Fixes the issue introduced in https://github.com/grpc/grpc/pull/33104,
where stopping the current run didn't reset `self.time_start_requested`,
`self.time_start_completed`, `self.time_start_stopped`. Because of this,
the subsetting test (the only one [redeploying the client
app](10001d16a9/tools/run_tests/xds_k8s_test_driver/tests/subsetting_test.py (L73C1-L74)))
started failing with:
```py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "xds_k8s_test_driver/tests/subsetting_test.py", line 76, in test_subsetting_basic
test_client: _XdsTestClient = self.startTestClient(
File "xds_k8s_test_driver/framework/xds_k8s_testcase.py", line 615, in startTestClient
test_client = self.client_runner.run(server_target=test_server.xds_uri,
File "xds_k8s_test_driver/framework/test_app/runners/k8s/k8s_xds_client_runner.py", line 110, in run
super().run()
File "xds_k8s_test_driver/framework/test_app/runners/k8s/k8s_base_runner.py", line 112, in run
raise RuntimeError(
RuntimeError: Deployment psm-grpc-client: has already been started at 2023-05-27T13:47:15.262461
```
This PR:
1. Instead of relying on the `time_start_requested`,
`time_start_stopped` to produce GCP links, tracks the history run of
each deployment. This fixes the issue described above, and adds support
for listing all past runs executed by a k8s runner.
2. Minor: remove the unnecessary call to `test_client.cleanup()` when
there's no past deployment runs (e.g. at the first iteration of `for i
in range(_NUM_CLIENTS):`)
This is another attempt to add support for vsock in grpc since previous
PRs(#24551, #21745) all closed without merging.
The VSOCK address family facilitates communication between
virtual machines and the host they are running on.
This patch will introduce new scheme: [vsock:cid:port] to
support VSOCK address family.
Fixes#32738.
---------
Signed-off-by: Yadong Qi <yadong.qi@intel.com>
Co-authored-by: AJ Heller <hork@google.com>
Co-authored-by: YadongQi <YadongQi@users.noreply.github.com>
It's completely legitimate to have a zero in a filename/include guard.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
- switch to json_object_loader for config parsing
- use `absl::string_view` instead of `const char*` for cert provider
names
- change cert provider registry to use a map instead of a vector
- remove unused mesh_ca cert provider factory
The PR does the following:
* Splits the single experiments.yaml file into two files:
experiments.yaml and rollouts.yaml.
* The experiments.yaml will now only include experiment definitions. The
default values of the experiments must now be specified in rollouts.yaml
* Removes the 'release' default value because it is not used.
* Adds an additional_constraints character string to ExperimentMetadata.
* Introduces a hook in src/core/lib/experiments/config.h to allow
registering arbitrary experiment constraint validation callbacks. These
callbacks would take an ExperimentMetadata object as input and return
the correct value to use for an experiment subject to additional
constraints.
Most of these data structures need to scale a bit like per-cpu, but not
entirely. We can have more than one cpu hit the same instance in most
cases, and probably want to cap out before the hundreds of shards some
platforms have.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
This test mode tries to create threads wherever it legally can to
maximize the chances of TSAN finding errors in our codebase.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
Allow for multiple `--grpc_experiments`, `--grpc_trace` command line
arguments to be added, accumulate them, and provide them to gRPC as one
thing.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
`tools/run_tests/sanity/check_absl_mutex.sh` was broken, a missing paren
crashed the script if run locally. It's unclear yet how our sanity
checks were not complaining about this, `run_tests.py` does not save the
log.
I've noticed we add the cleanup hook after setting up the
infrastructure. Thus, if infra setup failed, the cleanup won't work.
This fixes it, and adds extra checks to not call
`cls.test_client_runner` if it's not set.
The logger uses `absl::FPrintF` to write to stdout. After reading a
number of sources online, I got the impression that `std::fwrite` which
is used by `absl::FPrintF` is atomic so there is no locking required
here.
---------
Co-authored-by: rockspore <rockspore@users.noreply.github.com>
Fail test if client or server pods restarted during test.
