Cancel streams if we have too much concurrency on a single channel to
allow that server to recover.
There seems to be a convergence in the HTTP2 community about this being
a reasonable thing to do, so I'd like to try it in some real scenarios.
If this pans out well then I'll likely drop the
`red_max_concurrent_streams` and the `rstpit` experiments in preference
to this.
I'm also considering tying in resource quota so that under high memory
pressure we just default to this path.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Noticed that our behavior conflicts with what's mandated:
https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc9113.html#section-5.1.2
So here's a quick fix - I like it because it's not a disconnection,
which always feels like one outage avoided.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Instead of fixing a target size for writes, try to adapt it a little to
observed bandwidth.
The initial algorithm tries to get large writes within 100-1000ms
maximum delay - this range probably wants to be tuned, but let's see.
The hope here is that on slow connections we can not back buffer so much
and so when we need to send a ping-ack it's possible without great
delay.
Experiment 1: On RST_STREAM: reduce MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS for one round
trip.
Experiment 2: If a settings frame is outstanding with a lower
MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS than is configured, and we receive a new incoming
stream that would exceed the new cap, randomly reject it.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Cap requests per read, rst_stream handled per read.
If these caps are exceeded, offload processing of the connection to a
backing thread pool, and allow other connections to make progress.
Previously chttp2 would allow infinite requests prior to a settings ack
- as the agreed upon limit for requests in that state is infinite.
Instead, after MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS requests have been attempted,
start blanket cancelling requests until the settings ack is received.
This can be done efficiently without allocating request state
structures.
Isolate ping callback tracking to its own file.
Also takes the opportunity to simplify keepalive code by applying the
ping timeout to all pings.
Adds an experiment to allow multiple pings outstanding too (this was
originally an accidental behavior change of the work, but one that I
think may be useful going forward).
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
We disabled this a little while ago for lack of CI bandwidth, but #34404
ought to have freed up enough capacity that we can keep running this.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Summary -
On the server-side, we are changing the point at which we decide whether
a method is registered or not from the surface to the transport at the
point where we are done receiving initial metadata and before we invoke
the recv_initial_metadata_ready closures from the filters. The main
motivation for this is to allow filters to check whether the incoming
method is a registered or not. The exact use-case is for observability
where we only want to record the method if it is registered. We store
the information about the registered method in the initial metadata.
On the client-side, we also set information about whether the method is
registered or not in the outgoing initial metadata.
Since we are effectively changing the lookup point of the registered
method, there are slight concerns of this being a potentially breaking
change, so we are guarding this with an experiment to be safe.
Changes -
* Transport API changes -
* Along with `accept_stream_fn`, a new callback
`registered_method_matcher_cb` will be sent down as a transport op on
the server side. When initial metadata is received on the server side,
this callback is invoked. This happens before invoking the
`recv_initial_metadata_ready` closure.
* Metadata changes -
* We add a new non-serializable metadata trait `GrpcRegisteredMethod()`.
On the client-side, the value is a uintptr_t with a value of 1 if the
call has a registered/known method, or 0, if it's not known. On the
server side, the value is a (ChannelRegisteredMethod*). This metadata
information can be used throughout the stack to check whether a call is
registered or not.
* Server Changes -
* When a new transport connection is accepted, the server sets
`registered_method_matcher_cb` along with `accept_stream_fn`. This
function checks whether the method is registered or not and sets the
RegisteredMethod matcher in the metadata for use later.
* Client Changes -
* Set the metadata on call creation on whether the method is registered
or not.
Original PR was #34307, reverted in #34318 due to internal test
failures.
The first commit is a revert of the revert. The second commit contains
the fix.
The original idea here was that `SubchannelWrapper::Orphan()`, which is
called when the strong refcount reaches 0, would take a new weak ref and
then hop into the `WorkSerializer` before dropping that weak ref, thus
ensuring that the `SubchannelWrapper` is destroyed inside the
`WorkSerializer` (which is needed because the `SubchannelWrapper` dtor
cleans up some state in the channel related to the subchannel). The
problem is that `DualRefCounted<>::Unref()` itself actually increments
the weak ref count before calling `Orphan()` and then decrements it
afterwards. So in the case where the `SubchannelWrapper` is unreffed
outside of the `WorkSerializer` and no other thread happens to be
holding the `WorkSerializer`, the weak ref that we were taking in
`Orphan()` was unreffed inline, which meant that it wasn't actually the
last weak ref -- the last weak ref was the one taken by
`DualRefCounted<>::Unref()`, and it wasn't released until after the
`WorkSerializer` was released.
