This PR implements a work-stealing thread pool for use inside
EventEngine implementations. Because of historical risks here, I've
guarded the new implementation behind an experiment flag:
`GRPC_EXPERIMENTS=work_stealing`. Current default behavior is the
original thread pool implementation.
Benchmarks look very promising:
```
bazel test \
--test_timeout=300 \
--config=opt -c opt \
--test_output=streamed \
--test_arg='--benchmark_format=csv' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_min_time=0.15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_filter=_FanOut' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_repetitions=15' \
--test_arg='--benchmark_report_aggregates_only=true' \
test/cpp/microbenchmarks:bm_thread_pool
```
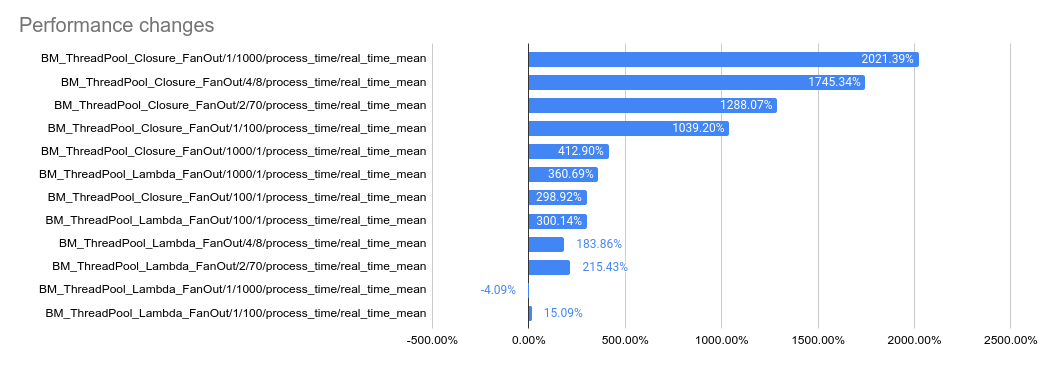
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results on my local machine (64
core ThreadRipper PRO 3995WX, 256GB memory), comparing this PR to
master:
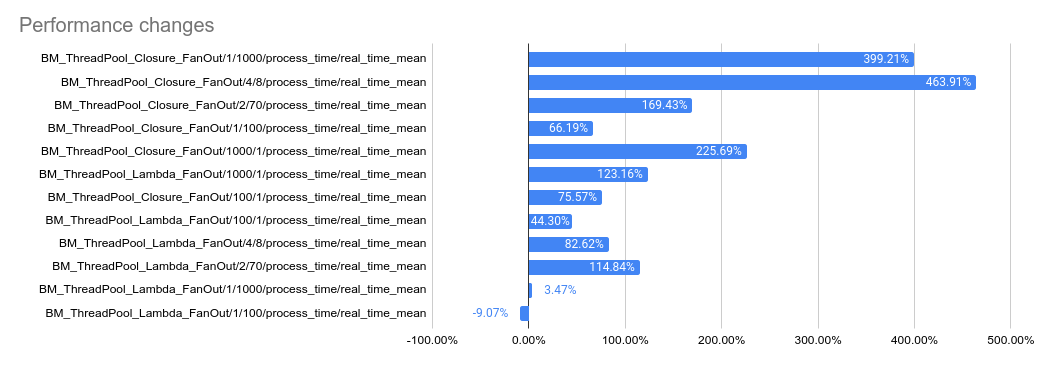
2023-05-04: `bm_thread_pool` benchmark results in the Linux RBE
environment (unsure of machine configuration, likely small), comparing
this PR to master.
---------
Co-authored-by: drfloob <drfloob@users.noreply.github.com>
Reverts grpc/grpc#32924. This breaks the build again, unfortunately.
From `test/core/event_engine/cf:cf_engine_test`:
```
error: module .../grpc/test/core/event_engine/cf:cf_engine_test does not depend on a module exporting 'grpc/support/port_platform.h'
```
@sampajano I recommend looking into CI tests to catch iOS problems
before merging. We can enable EventEngine experiments in the CI
generally once this PR lands, but this broken test is not one of those
experiments. A normal build should have caught this.
cc @HannahShiSFB
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
@sampajano
If an engine is created, it should be fully functional regardless of
whether gRPC-core experiments are on or off. The trade-off for now is
that when the core experiments are not enabled, the engine will be
slowly polling with nothing to do.