#### Testing
Tested locally, test will fail with message similar to:
```
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/local/google/home/xuanwn/workspace/xds/grpc/tools/run_tests/xds_k8s_test_driver/framework/xds_k8s_testcase.py", line 501, in tearDown
))
AssertionError: 5 != 0 : Server pods unexpectedly restarted {sever_restarts} times during test.
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Ran 1 test in 886.867s
```
Better logging for `assertRpcStatusCodes`.
(got tired of looking up the status names)
#### Unexpected status found
Before:
```
AssertionError: AssertionError: Expected only status 15 but found status 0 for method UNARY_CALL:
stats_per_method {
key: "UNARY_CALL"
value {
result {
key: 0
value: 251
}
}
}
```
After:
```
AssertionError: Expected only status (15, DATA_LOSS), but found status (0, OK) for method UNARY_CALL:
stats_per_method {
key: "UNARY_CALL"
value {
result {
key: 0
value: 251
}
}
}
```
#### No traffic with expected status
Before:
```
AssertionError: 0 not greater than 0
```
After:
```
AssertionError: 0 not greater than 0 : Expected non-zero RPCs with status (15, DATA_LOSS) for method UNARY_CALL, got:
stats_per_method {
key: "UNARY_CALL"
value {
result {
key: 0
value: 251
}
result {
key: 15
value: 0
}
}
}
```
Before this change, `Found subchannel in state READY` and `Channel to
xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 transitioned to state ` would dump the full
channel/subchannel, in some implementations that expose
ChannelData.trace (f.e. go) would add 300 extra lines of log.
Now we print a brief repr-like chanel/subchannel info:
```
Found subchannel in state READY: <Subchannel subchannel_id=9 target=10.110.1.44:8080 state=READY>
Channel to xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 transitioned to state READY: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=READY>
```
Also while waiting for the channel, we log channel_id now too:
```
Waiting to report a READY channel to xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=TRANSIENT_FAILURE>
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=TRANSIENT_FAILURE>
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=TRANSIENT_FAILURE>
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=TRANSIENT_FAILURE>
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=TRANSIENT_FAILURE>
Server channel: <Channel channel_id=2 target=xds:///psm-grpc-server:61404 state=READY>
```
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: Yash Tibrewal <yashkt@google.com>
Co-authored-by: Stanley Cheung <stanleycheung@google.com>
Co-authored-by: AJ Heller <hork@google.com>
Co-authored-by: Yijie Ma <yijiem.main@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: apolcyn <apolcyn@google.com>
Co-authored-by: Jan Tattermusch <jtattermusch@google.com>
Similar to what we already do in other test suites:
- Try cleaning up resources three times.
- If unsuccessful, don't fail the test and just log the error. The
cleanup script should be the one to deal with this.
ref b/282081851
Add a new binary that runs all core end2end tests in fuzzing mode.
In this mode FuzzingEventEngine is substituted for the default event
engine. This means that time is simulated, as is IO. The FEE gets
control of callback delays also.
In our tests the `Step()` function becomes, instead of a single call to
`completion_queue_next`, a series of calls to that function and
`FuzzingEventEngine::Tick`, driving forward the event loop until
progress can be made.
PR guide:
---
**New binaries**
`core_end2end_test_fuzzer` - the new fuzzer itself
`seed_end2end_corpus` - a tool that produces an interesting seed corpus
**Config changes for safe fuzzing**
The implementation tries to use the config fuzzing work we've previously
deployed in api_fuzzer to fuzz across experiments. Since some
experiments are far too experimental to be safe in such fuzzing (and
this will always be the case):
- a new flag is added to experiments to opt-out of this fuzzing
- a new hook is added to the config system to allow variables to
re-write their inputs before setting them during the fuzz
**Event manager/IO changes**
Changes are made to the event engine shims so that tcp_server_posix can
run with a non-FD carrying EventEngine. These are in my mind a bit
clunky, but they work and they're in code that we expect to delete in
the medium term, so I think overall the approach is good.