To this this problem, we move the code from the `SubchannelWrapper` dtor
that cleans up the channel's state into the `WorkSerializer` callback
that is scheduled in `Orphan()`. Thus, regardless of whether or not the
last weak ref is released inside of the `WorkSerializer`, we are
definitely doing that cleanup inside the `WorkSerializer`, which is what
we actually care about.
Also adds an experiment to guard this behavior.
Most recent attempt was #34320, reverted in #34335.
The first commit here is a pure revert. The second commit fixes the
outlier_detection unit test to pass both with and without the
experiment.
In certain situations the current flow control algorithm can result in
sending one flow control update write for every write sent (known
situation: rollout of promise based server calls with qps_test).
Fix things up so that the updates are only sent when truly needed, and
then fix the fallout (turns out our fuzzer had some bugs)
I've placed actual logic changes behind an experiment so that it can be
incrementally & safely rolled out.
We added this as an exploratory measure for a customer that thought they
were using open census (this turned out to be emphatically false).
Remove it since it's probably not how we ultimately want to do this, and
wait for something better to come along.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Over the past 5 days, this experiment has not introduced any new flakes,
nor increased any flake rates. Let's enable it for debug builds. To
prevent issues over the weekend, I plan to merge it next week, July 31st
(with announcement).
This PR implements a c-ares based DNS resolver for EventEngine with the
reference from the original
[grpc_ares_wrapper.h](../blob/master/src/core/ext/filters/client_channel/resolver/dns/c_ares/grpc_ares_wrapper.h).
The PosixEventEngine DNSResolver is implemented on top of that. Tests
which use the client channel resolver API
([resolver.h](../blob/master/src/core/lib/resolver/resolver.h#L54)) are
ported, namely the
[resolver_component_test.cc](../blob/master/test/cpp/naming/resolver_component_test.cc)
and the
[cancel_ares_query_test.cc](../blob/master/test/cpp/naming/cancel_ares_query_test.cc).
The WindowsEventEngine DNSResolver will use the same EventEngine's
grpc_ares_wrapper and will be worked on next.
The
[resolve_address_test.cc](https://github.com/grpc/grpc/blob/master/test/core/iomgr/resolve_address_test.cc)
which uses the iomgr
[DNSResolver](../blob/master/src/core/lib/iomgr/resolve_address.h#L44)
API has been ported to EventEngine's dns_test.cc. That leaves only 2
tests which use iomgr's API, notably the
[dns_resolver_cooldown_test.cc](../blob/master/test/core/client_channel/resolvers/dns_resolver_cooldown_test.cc)
and the
[goaway_server_test.cc](../blob/master/test/core/end2end/goaway_server_test.cc)
which probably need to be restructured to use EventEngine DNSResolver
(for one thing they override the original grpc_ares_wrapper's free
functions). I will try to tackle these in the next step.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
The intuition here is that these strings may end up in the hpack table,
and then unnecessarily extend the lifetime of the read blocks.
Instead, take a copy of these short strings when we need to and allow
the incoming large memory object to be discarded.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
The PR does the following:
* Splits the single experiments.yaml file into two files:
experiments.yaml and rollouts.yaml.
* The experiments.yaml will now only include experiment definitions. The
default values of the experiments must now be specified in rollouts.yaml
* Removes the 'release' default value because it is not used.
* Adds an additional_constraints character string to ExperimentMetadata.
* Introduces a hook in src/core/lib/experiments/config.h to allow
registering arbitrary experiment constraint validation callbacks. These
callbacks would take an ExperimentMetadata object as input and return
the correct value to use for an experiment subject to additional
constraints.
We defaulted this on 5 months ago, and it seems to be working... let's
remove the experiment bit!
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
I have not been able to reproduce the non-empty pool @ shutdown bug in
around 200k runs of various kinds. Now that experiments are marked flaky
by default, any similar failures should not block PR submission, and
this will give me good signal if the bugs reproduce more frequently in
the CI environment.
I have a fix in theory, but I don't think it should be necessary. If the
bug reproduces, I'll try the fix.