---------
Co-authored-by: drfloob <drfloob@users.noreply.github.com>
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
This is a big rewrite of global config.
It does a few things, all somewhat intertwined:
1. centralize the list of configuration we have to a yaml file that can
be parsed, and code generated from it
2. add an initialization and a reset stage so that config vars can be
centrally accessed very quickly without the need for caching them
3. makes the syntax more C++ like (less macros!)
4. (optionally) adds absl flags to the OSS build
This first round of changes is intended to keep the system where it is
without major changes. We pick up absl flags to match internal code and
remove one point of deviation - but importantly continue to read from
the environment variables. In doing so we don't force absl flags on our
customers - it's possible to configure grpc without the flags - but
instead allow users that do use absl flags to configure grpc using that
mechanism. Importantly this lets internal customers configure grpc the
same everywhere.
Future changes along this path will be two-fold:
1. Move documentation generation into the code generation step, so that
within the source of truth yaml file we can find all documentation and
data about a configuration knob - eliminating the chance of forgetting
to document something in all the right places.
2. Provide fuzzing over configurations. Currently most config variables
get stashed in static constants across the codebase. To fuzz over these
we'd need a way to reset those cached values between fuzzing rounds,
something that is terrifically difficult right now, but with these
changes should simply be a reset on `ConfigVars`.
<!--
If you know who should review your pull request, please assign it to
that
person, otherwise the pull request would get assigned randomly.
If your pull request is for a specific language, please add the
appropriate
lang label.
-->
---------
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>
There are potentially surprising deployment bugs that can cause `EMFILE`
to be hit. For example, file descriptor limits can be easily reached if
- the round robin LB policy is used
- the load balancer hands out an assignment with a lot of backends
- using debian's default 1024 file descriptor limit.
To make such problems more apparent, we can pay special attention to
this error and log ERROR when it happens.
Related: b/265199104
* [EventEngine] Update EventEngine client experiment
This bumps the expiry timeline, and guards certain poller behavior
behind the flag. The Epoll1 poller has been shown to not support fork
events, which is a problem for Python. Fixes for that are incoming, but
for now, the poller instantiation is guarded behind the flag as well.
* force the EE endpoint experiment on for posix EventEngine tests
* fix experiment code, it was not respecting forced values
* [iwyu] Add missing #include <type_traits> to fix build breakage with LLVM after e0a66116fc
* Update IWYU mappings
New libc++ doesn't provide <type_traits> when including <utility>.
* run iwyu
Co-authored-by: alexfh <alexfh@google.com>
* Revert "Revert "[EventEngine] Refactor TimerManager to leverage a shared ThreadPool (#31392)" (#31425)"
This reverts commit 1cbf6d64ae.
* fix deadlock on windows engine shutdown
* Refactor ThreadManager to leverage a shared ThreadPool
This is a step towards a work-stealing thread pool implementation:
unifying thread pools so that work stealing affects timer callbacks as
well.
A subsequent step will expose the timeout logic so that the timer wakeup
and check can be triggered externally (by pollers, in the common case).
* fix atomic uint64_t type missing on some platforms
* sanitize + platform fixes
* ->quiesce
* shut down the timer manager to release the main thread
* roll back atomics
* use a dedicated thread for timer_manager to prevent local execution (work stealing)
* drain the pools after timer manager tests; sanitize
* iwyu
* reintroduce fork handling
* sanitize
* fix
* Remove ResetDefaultEventEngine
Now that it is a weak_ptr, there's no need to explicitly reset it. When
the tracked shared_ptr is deleted, the weak_ptr will fail to lock, and a
new default EventEngine will be created.
* forget existing engine with FactoryReset
* init/shutdown in event engine for now
* fix
* fix
* fix windows deadlock
* Automated change: Fix sanity tests
* fix
* better windows fix
Co-authored-by: AJ Heller <hork@google.com>
Co-authored-by: ctiller <ctiller@users.noreply.github.com>