**Changes to time**
A small tweak is made to fix a bug initializing time for fuzzers in
time.cc - we were previously failing to initialize
`g_process_epoch_cycles`
**Changes to `Crash`**
A version that prints to stdio is added so that we can reliably print a
crash from the fuzzer.
**Changes to CqVerifier**
Hooks are added to allow the top level loop to hook the verification
functions with a function that steps time between CQ polls.
**Changes to end2end fixtures**
State machinery moves from the fixture to the test infra, to keep the
customizations for fuzzing or not in one place. This means that fixtures
are now just client/server factories, which is overall nice.
It did necessitate moving some bespoke machinery into
h2_ssl_cert_test.cc - this file is beginning to be problematic in
borrowing parts but not all of the e2e test machinery. Some future PR
needs to solve this.
A cq arg is added to the Make functions since the cq is now owned by the
test and not the fixture.
**Changes to test registration**
`TEST_P` is replaced by `CORE_END2END_TEST` and our own test registry is
used as a first depot for test information.
The gtest version of these tests: queries that registry to manually
register tests with gtest. This ultimately changes the name of our tests
again (I think for the last time) - the new names are shorter and more
readable, so I don't count this as a regression.
The fuzzer version of these tests: constructs a database of fuzzable
tests that it can consult to look up a particular suite/test/config
combination specified by the fuzzer to fuzz against. This gives us a
single fuzzer that can test all 3k-ish fuzzing ready tests and cross
polinate configuration between them.
**Changes to test config**
The zero size registry stuff was causing some problems with the event
engine feature macros, so instead I've removed those and used GTEST_SKIP
in the problematic tests. I think that's the approach we move towards in
the future.
**Which tests are included**
Configs that are compatible - those that do not do fd manipulation
directly (these are incompatible with FuzzingEventEngine), and those
that do not join threads on their shutdown path (as these are
incompatible with our cq wait methodology). Each we can talk about in
the future - fd manipulation would be a significant expansion of
FuzzingEventEngine, and is probably not worth it, however many uses of
background threads now should probably evolve to be EventEngine::Run
calls in the future, and then would be trivially enabled in the fuzzers.
Some tests currently fail in the fuzzing environment, a
`SKIP_IF_FUZZING` macro is used for these few to disable them if in the
fuzzing environment. We'll burn these down in the future.
**Changes to fuzzing_event_engine**
Changes are made to time: an exponential sweep forward is used now -
this catches small time precision things early, but makes decade long
timers (we have them) able to be used right now. In the future we'll
just skip time forward to the next scheduled timer, but that approach
doesn't yet work due to legacy timer system interactions.
Changes to port assignment: we ensure that ports are legal numbers
before assigning them via `grpc_pick_port_or_die`.
A race condition between time checking and io is fixed.
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
Resolve `TESTING_VERSION` to `dev-VERSION` when the job is initiated by
a user, and not the CI. Override this behavior with setting
`FORCE_TESTING_VERSION`.
This solves the problem with the manual job runs executed against a WIP
branch (f.e. a PR) overriding the tag of the CI-built image we use for
daily testing.
The `dev` and `dev-VERSION` "magic" values supported by the
`--testing_version` flag:
- `dev` and `dev-master` and treated as `master`: all
`config.version_gte` checks resolve to `True`.
- `dev-VERSION` is treated as `VERSION`: `dev-v1.55.x` is treated as
simply `v1.55.x`. We do this so that when manually running jobs for old
branches the feature skip check still works, and unsupported tests are
skipped.
This changes will take care of all langs/branches, no backports needed.
ref b/256845629
This makes the JSON API visible as part of the C-core API, but in the
`experimental` namespace. It will be used as part of various
experimental APIs that we will be introducing in the near future, such
as the audit logging API.
This file does not contain a shebang, and whenever I try and run it it
wedges my console into some weird state.