#thistimeforsure
a863532c62 adds some debug to help track
which batches get leaked by a transport
3203e75ec5 makes connected_channel respect
the high level intent of cancellation better (and fixes the last reason
we needed to turn these tests off)
aaf5fa036b re-enables testing of c++ e2e
tests with server based promise calls
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
This PR implements a work-stealing thread pool for use inside
EventEngine implementations. Because of historical risks here, I've
guarded the new implementation behind an experiment flag:
`GRPC_EXPERIMENTS=work_stealing`. Current default behavior is the
original thread pool implementation.
Benchmarks look very promising:
```
bazel test \
--test_timeout=300 \
--config=opt -c opt \
--test_output=streamed \
--test_arg='--benchmark_format=csv' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_min_time=0.15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_filter=_FanOut' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_repetitions=15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_report_aggregates_only=true' \
test/cpp/microbenchmarks:bm_thread_pool
```
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results on my local machine (64
core ThreadRipper PRO 3995WX, 256GB memory), comparing this PR to
master:
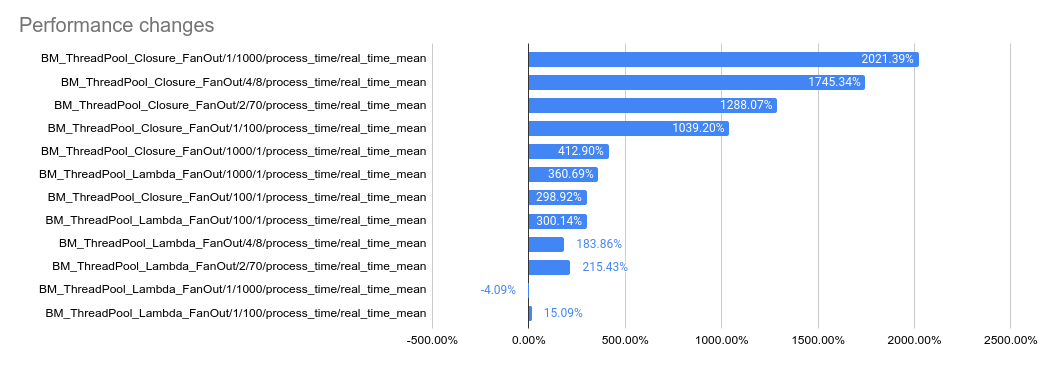
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results in the Linux RBE
environment (unsure of machine configuration, likely small), comparing
this PR to master.
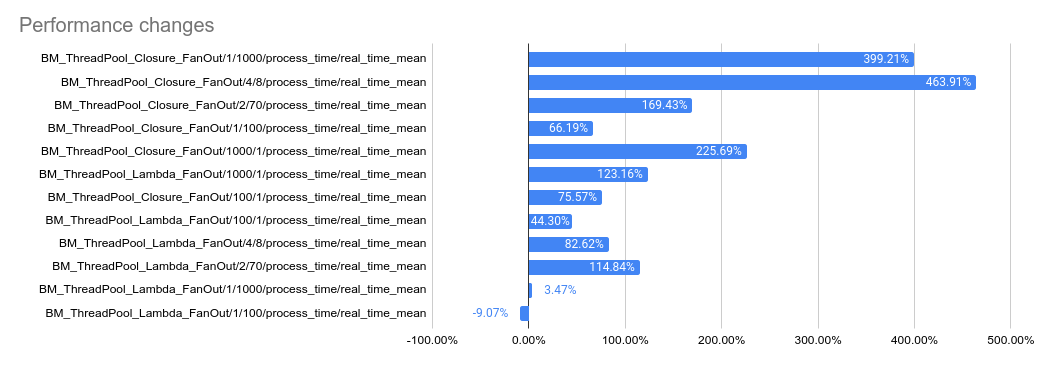
---------
Co-authored-by: drfloob <drfloob@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
Makes some awkward fixes to compression filter, call, connected channel
to hold the semantics we have upheld now in tests.
Once the fixes described here
https://github.com/grpc/grpc/blob/master/src/core/lib/channel/connected_channel.cc#L636
are in this gets a lot less ad-hoc, but that's likely going to be
post-landing promises client & server side.
We specifically need special handling for server side cancellation in
response to reads wrt the inproc transport - which doesn't track
cancellation thoroughly enough itself.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>