cv2 |
||||
import numpy as np |
||||
|
||||
from ultralytics.utils.checks import check_imshow |
||||
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SpeedEstimator: |
||||
"""A class to estimation speed of objects in real-time video stream based on their tracks.""" |
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self): |
||||
"""Initializes the speed-estimator class with default values for Visual, Image, track and speed parameters.""" |
||||
|
||||
# Visual & im0 information |
||||
self.im0 = None |
||||
self.annotator = None |
||||
self.view_img = False |
||||
|
||||
# Region information |
||||
self.reg_pts = [(20, 400), (1260, 400)] |
||||
self.region_thickness = 3 |
||||
|
||||
# Predict/track information |
||||
self.clss = None |
||||
self.names = None |
||||
self.boxes = None |
||||
self.trk_ids = None |
||||
self.trk_pts = None |
||||
self.line_thickness = 2 |
||||
self.trk_history = defaultdict(list) |
||||
|
||||
# Speed estimator information |
||||
self.current_time = 0 |
||||
self.dist_data = {} |
||||
self.trk_idslist = [] |
||||
self.spdl_dist_thresh = 10 |
||||
self.trk_previous_times = {} |
||||
self.trk_previous_points = {} |
||||
|
||||
# Check if environment support imshow |
||||
self.env_check = check_imshow(warn=True) |
||||
|
||||
def set_args( |
||||
self, |
||||
reg_pts, |
||||
names, |
||||
view_img=False, |
||||
line_thickness=2, |
||||
region_thickness=5, |
||||
spdl_dist_thresh=10, |
||||
): |
||||
""" |
||||
Configures the speed estimation and display parameters. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
reg_pts (list): Initial list of points defining the speed calculation region. |
||||
names (dict): object detection classes names |
||||
view_img (bool): Flag indicating frame display |
||||
line_thickness (int): Line thickness for bounding boxes. |
||||
region_thickness (int): Speed estimation region thickness |
||||
spdl_dist_thresh (int): Euclidean distance threshold for speed line |
||||
""" |
||||
if reg_pts is None: |
||||
print('Region points not provided, using default values') |
||||
else: |
||||
self.reg_pts = reg_pts |
||||
self.names = names |
||||
self.view_img = view_img |
||||
self.line_thickness = line_thickness |
||||
self.region_thickness = region_thickness |
||||
self.spdl_dist_thresh = spdl_dist_thresh |
||||
|
||||
def extract_tracks(self, tracks): |
||||
""" |
||||
Extracts results from the provided data. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
tracks (list): List of tracks obtained from the object tracking process. |
||||
""" |
||||
self.boxes = tracks[0].boxes.xyxy.cpu() |
||||
self.clss = tracks[0].boxes.cls.cpu().tolist() |
||||
self.trk_ids = tracks[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist() |
||||
|
||||
def store_track_info(self, track_id, box): |
||||
""" |
||||
Store track data. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
track_id (int): object track id. |
||||
box (list): object bounding box data |
||||
""" |
||||
track = self.trk_history[track_id] |
||||
bbox_center = (float((box[0] + box[2]) / 2), float((box[1] + box[3]) / 2)) |
||||
track.append(bbox_center) |
||||
|
||||
if len(track) > 30: |
||||
track.pop(0) |
||||
|
||||
self.trk_pts = np.hstack(track).astype(np.int32).reshape((-1, 1, 2)) |
||||
return track |
||||
|
||||
def plot_box_and_track(self, track_id, box, cls, track): |
||||
""" |
||||
Plot track and bounding box. |
||||
|
||||
Args: |
||||
track_id (int): object track id. |
||||
box (list): object bounding box data |
||||
cls (str): object class name |
||||
track (list): tracking history for tracks path drawing |
||||
""" |
||||
speed_label = str(int( |
||||
self.dist_data[track_id])) + 'km/ph' if track_id in self.dist_data else self.names[int(cls)] |
||||
bbox_color = colors(int(track_id)) if track_id in self.dist_data else (255, 0, 255) |
||||
|
||||
self.annotator.box_label(box, speed_label, bbox_color) |
||||
|
||||
cv2.polylines(self.im0, [self.trk_pts], isClosed=False, color=(0, 255, 0), thickness=1) |
||||
cv2.circle(self.im0, (int(track[-1][0]), int(track[-1][1])), 5, bbox_color, -1) |
||||
|
||||
def calculate_speed(self, trk_id, track): |
||||
""" |
||||
Calculation of object speed |
||||
Args: |
||||
trk_id (int): object track id. |
||||
track (list): tracking history for tracks path drawing |
||||
""" |
||||
|
||||
if self.reg_pts[0][0] < track[-1][0] < self.reg_pts[1][0]: |
||||
|
||||
if (self.reg_pts[1][1] - self.spdl_dist_thresh < track[-1][1] < self.reg_pts[1][1] + self.spdl_dist_thresh): |
||||
direction = 'known' |
||||
|
||||
elif (self.reg_pts[0][1] - self.spdl_dist_thresh < track[-1][1] < |
||||
self.reg_pts[0][1] + self.spdl_dist_thresh): |
||||
direction = 'known' |
||||
|
||||
else: |
||||
direction = 'unknown' |
||||
|
||||
if self.trk_previous_times[trk_id] != 0 and direction != 'unknown': |
||||
|
||||
if trk_id not in self.trk_idslist: |
||||
self.trk_idslist.append(trk_id) |
||||
|
||||
time_difference = time() - self.trk_previous_times[trk_id] |
||||
if time_difference > 0: |
||||
dist_difference = np.abs(track[-1][1] - self.trk_previous_points[trk_id][1]) |
||||
speed = dist_difference / time_difference |
||||
self.dist_data[trk_id] = speed |
||||
|
||||
self.trk_previous_times[trk_id] = time() |
||||
self.trk_previous_points[trk_id] = track[-1] |
||||
|
||||
def estimate_speed(self, im0, tracks): |
||||
""" |
||||
Calculate object based on tracking data |
||||
Args: |
||||
im0 (nd array): Image |
||||
tracks (list): List of tracks obtained from the object tracking process. |
||||
""" |
||||
self.im0 = im0 |
||||
if tracks[0].boxes.id is None: |
||||
if self.view_img and self.env_check: |
||||
self.display_frames() |
||||
return |
||||
else: |
||||
return |
||||
|
||||
self.extract_tracks(tracks) |
||||
|
||||
self.annotator = Annotator(self.im0, line_width=2) |
||||
self.annotator.draw_region(reg_pts=self.reg_pts, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=self.region_thickness) |
||||
|
||||
for box, trk_id, cls in zip(self.boxes, self.trk_ids, self.clss): |
||||
|
||||
track = self.store_track_info(trk_id, box) |
||||
|
||||
if trk_id not in self.trk_previous_times: |
||||
self.trk_previous_times[trk_id] = 0 |
||||
|
||||
self.plot_box_and_track(trk_id, box, cls, track) |
||||
self.calculate_speed(trk_id, track) |
||||
|
||||
if self.view_img and self.env_check: |
||||
self.display_frames() |
||||
|
||||
return im0 |
||||
|
||||
def display_frames(self): |
||||
"""Display frame.""" |
||||
cv2.imshow('Ultralytics Speed Estimation', self.im0) |
||||
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'): |
||||
return |
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__': |
||||
SpeedEstimator() |
||||
Loading…
Reference in new issue