There's a .sh file with the same name that should be run instead. Remove
the executable bit of the thing we shouldn't run directly so we, like,
don't.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
Previously the error message didn't provide much context, example:
```py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/tmpfs/tmp/tmp.BqlenMyXyk/grpc/tools/run_tests/xds_k8s_test_driver/tests/affinity_test.py", line 127, in test_affinity
self.assertLen(
AssertionError: [] has length of 0, expected 1.
```
ref b/279990584.
This PR implements a work-stealing thread pool for use inside
EventEngine implementations. Because of historical risks here, I've
guarded the new implementation behind an experiment flag:
`GRPC_EXPERIMENTS=work_stealing`. Current default behavior is the
original thread pool implementation.
Benchmarks look very promising:
```
bazel test \
--test_timeout=300 \
--config=opt -c opt \
--test_output=streamed \
--test_arg='--benchmark_format=csv' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_min_time=0.15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_filter=_FanOut' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_repetitions=15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_report_aggregates_only=true' \
test/cpp/microbenchmarks:bm_thread_pool
```
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results on my local machine (64
core ThreadRipper PRO 3995WX, 256GB memory), comparing this PR to
master:
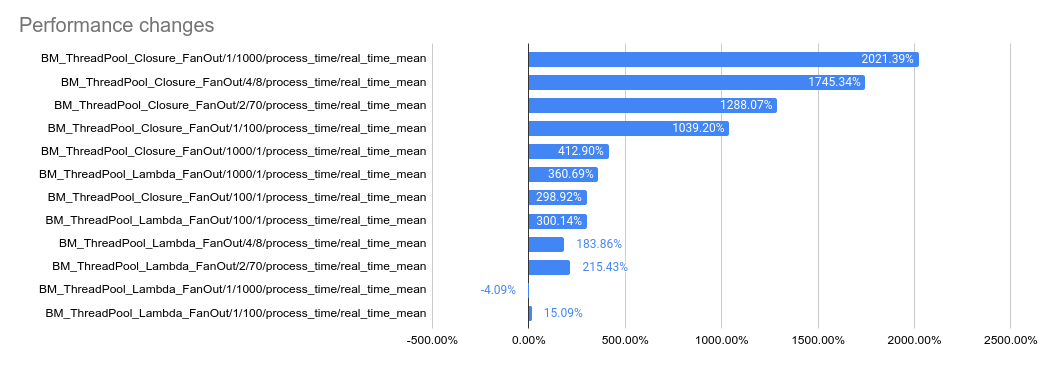
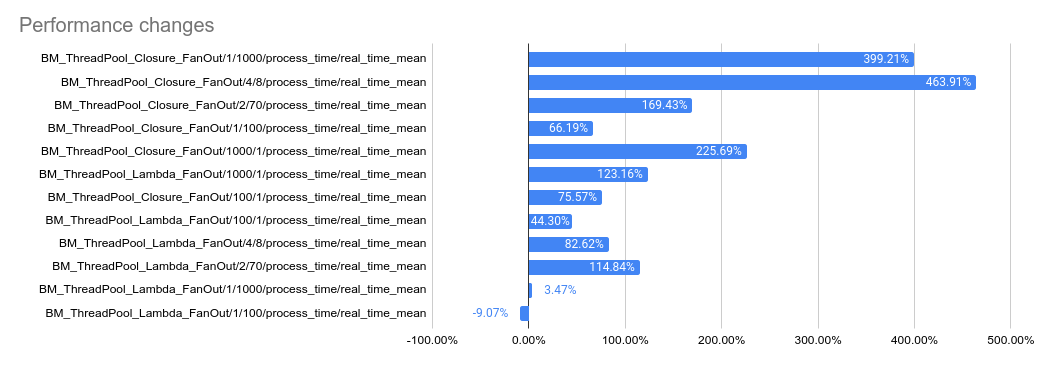
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results in the Linux RBE
environment (unsure of machine configuration, likely small), comparing
this PR to master.
---------
Co-authored-by: drfloob <drfloob@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: Sergii Tkachenko <hi@sergii.org>